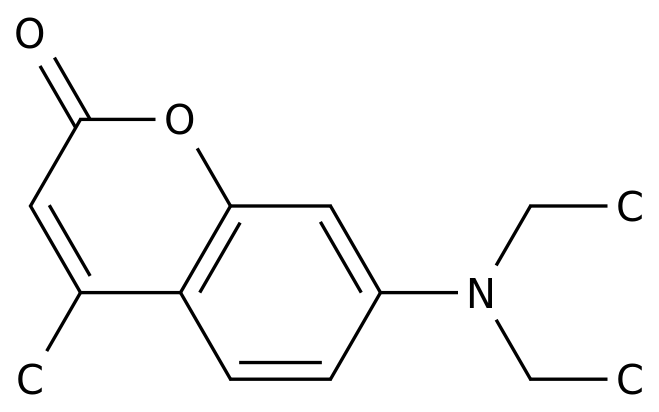
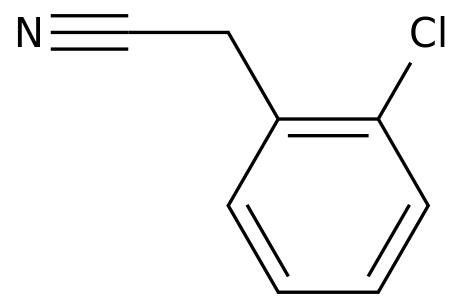
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
1.
Tensile strength? Tensile strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand before it is stretched
.
Some non-brittle materials deform before breaking, but Kevlar® (aramid) fibers, carbon fibers, and E-glass fibers are fragile, and there is almost no deformation to break
.
Tensile strength is measured by the force per unit area (Pa or Pascals)
.
? Stress is force, strain is deflection due to stress
.
The following table shows three commonly used reinforcing fibers: carbon fiber, aramid fiber, glass fiber and epoxy resin tensile strength comparison, it is worth noting that these figures are only for comparison, they can vary with the manufacturing process, epoxy resin composition, aromatic The change of fiber formula, precursor fiber of carbon fiber, etc.
, the unit is MPa
.
? 2.
Density and strength-to-weight ratio? When comparing the densities of the three materials, you can see significant differences in the three fibers
.
If you make three samples of exactly the same size and weight, you will soon find that Kevlar® fiber is much lighter, followed by carbon fiber, and E-glass fiber is the heaviest
.
? Therefore, for the same weight of composite materials, carbon fiber or Kevlar? can obtain higher strength
.
In other words, any structure made of carbon fiber or Kevlar® composite material that requires a given strength is smaller or thinner than a structure made of glass fiber
.
? After making the samples and testing, you will find that the weight of the glass fiber composite is almost twice that of Kevlar? or carbon fiber laminate
.
This means that using Kevlar® or carbon fiber can save a lot of weight
.
This characteristic is called the strength-to-weight ratio
.
?? 3.
Young's modulus? Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of an elastic material and a method of describing materials
.
It is defined as the ratio of uniaxial (in one direction) stress to uniaxial strain (deformation in the same direction)
.
Young's modulus = stress/strain, which means that a material with a high Young's modulus is harder than a material with a low Young's modulus
.
? The stiffness of carbon fiber, Kevlar? and glass fiber is very different
.
The stiffness of carbon fiber is about twice that of aramid fiber, and the stiffness is 5 times higher than that of glass fiber
.
The disadvantage of carbon fiber's excellent stiffness is that it tends to be more brittle
.
When it fails, it tends not to show too much strain or deformation
.
? 4.
Flammability and thermal degradation? Both Kevlar? and carbon fiber are resistant to high temperatures, and neither has a melting point
.
Both materials have been used in protective clothing and fire-resistant fabrics
.
The glass fiber will eventually melt, but it also has high temperature resistance
.
Of course, frosted glass fiber used in buildings can also improve fire resistance
.
? Carbon fiber and Kevlar? are used to make protective fire-fighting or welding blankets or clothing
.
Kevlar gloves are commonly used in the meat industry to protect hands when using knives
.
Since fibers are rarely used alone, the heat resistance of the matrix (usually epoxy resin) is also important
.
After being heated, the epoxy resin will soften quickly
.
? 5.
Electrical conductivity? Carbon fiber can conduct electricity, but Kevlar? and glass fiber do not
.
