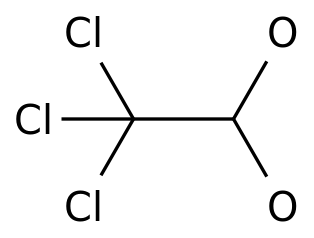
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Cancer progression includes the gradual loss of differentiated phenotypes and the acquisition of progenitor cell-like and stem cell-like characteristics.
Undifferentiated primary tumors are more likely to cause cancer cells to spread to distant organs, leading to disease progression and poor prognosis, especially because metastasis is often resistant to existing treatments.
Since an article by CELL in 18 years proposed a stemness index to assess the degree of carcinogenic dedifferentiation, a large number of related high-level studies have been derived.
Last year, I introduced to you an analysis article based on the dryness index.
I don’t know how much you learned.
Some people may not catch up with the popularity of last year, so today I will introduce you a new dryness index analysis article.
The article is based on the dryness index, uses a large number of machine learning algorithms, and combines clinical samples to provide guidance for the clinical application of dryness index-related markers.
The article was published in BRIEFS IN BIOINFORMATICS (IF: 8.
99) in April.
Machine learning + life letter + clinical is equal to 6 + ideas Scanning code reservation machine learning reveals the characteristics of dryness and distinguishing prognosis among 906 glioblastoma patients, an attractive new dryness classification in terms of immunotherapy and temozolomide response 1.
Abstract: Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most malignant and fatal intracranial tumor, and treatment options are extremely limited.
Immunotherapy has been extensively studied in GBM, but none of the treatments can significantly prolong the overall survival of unselected patients.
Considering that GBM cancer stem cells (CSCs) play a non-negligible role in tumorigenesis and resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, the authors propose a new classification of GBM based on stemness and screen out subgroups that are more sensitive to immunotherapy.
Two GBM subtypes were identified by consensus clustering, and there are significant differences in OS, TMB, TME and immunotherapy response.
2.
Material method: PCBC, TCGA-GBM, CGGA, GISTRIC 2.
0, PUMCH cohort, COLR, ESTIMATE, ssGSEA, GSVA, TIDE, CMap, LASSO, SVM, RFB, XGBoost, qRT-PCR.
3.
Results: 1.
Correlation between stemness index and clinical features Figure 1.
Correlation between clinical and molecular features and mRNAsi in GBM patients 2.
Correlation between stemness index and TIME pattern Figure 2.
Tumor microenvironment patterns and immunity in GBM patients Genomic characteristics and mRNAsi correlation 3.
mRNAsi and GBM patients mutually exclusive OS and PFS outcome correlation Figure 3.
High and low mRNAsi group survival analysis and differential expression analysis Figure 4.
Different clinical features grouping mRNAsi prognostic efficacy 4.
Identify different survival outcomes and functions Annotation and clinical features of stem subtypes Figure 5.
Identifying two stem subtypes with different survival outcomes and functional annotations Figure 6.
Different clinical features grouping mRNAsi prognostic efficacy 5.
Dry subtype 1 has higher CNA burden And TMB Figure 7.
Clinicopathological features and somatic mutations of stem subtypes 1 and 2.
6.
Dry subtypes have different TIME and immune genomic patterns.
Dry subtype 1 is more sensitive to immunotherapy and resistant to TMZ force.
Figure 8.
Different TIME and immune genomic patterns result in two dry subtypes with different immunotherapy and TMZ responses.
7.
Identify potential compounds of two dry subtypes.
Figure 9.
MoA analysis reveals two subtypes of different compounds.
Targeted pathway 8.
Construction and verification of stemness subtype predictors, and the application of stemness classification in two independent cohorts.
Figure 10.
Different machine learning algorithms to identify important features.
Figure 11.
Dryness subtype predictor construction and identification.
12.
Summary of TIME characterization and clinical characteristics of independent cohort: If you did not catch up with last year's thinking, and now you want to refer to last year's thinking again, you may feel a bit old, then today's thinking is believed to provide you with different insights.
Biometrics analysis plus machine learning algorithms, combined with wet experiment verification and real clinical samples, are very worthy of learning.
If you want to refer to life letter analysis, today’s article is very suitable for you.
