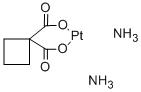
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
*Only for medical professionals to read and refer to Fudan cancer experts to interpret the latest progress in 2021ASCO liver cancer diagnosis and treatment! The 2021 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) will be held in the form of an online conference from June 4th to June 8th
.
As the most influential international cancer conference with the largest audience, it has brought the latest advances in cancer frontier academics to scholars from all walks of life
.
This time ASCO announced blockbuster studies in many cancer fields.
The "Experts on Complex Tumors will take you to the 2021 ASCO-Liver Cancer Special" invited Professor Wang Lu and Zhang Wei from Fudan University Affiliated Tumor Hospital to interpret the blockbuster studies of liver cancer from multiple perspectives.
, Deliver cutting-edge dynamics
.
Scan the code to watch the wonderful live replay of the FOHAIC-1 study: Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy (HAIC-FO) with FOLFOX as the plan compared with sorafenib in patients with advanced liver cancer 1.
Baseline critically ill patients accounted for a larger proportion, and the study design was closer Real-world situation The study randomly divided 551 patients into the HAIC-FO group and the sorafenib group 1:1.
The patients included in the study had a heavier baseline tumor burden and large intrahepatic tumors (the average tumor diameter was approximately 11cm), the patients with Child-Pugh grade B of liver function are about 30% in both groups, and the patients with PS score of 2 are as high as 24.
6% and 17.
4% in HAIC-FO group and sorafenib group, respectively.
41.
5% and 39.
4% of patients with tumor involving liver ≥50%, respectively
.
Patients with tumor involving liver ≥50% and/or portal vein tumor thrombus Vp-4 were 53.
8% and 44.
7% in the two groups, respectively
.
Patient baseline condition 2.
The ORR and OS results of the HAIC-FO group were far superior to sorafenib.
In this study, the objective response rates (ORR) of the HAIC-FO group and sorafenib group were 31.
5% and 1.
5% (P< 0.
001) (RECIST 1.
1), the ORR results of intrahepatic and overall diseases were basically the same.
The ORR of the HAIC-FO group outperformed the sorafenib group, and there were significant statistical differences
.
Under the mRECIST evaluation standard, the ORRs of the HAIC-FO group and the sorafenib group were 35.
4% and 5.
3% (P<0.
001), which were slightly higher than the ORR under the RECIST 1.
1 evaluation standard
.
The main endpoint of the study, overall survival (OS), also showed a large difference in efficacy.
The median OS of the HAIC-FO group and the sorafenib group were 13.
9 months (10.
6-17.
2 months) and 8.
2, respectively.
Months (7.
5-9.
0 months), and there is a statistical difference (P<0.
001)
.
OS curve of HAIC-FO group and sorafenib group 3.
HAIC-FO treatment helps more patients with advanced liver cancer downgrade and achieve the purpose of resection.
Subgroup analysis explored whether patients are treated with HAIC-FO or sorafenib It can achieve the transformation from unresectable to surgically resectable.
In recent years, many studies have shown that HAIC-FO can downgrade 10-20% of unresectable patients and achieve the purpose of surgical resection
.
In the subgroup analysis of this study, 12.
3% (16/130) of patients in the HAIC-FO group reached downstage, and 0.
8% (1/132) in the sorafenib group
.
After transformation, the OS of the HAIC-FO group was much better than that of the sorafenib group
.
Among the sub-ethnic groups with high-risk factors, the OS of the HAIC-FO group also showed obvious advantages
.
4.
Safety results: the safety of HAIC-FO group.
As the sorafenib group and the patients tolerated well, the incidence of grade 3 or 4 adverse events in the HAIC-FO group was 20.
3%, while the rate of adverse events in the sorafenib group was 20.
3%.
The data is 48.
1%
.
The main complication in the HAIC-FO group was acute abdominal pain (40.
6%), especially in the late stage of oxaliplatin perfusion, but the side effects such as pain caused by the infusion did not cause the patients to give up HAIC-FO treatment
.
5.
The HAIC-FO group showed advantages in OS, ORR, and safety for patients with advanced high-load liver cancer.
In this study, 18 mutations were found, including the common ARID1A and STAT3, but they were not found in CR/ In patients with PR and SD/PD, there is a difference in the proportion of these 18 mutated genes
.