Kevlar® is used for the cable in the transmission tower
.
Although it does not conduct electricity, it can absorb water, and water does conduct electricity
.
Therefore, in such applications, a waterproof coating must be applied to the Kevlar
.
? Because carbon fiber can conduct electricity, when it comes into contact with other metal parts, galvanic corrosion becomes a problem
.
6.
UV degradation? Aramid fiber will degrade under sunlight and high UV environment
.
Carbon fiber or glass fiber is not very sensitive to ultraviolet radiation
.
However, some common substrates, such as epoxy resin, remain in the sun, which will turn white and lose strength.
Polyester and vinyl ester resins are more resistant to ultraviolet rays, but are weaker than epoxy resins
.
7.
Anti-fatigue? If parts are repeatedly bent and straightened, they will eventually fail due to fatigue
.
Carbon fiber is somewhat sensitive to fatigue and tends to fail catastrophically, while Kevlar® is more resistant to fatigue
.
Glass fiber is somewhere in between
.
8.
Wear resistance? Kevlar® has strong wear resistance, which makes it difficult to cut
.
One of the common uses of Kevlar® is as a protective glove for areas where the hand may be cut by glass or where sharp blades are used
.
The resistance of carbon fiber and glass fiber is weak
.
9.
Chemical resistance? Aramid fiber is sensitive to strong acids, strong alkalis and certain oxidants (such as sodium hypochlorite), which can cause fiber degradation
.
Ordinary chlorine bleach (such as Clorox?) and hydrogen peroxide cannot be used with Kevlar?, oxygen bleach (such as sodium perborate) can be used without damaging the aramid fiber
.
? Carbon fiber is very stable and not sensitive to chemical degradation
.
However, epoxy compounds will degrade
.
10.
Matrix bonding performance? In order to make carbon fiber, Kevlar® and glass play the best performance, they must be kept in place in the matrix (usually epoxy resin)
.
Therefore, the ability of epoxy resin and various fibers to bond together is very important
.
? Carbon fiber and glass fiber can be easily adhered to epoxy, but the strength of the aramid fiber-epoxy bond is not as expected, and this reduced adhesion makes water infiltration occur
.
As a result, aramid fibers tend to absorb water, coupled with undesirable adhesion to epoxy resin, which means that if the surface of the kevlar? composite material is damaged and water may enter, then Kevlar? may absorb water along the fiber, and Weaken composite materials
.
11.
Color and weaving.
The natural state of aramid is light golden, it can be colored, and now there are many good shades
.
Fiberglass is also available in colored versions
.
Carbon fiber is always black and can be blended with colored aramid, but it cannot be colored by itself
.
Tensile strength? Tensile strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand before it is stretched
.
Some non-brittle materials deform before breaking, but Kevlar® (aramid) fibers, carbon fibers, and E-glass fibers are fragile, and there is almost no deformation to break
.
Tensile strength is measured by the force per unit area (Pa or Pascals)
.
? Stress is force, strain is deflection due to stress
.
The following table shows three commonly used reinforcing fibers: carbon fiber, aramid fiber, glass fiber and epoxy resin tensile strength comparison, it is worth noting that these figures are only for comparison, they can vary with the manufacturing process, epoxy resin composition, aromatic The change of fiber formula, precursor fiber of carbon fiber, etc.
, the unit is MPa
.
? 2.
Density and strength-to-weight ratio? When comparing the densities of the three materials, you can see significant differences in the three fibers
.
If you make three samples of exactly the same size and weight, you will soon find that Kevlar® fiber is much lighter, followed by carbon fiber, and E-glass fiber is the heaviest
.
? Therefore, for the same weight of composite materials, carbon fiber or Kevlar? can obtain higher strength
.
In other words, any structure made of carbon fiber or Kevlar® composite material that requires a given strength is smaller or thinner than a structure made of glass fiber
.
? After making the samples and testing, you will find that the weight of the glass fiber composite is almost twice that of Kevlar? or carbon fiber laminate
.
This means that using Kevlar® or carbon fiber can save a lot of weight
.
This characteristic is called the strength-to-weight ratio
.
?? 3.
Young's modulus? Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of an elastic material and a method of describing materials
.
It is defined as the ratio of uniaxial (in one direction) stress to uniaxial strain (deformation in the same direction)
.