If you want to explore how the results of life letter analysis can be combined with clinical applications, then today’s thinking is also very suitable for you. Machine learning + life letter + clinical is equal to 6 + ideas scan code reservation
Undifferentiated primary tumors are more likely to cause cancer cells to spread to distant organs, leading to disease progression and poor prognosis, especially because metastasis is often resistant to existing treatments.
Since an article by CELL in 18 years proposed a stemness index to assess the degree of carcinogenic dedifferentiation, a large number of related high-level studies have been derived.
Last year, I introduced to you an analysis article based on the dryness index.
I don’t know how much you learned.
Some people may not catch up with the popularity of last year, so today I will introduce you a new dryness index analysis article.
The article is based on the dryness index, uses a large number of machine learning algorithms, and combines clinical samples to provide guidance for the clinical application of dryness index-related markers.
The article was published in BRIEFS IN BIOINFORMATICS (IF: 8.
99) in April.
Machine learning + life letter + clinical is equal to 6 + ideas Scanning code reservation machine learning reveals the characteristics of dryness and distinguishing prognosis among 906 glioblastoma patients, an attractive new dryness classification in terms of immunotherapy and temozolomide response 1.
Abstract: Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most malignant and fatal intracranial tumor, and treatment options are extremely limited.
Immunotherapy has been extensively studied in GBM, but none of the treatments can significantly prolong the overall survival of unselected patients.
Considering that GBM cancer stem cells (CSCs) play a non-negligible role in tumorigenesis and resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, the authors propose a new classification of GBM based on stemness and screen out subgroups that are more sensitive to immunotherapy.
Two GBM subtypes were identified by consensus clustering, and there are significant differences in OS, TMB, TME and immunotherapy response.
2.
Material method: PCBC, TCGA-GBM, CGGA, GISTRIC 2.
0, PUMCH cohort, COLR, ESTIMATE, ssGSEA, GSVA, TIDE, CMap, LASSO, SVM, RFB, XGBoost, qRT-PCR.
3.
Results: 1.
Correlation between stemness index and clinical features Figure 1.
Correlation between clinical and molecular features and mRNAsi in GBM patients 2.
Correlation between stemness index and TIME pattern Figure 2.
Tumor microenvironment patterns and immunity in GBM patients Genomic characteristics and mRNAsi correlation 3.
mRNAsi and GBM patients mutually exclusive OS and PFS outcome correlation Figure 3.
High and low mRNAsi group survival analysis and differential expression analysis Figure 4.
Different clinical features grouping mRNAsi prognostic efficacy 4.
Identify different survival outcomes and functions Annotation and clinical features of stem subtypes Figure 5.
Identifying two stem subtypes with different survival outcomes and functional annotations Figure 6.
Different clinical features grouping mRNAsi prognostic efficacy 5.
Dry subtype 1 has higher CNA burden And TMB Figure 7.
Clinicopathological features and somatic mutations of stem subtypes 1 and 2.
6.
Dry subtypes have different TIME and immune genomic patterns.
Dry subtype 1 is more sensitive to immunotherapy and resistant to TMZ force.
Figure 8.
Different TIME and immune genomic patterns result in two dry subtypes with different immunotherapy and TMZ responses.
7.
Identify potential compounds of two dry subtypes.
Figure 9.
MoA analysis reveals two subtypes of different compounds.
Targeted pathway 8.
Construction and verification of stemness subtype predictors, and the application of stemness classification in two independent cohorts.
Figure 10.
Different machine learning algorithms to identify important features.
Figure 11.
Dryness subtype predictor construction and identification.
12.
Summary of TIME characterization and clinical characteristics of independent cohort: If you did not catch up with last year's thinking, and now you want to refer to last year's thinking again, you may feel a bit old, then today's thinking is believed to provide you with different insights.
Biometrics analysis plus machine learning algorithms, combined with wet experiment verification and real clinical samples, are very worthy of learning.
If you want to refer to life letter analysis, today’s article is very suitable for you.
If you want to explore how the results of life letter analysis can be combined with clinical applications, then today’s thinking is also very suitable for you. Machine learning + life letter + clinical is equal to 6 + ideas scan code reservation