This study of 18 mutant genes showed that patients with advanced high-burden liver cancer with HAIC-FO as the treatment plan were generally better than sorafenib in terms of OS, ORR and safety.
At the same time, the HAIC-FO group showed More obvious advantages of tumor retraction (median time to remission 2.
2 months)
.
At the same time, the median tumor-free time after downstage resection in the HAIC-FO group can reach 16.
4 g months, and the 1-year OS rate can reach 93.
8%
.
In the subgroup analysis, the median OS of patients with liver involvement ≥50% or and/or portal vein tumor thrombus grade Vp-4 can reach 10.
8 months, and the biomarker prediction model for curative effect is still under development and exploration.
We look forward to this The follow-up results of this study
.
Comparing the effects of HAIC neoadjuvant therapy with FOLFOX on the survival benefits of BCLC staging A/B 1.
The prognosis of patients beyond Milan standard is poor.
This study explored whether the HAIC-FO regimen neoadjuvant therapy can effectively improve the prognosis beyond Milan Standard liver cancer patients have poor prognosis factors.
Previous studies have shown that the incidence of microvascular invasion (MVI) in such patients is as high as 50%-60%.
MVI is an important factor leading to poor prognosis after liver cancer surgery, but it is currently lacking.
Means to reduce the recurrence and metastasis of such patients, so there is still controversy about whether to perform surgical resection or liver transplantation for patients who exceed the Milan standard
.
For patients whose BCLC stage A does not exceed the Milan standard, the 1-year OS rate after surgery is more than 90%, but the patients who exceed the Milan standard are only 75.
8%, and the 3-year OS rate and 5-year OS rate are only 48.
1% and 10.
7%.
.
Due to the unsatisfactory data, this multicenter randomized controlled phase III clinical trial was carried out
.
The study compared whether HAIC neoadjuvant treatment with FOLFOX as a regimen has an effect on the survival benefit of BCLC staging A/B beyond the Milan standard.
The primary study endpoint is OS, and the secondary study endpoints are PFS and recurrence-free survival (RFS).
) And security
.
Comparison of OS survival of patients beyond Milan standard 2.
Two patients reached CR after HAIC neoadjuvant treatment.
The study first carried out preliminary screening of patients and divided them into direct operation group and HAIC-FO neoadjuvant treatment group.
The initial study included 256 patients In the end, 99 patients and 100 patients in the two groups can be evaluated for efficacy
.
The baseline conditions of the two groups of patients were balanced
.
Study Design There are 2 typical cases in the study.
In case 1, there was a huge tumor in the right lobe and the middle of the liver before treatment, but after four cycles of HAIC neoadjuvant treatment, the tumor achieved complete imaging remission (CR) and postoperative pathology The same performance is CR
.
In case 2, there was a huge tumor lesion in the right lobe of the liver before treatment.
After four cycles of HAIC neoadjuvant treatment, the tumor reached CR and the pathological CR after the operation
.
Case 1 Imaging and postoperative pathology Figure Case 2 Imaging and postoperative pathology Figure 3.
Neoadjuvant therapy can improve the incidence of MVI and prolong the patient’s OS, but there is no significant difference in RFS.
The incidence of MVI was 39.
0% in the baseline situation of patients After neoadjuvant therapy, only 11.
4% of patients had MVI
.
In the neoadjuvant treatment group, 88.
9% of patients underwent surgical resection, ORR was 63.
6%, disease control rate was 96.
0%, 53.
3% of patients achieved PR, 10.
1% of patients achieved pathological CR, 32.
3% of patients had SD, 4.
0 % Of patients have tumor progression (PD)
.
The efficacy of patients in the neoadjuvant therapy group and the direct surgery group were 92.
9% and 79.
5%, respectively, the 2-year OS rates were 78.
6% and 62.
0%, and the 3-year OS rates were 63.
5% and 46.
3% (P=0.
016) ), it can be seen that neoadjuvant therapy has significantly improved the survival benefits of patients
.
Compared with the direct operation group, the PFS rate of the OS curve neoadjuvant treatment group of the two groups was significantly improved (P=0.
017), but there was no statistical difference in RFS
.
The PFS curve of the two groups of patients Professor Wang Lu & Professor Zhang Yu commented on Professor Wang Lu: HAIC is a local treatment method for liver cancer.
With the publication of a series of research results, it has shown very good efficacy, but there are also reports to the contrary.