Young's modulus = stress/strain, which means that a material with a high Young's modulus is harder than a material with a low Young's modulus
.
? The stiffness of carbon fiber, Kevlar? and glass fiber is very different
.
The stiffness of carbon fiber is about twice that of aramid fiber, and the stiffness is 5 times higher than that of glass fiber
.
The disadvantage of carbon fiber's excellent stiffness is that it tends to be more brittle
.
When it fails, it tends not to show too much strain or deformation
.
? 4.
Flammability and thermal degradation? Both Kevlar? and carbon fiber are resistant to high temperatures, and neither has a melting point
.
Both materials have been used in protective clothing and fire-resistant fabrics
.
The glass fiber will eventually melt, but it also has high temperature resistance
.
Of course, frosted glass fiber used in buildings can also improve fire resistance
.
? Carbon fiber and Kevlar? are used to make protective fire-fighting or welding blankets or clothing
.
Kevlar gloves are commonly used in the meat industry to protect hands when using knives
.
Since fibers are rarely used alone, the heat resistance of the matrix (usually epoxy resin) is also important
.
After being heated, the epoxy resin will soften quickly
.
? 5.
Electrical conductivity? Carbon fiber can conduct electricity, but Kevlar? and glass fiber do not
.
Kevlar® is used for the cable in the transmission tower
.
Although it does not conduct electricity, it can absorb water, and water does conduct electricity
.
Therefore, in such applications, a waterproof coating must be applied to the Kevlar
.
? Because carbon fiber can conduct electricity, when it comes into contact with other metal parts, galvanic corrosion becomes a problem
.
6.
UV degradation? Aramid fiber will degrade under sunlight and high UV environment
.
Carbon fiber or glass fiber is not very sensitive to ultraviolet radiation
.
However, some common substrates, such as epoxy resin, remain in the sun, which will turn white and lose strength.
Polyester and vinyl ester resins are more resistant to ultraviolet rays, but are weaker than epoxy resins
.
7.
Anti-fatigue? If parts are repeatedly bent and straightened, they will eventually fail due to fatigue
.
Carbon fiber is somewhat sensitive to fatigue and tends to fail catastrophically, while Kevlar® is more resistant to fatigue
.
Glass fiber is somewhere in between
.
8.
Wear resistance? Kevlar® has strong wear resistance, which makes it difficult to cut
.
One of the common uses of Kevlar® is as a protective glove for areas where the hand may be cut by glass or where sharp blades are used
.
The resistance of carbon fiber and glass fiber is weak
.
9.
Chemical resistance? Aramid fiber is sensitive to strong acids, strong alkalis and certain oxidants (such as sodium hypochlorite), which can cause fiber degradation
.
Ordinary chlorine bleach (such as Clorox?) and hydrogen peroxide cannot be used with Kevlar?, oxygen bleach (such as sodium perborate) can be used without damaging the aramid fiber
.
? Carbon fiber is very stable and not sensitive to chemical degradation
.
However, epoxy compounds will degrade
.
10.
Matrix bonding performance? In order to make carbon fiber, Kevlar® and glass play the best performance, they must be kept in place in the matrix (usually epoxy resin)
.
Therefore, the ability of epoxy resin and various fibers to bond together is very important
.
? Carbon fiber and glass fiber can be easily adhered to epoxy, but the strength of the aramid fiber-epoxy bond is not as expected, and this reduced adhesion makes water infiltration occur
.
As a result, aramid fibers tend to absorb water, coupled with undesirable adhesion to epoxy resin, which means that if the surface of the kevlar? composite material is damaged and water may enter, then Kevlar? may absorb water along the fiber, and Weaken composite materials
.
11.
Color and weaving.
The natural state of aramid is light golden, it can be colored, and now there are many good shades
.
Fiberglass is also available in colored versions
.
Carbon fiber is always black and can be blended with colored aramid, but it cannot be colored by itself
.




![disodium 4,4'-bis[[4-anilino-6-[(2-carbamoylethyl)(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-1,3,5,-triazin-2-yl]amino]stilbene-2,2'-disulphonate CAS NO 27344-06-5](https://file.echemi.com/fileManage/upload/cas/77/e1abc71f-648d-403c-93fe-69b5c9401d56.gif)