How does Professor Ji think about the efficacy of HAIC treatment? Professor Zhang Wei: From my personal experience, the HAIC treatment is effective.
We conducted a small sample study before.
Among more than 30 patients, the ORR reached more than 90%, and 15 of them were given the opportunity of surgical resection
.
In the past, the survival period of advanced liver cancer was only 3-6 months.
Now, through the drug treatment of HAIC combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibody, the tumor can be rapidly reduced, and even the purpose of surgical resection can be achieved.
This actually brings a great deal to patients with advanced liver cancer.
hope
.
Professor Wang Lu: Then I would like to ask advanced patients, which can be divided into locally advanced patients and patients with extrahepatic metastases.
What are the main types of patients receiving HAIC treatment? Professor Zhang Yu: Some experts think that it should be used for locally advanced stage.
Because of its transformation effect, I personally have different opinions, because my current patients include patients with locally advanced stage that can be transformed, and some patients who are impossible to transform at all.
For example, people with multiple bone metastases and lung metastases actually receive HAIC and PD-1 monoclonal antibody combined with TKI treatment, which can also effectively control the disease
.
Expert profile Wang Lu Wang Lu is currently the director of liver surgery, chief physician, and doctoral tutor of Fudan University Affiliated Tumor Hospital.
He is mainly engaged in the surgical treatment of liver and gallbladder tumors.
At present, he has performed nearly 800 cases of liver and gallbladder operations per year and has completed laparoscopic liver resection.
There are more than 1,000 cases, which is at the international leading level
.
He is a member of the International Surgery Association (ISS), a member of the International Liver Cancer Association (ILCA), a member of the International Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Association (IHPBA), and a founding member of the International Laparoscopic Liver Resection Association
.
Vice-chairmen, standing committee members and members of many domestic academic societies
.
Expert profile Zhang Zhi, deputy chief physician of the Department of Liver Surgery, Fudan University Tumor Hospital, and professor, member of the Standing Committee of the Liver Cancer Professional Committee of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Member of the Standing Committee of the Biliary Tumor Professional Committee of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Member of the Professional Committee of Tumor Precision Therapy of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Society Member of the Surgical Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association Member of the Standing Committee of the Professional Committee of Liver Surgery Member of the Professional Committee of Oncology Surgery of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association Surgery Branch Member of the Committee of Biliary Tumor Experts of the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO)
.
As the most influential international cancer conference with the largest audience, it has brought the latest advances in cancer frontier academics to scholars from all walks of life
.
This time ASCO announced blockbuster studies in many cancer fields.
The "Experts on Complex Tumors will take you to the 2021 ASCO-Liver Cancer Special" invited Professor Wang Lu and Zhang Wei from Fudan University Affiliated Tumor Hospital to interpret the blockbuster studies of liver cancer from multiple perspectives.
, Deliver cutting-edge dynamics
.
Scan the code to watch the wonderful live replay of the FOHAIC-1 study: Hepatic Arterial Infusion Chemotherapy (HAIC-FO) with FOLFOX as the plan compared with sorafenib in patients with advanced liver cancer 1.
Baseline critically ill patients accounted for a larger proportion, and the study design was closer Real-world situation The study randomly divided 551 patients into the HAIC-FO group and the sorafenib group 1:1.
The patients included in the study had a heavier baseline tumor burden and large intrahepatic tumors (the average tumor diameter was approximately 11cm), the patients with Child-Pugh grade B of liver function are about 30% in both groups, and the patients with PS score of 2 are as high as 24.
6% and 17.
4% in HAIC-FO group and sorafenib group, respectively.
41.
5% and 39.
4% of patients with tumor involving liver ≥50%, respectively
.
Patients with tumor involving liver ≥50% and/or portal vein tumor thrombus Vp-4 were 53.
8% and 44.
7% in the two groups, respectively
.
Patient baseline condition 2.
The ORR and OS results of the HAIC-FO group were far superior to sorafenib.
In this study, the objective response rates (ORR) of the HAIC-FO group and sorafenib group were 31.
5% and 1.
5% (P< 0.
001) (RECIST 1.
1), the ORR results of intrahepatic and overall diseases were basically the same.
The ORR of the HAIC-FO group outperformed the sorafenib group, and there were significant statistical differences
.
Under the mRECIST evaluation standard, the ORRs of the HAIC-FO group and the sorafenib group were 35.
4% and 5.
3% (P<0.
001), which were slightly higher than the ORR under the RECIST 1.
1 evaluation standard
.
The main endpoint of the study, overall survival (OS), also showed a large difference in efficacy.
The median OS of the HAIC-FO group and the sorafenib group were 13.
9 months (10.
6-17.
2 months) and 8.
2, respectively.
Months (7.
5-9.
0 months), and there is a statistical difference (P<0.
001)
.
OS curve of HAIC-FO group and sorafenib group 3.
HAIC-FO treatment helps more patients with advanced liver cancer downgrade and achieve the purpose of resection.
Subgroup analysis explored whether patients are treated with HAIC-FO or sorafenib It can achieve the transformation from unresectable to surgically resectable.
In recent years, many studies have shown that HAIC-FO can downgrade 10-20% of unresectable patients and achieve the purpose of surgical resection
.
In the subgroup analysis of this study, 12.
3% (16/130) of patients in the HAIC-FO group reached downstage, and 0.
8% (1/132) in the sorafenib group
.
After transformation, the OS of the HAIC-FO group was much better than that of the sorafenib group
.
Among the sub-ethnic groups with high-risk factors, the OS of the HAIC-FO group also showed obvious advantages
.
4.
Safety results: the safety of HAIC-FO group.
As the sorafenib group and the patients tolerated well, the incidence of grade 3 or 4 adverse events in the HAIC-FO group was 20.
3%, while the rate of adverse events in the sorafenib group was 20.
3%.
The data is 48.
1%
.
The main complication in the HAIC-FO group was acute abdominal pain (40.
6%), especially in the late stage of oxaliplatin perfusion, but the side effects such as pain caused by the infusion did not cause the patients to give up HAIC-FO treatment
.
5.
The HAIC-FO group showed advantages in OS, ORR, and safety for patients with advanced high-load liver cancer.
In this study, 18 mutations were found, including the common ARID1A and STAT3, but they were not found in CR/ In patients with PR and SD/PD, there is a difference in the proportion of these 18 mutated genes
.
This study of 18 mutant genes showed that patients with advanced high-burden liver cancer with HAIC-FO as the treatment plan were generally better than sorafenib in terms of OS, ORR and safety.
At the same time, the HAIC-FO group showed More obvious advantages of tumor retraction (median time to remission 2.
2 months)
.
At the same time, the median tumor-free time after downstage resection in the HAIC-FO group can reach 16.
4 g months, and the 1-year OS rate can reach 93.
8%
.
In the subgroup analysis, the median OS of patients with liver involvement ≥50% or and/or portal vein tumor thrombus grade Vp-4 can reach 10.
8 months, and the biomarker prediction model for curative effect is still under development and exploration.
We look forward to this The follow-up results of this study
.
Comparing the effects of HAIC neoadjuvant therapy with FOLFOX on the survival benefits of BCLC staging A/B 1.
The prognosis of patients beyond Milan standard is poor.
This study explored whether the HAIC-FO regimen neoadjuvant therapy can effectively improve the prognosis beyond Milan Standard liver cancer patients have poor prognosis factors.
Previous studies have shown that the incidence of microvascular invasion (MVI) in such patients is as high as 50%-60%.
MVI is an important factor leading to poor prognosis after liver cancer surgery, but it is currently lacking.
Means to reduce the recurrence and metastasis of such patients, so there is still controversy about whether to perform surgical resection or liver transplantation for patients who exceed the Milan standard
.
For patients whose BCLC stage A does not exceed the Milan standard, the 1-year OS rate after surgery is more than 90%, but the patients who exceed the Milan standard are only 75.
8%, and the 3-year OS rate and 5-year OS rate are only 48.
1% and 10.
7%.
.
Due to the unsatisfactory data, this multicenter randomized controlled phase III clinical trial was carried out
.
The study compared whether HAIC neoadjuvant treatment with FOLFOX as a regimen has an effect on the survival benefit of BCLC staging A/B beyond the Milan standard.
The primary study endpoint is OS, and the secondary study endpoints are PFS and recurrence-free survival (RFS).
) And security
.
Comparison of OS survival of patients beyond Milan standard 2.
Two patients reached CR after HAIC neoadjuvant treatment.
The study first carried out preliminary screening of patients and divided them into direct operation group and HAIC-FO neoadjuvant treatment group.
The initial study included 256 patients In the end, 99 patients and 100 patients in the two groups can be evaluated for efficacy
.
The baseline conditions of the two groups of patients were balanced
.
Study Design There are 2 typical cases in the study.
In case 1, there was a huge tumor in the right lobe and the middle of the liver before treatment, but after four cycles of HAIC neoadjuvant treatment, the tumor achieved complete imaging remission (CR) and postoperative pathology The same performance is CR
.
In case 2, there was a huge tumor lesion in the right lobe of the liver before treatment.
After four cycles of HAIC neoadjuvant treatment, the tumor reached CR and the pathological CR after the operation
.
Case 1 Imaging and postoperative pathology Figure Case 2 Imaging and postoperative pathology Figure 3.
Neoadjuvant therapy can improve the incidence of MVI and prolong the patient’s OS, but there is no significant difference in RFS.
The incidence of MVI was 39.
0% in the baseline situation of patients After neoadjuvant therapy, only 11.
4% of patients had MVI
.
In the neoadjuvant treatment group, 88.
9% of patients underwent surgical resection, ORR was 63.
6%, disease control rate was 96.
0%, 53.
3% of patients achieved PR, 10.
1% of patients achieved pathological CR, 32.
3% of patients had SD, 4.
0 % Of patients have tumor progression (PD)
.
The efficacy of patients in the neoadjuvant therapy group and the direct surgery group were 92.
9% and 79.
5%, respectively, the 2-year OS rates were 78.
6% and 62.
0%, and the 3-year OS rates were 63.
5% and 46.
3% (P=0.
016) ), it can be seen that neoadjuvant therapy has significantly improved the survival benefits of patients
.
Compared with the direct operation group, the PFS rate of the OS curve neoadjuvant treatment group of the two groups was significantly improved (P=0.
017), but there was no statistical difference in RFS
.
The PFS curve of the two groups of patients Professor Wang Lu & Professor Zhang Yu commented on Professor Wang Lu: HAIC is a local treatment method for liver cancer.
With the publication of a series of research results, it has shown very good efficacy, but there are also reports to the contrary.
How does Professor Ji think about the efficacy of HAIC treatment? Professor Zhang Wei: From my personal experience, the HAIC treatment is effective.
We conducted a small sample study before.
Among more than 30 patients, the ORR reached more than 90%, and 15 of them were given the opportunity of surgical resection
.
In the past, the survival period of advanced liver cancer was only 3-6 months.
Now, through the drug treatment of HAIC combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibody, the tumor can be rapidly reduced, and even the purpose of surgical resection can be achieved.
This actually brings a great deal to patients with advanced liver cancer.
hope
.
Professor Wang Lu: Then I would like to ask advanced patients, which can be divided into locally advanced patients and patients with extrahepatic metastases.
What are the main types of patients receiving HAIC treatment? Professor Zhang Yu: Some experts think that it should be used for locally advanced stage.
Because of its transformation effect, I personally have different opinions, because my current patients include patients with locally advanced stage that can be transformed, and some patients who are impossible to transform at all.
For example, people with multiple bone metastases and lung metastases actually receive HAIC and PD-1 monoclonal antibody combined with TKI treatment, which can also effectively control the disease
.
Expert profile Wang Lu Wang Lu is currently the director of liver surgery, chief physician, and doctoral tutor of Fudan University Affiliated Tumor Hospital.
He is mainly engaged in the surgical treatment of liver and gallbladder tumors.
At present, he has performed nearly 800 cases of liver and gallbladder operations per year and has completed laparoscopic liver resection.
There are more than 1,000 cases, which is at the international leading level
.
He is a member of the International Surgery Association (ISS), a member of the International Liver Cancer Association (ILCA), a member of the International Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Association (IHPBA), and a founding member of the International Laparoscopic Liver Resection Association
.
Vice-chairmen, standing committee members and members of many domestic academic societies
.
Expert profile Zhang Zhi, deputy chief physician of the Department of Liver Surgery, Fudan University Tumor Hospital, and professor, member of the Standing Committee of the Liver Cancer Professional Committee of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Member of the Standing Committee of the Biliary Tumor Professional Committee of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association Member of the Professional Committee of Tumor Precision Therapy of the Chinese Anti-Cancer Society Member of the Surgical Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association Member of the Standing Committee of the Professional Committee of Liver Surgery Member of the Professional Committee of Oncology Surgery of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association Surgery Branch Member of the Committee of Biliary Tumor Experts of the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO)