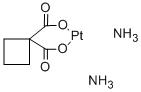
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
1.
Mediastinal lymph node map
Atlas of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes 1.
Atlas of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes
IASLC lymph node map 2009
IASLC lymph node map 2009The division of mediastinal lymph nodes
2.Mediastinal lymph node division II, mediastinal lymph node division II, mediastinal lymph node division
IASLC map (1)
IASLC map (1)Group 1 lymph nodes (low cervical, supraclavicular, and sternal notch nodes) are the lower cervical, supraclavicular, and sternal notch nodes
.
Upper bound: the lower border of the cricoid cartilage, lower bound: the upper border of the clavicle and the manubrium, the midline of the trachea as the border between 1R and 1L
.
Group 1 lymph nodes (low cervical, supraclavicular, and sternal notch nodes) are the lower cervical, supraclavicular, and sternal notch nodes
IASLC map(2)
IASLC map(2)Group 2 lymph nodes (upper paratracheal lymph nodes)
.
Group 2 lymph nodes (upper paratracheal lymph nodes)
A loss plane at the left edge of the trachea distinguishes left and right group 2 lymph nodes
IASLC map(3)
IASLC map(3)The third group of lymph nodes is divided into anterior prevascular nodes (3A, pre- vascular ) and posterior retrotracheal nodes (3p pre-trotracheal)
.
The third group of lymph nodes is divided into anterior prevascular nodes (3A, pre- vascular ) and posterior retrotracheal nodes (3p pre-trotracheal)
3p: Not immediately adjacent to the trachea, but behind the esophagus and anterior to the spine
.
Upper bound: superior border of manubrium, lower bound: tracheal carina
3A: Not immediately adjacent to the trachea, but anterior to the blood vessels
.
The upper bound: the upper border of the manubrium, the lower bound: the tracheal carina
.
3A: Not immediately adjacent to the trachea, but anterior to the blood vessels
.
The upper bound: the upper border of the manubrium, the lower bound: the tracheal carina
.
3A: Not immediately adjacent to the trachea, but anterior to the blood vessels
3p: Not immediately adjacent to the trachea, but behind the esophagus and anterior to the spine
.
Upper bound: superior border of manubrium, lower bound: tracheal carina
.
Upper bound: superior border of manubrium, lower bound: tracheal carina
IASLC map(4)
IASLC map(4)Lymph nodes in group 4 (lower paratracheal) are similar to group 2 and are also located around the trachea, but caudal to the plane of the aortic arch
.
Lymph nodes in group 4 (lower paratracheal) are similar to group 2 and are also located around the trachea, but caudal to the plane of the aortic arch
.
The right inferior paratracheal lymph node (4R) extends to the left border of the trachea
.
Upper bound: cross-section of the intersection of the caudal border of the innominate (left brachiocephalic) vein with the trachea, lower bound: the inferior border of the azygos vein
.
The left inferior paratracheal lymph node (4L) is located to the left of the left border of the trachea and includes all paratracheal lymph nodes located medial to the pulmonary ligament
.
Upper bound: the upper border of the aortic arch, lower bound: the upper border of the left main pulmonary artery
.
The sagittal plane on the left side of the trachea is the dividing line between the left group 4 lymph node (4L) and the right group 4 lymph node (4R)
.
.
IASLC map(5, 6)
IASLC map(5, 6)Groups 5 and 6 lymph nodes (group 5 subaortic lymph nodes, subaortic; group 6 para-aortic lymph nodes, para-aortic) could not be detected by EBUS-TBNA
.
.
Subaortic lymph nodes, also known as aorto-pulmonary window lymph nodes, are located on the lateral side of the pulmonary ligament or the aorta or the left pulmonary artery, proximal to the first branch of the left pulmonary artery, and are surrounded by the mediastinal pleura
.
The lymph nodes in the AP window are located lateral to the pulmonary ligament, not between the aorta and the pulmonary trunk, but lateral to these vessels
.
.
The lymph nodes in the AP window are located lateral to the pulmonary ligament, not between the aorta and the pulmonary trunk, but lateral to these vessels
.
Para-aortic lymph nodes are the ascending aorta or phrenic lymph nodes.
The lymph nodes are located laterally and anteriorly of the ascending aorta and the aortic arch, between the upper and lower borders of the aortic arch
.
The lymph nodes are located laterally and anteriorly of the ascending aorta and the aortic arch, between the upper and lower borders of the aortic arch
.
IASLC map(7)
IASLC map(7)Group 7 lymph nodes (subcarinal nodes) are located at the end of the tracheal carina and are not associated with the lower lobe bronchi or the internal pulmonary arteries
.
On the left, it is bounded by the superior border of the left lower lobe bronchus; on the right, it is bounded by the inferior border of the right middle bronchus
.
.
On the left, it is bounded by the superior border of the left lower lobe bronchus; on the right, it is bounded by the inferior border of the right middle bronchus
.
IASLC map(8)
IASLC map(8)Group 8 lymph nodes (paraesophageal) are located below the subcarinal lymph nodes and extend to the diaphragm
.
.
PET image showing increased FDG uptake in lymph nodes, while CT in the same cross-section did not show enlarged lymph nodes (blue arrows), a node with a high probability of cancer metastasis, PET is more specific for non-enlarged nodes than for enlarged ones lymph nodes
.
.
IASLC map(9)
IASLC map(9)Group 9 lymph nodes (Pulmonary Ligament) are located within the pulmonary ligament and include the lymph nodes in the posterior wall and in the lower part of the inferior pulmonary vein
.
The pulmonary ligament is the downward extension of the mediastinal pleura that surrounds the hilum after the mediastinal pleura is folded
.
.
The pulmonary ligament is the downward extension of the mediastinal pleura that surrounds the hilum after the mediastinal pleura is folded
.
IASLC map(10)
IASLC map(10)Group 10 lymph nodes (hilar) proximal lobe lymph nodes, including all main bronchi and hilar lymph nodes adjacent to the vessels
.
On the right, it extends from the inferior border of the azygos vein to the interlobar region; on the left, it extends from the superior border of the pulmonary artery to the interlobar region
.
.
On the right, it extends from the inferior border of the azygos vein to the interlobar region; on the left, it extends from the superior border of the pulmonary artery to the interlobar region
.
IASLC map(11-14)
IASLC map(11-14)The 11th group, the interlobar lymph nodes (11, interlobar), is located at the bronchial bifurcation
.
The left group 11 lymph node is below the second carina
.
The 11th lymph node on the right is further divided into 11s and 11i
.
.
The left group 11 lymph node is below the second carina
.
The 11th lymph node on the right is further divided into 11s and 11i
.
Group 12 lymph nodes (12, lobar) are located at the origin of the lobar bronchi
.
.
3.
Lymph node biopsy: mediastinoscopy, endoscopic ultrasonography with fine needle aspiration (EUS)
Lymph node biopsy: mediastinoscopy, endoscopic ultrasonography with fine needle aspiration (EUS)
Conventional mediastinoscopy: The following groups of lymph nodes can be biopsied by cervical mediastinoscopy: upper paratracheal nodes (2L, 2R), lower paratracheal nodes (4L, 4R), and subcarinal nodes (7)
.
The supraclavicular lymph nodes (1) are located above the upper border of the manubrium and cannot be examined by routine cervical mediastinoscopy
.
.
The supraclavicular lymph nodes (1) are located above the upper border of the manubrium and cannot be examined by routine cervical mediastinoscopy
.
Expanded mediastinoscopy: Tumors in the upper lobe of the left lung may metastasize to sub-aortic lymph nodes (5) and para-aortic lymph nodes (6)
.
These two groups of lymph nodes cannot be biopsied by conventional cervical mediastinoscopy
.
Expanded mediastinoscopy can replace the anterior-second intercostal space mediastinotomy for exploration of mediastinal lymph nodes
.
Expanded mediastinoscopes are not easy to maneuver and are therefore less routinely used
.
.
These two groups of lymph nodes cannot be biopsied by conventional cervical mediastinoscopy
.
Expanded mediastinoscopy can replace the anterior-second intercostal space mediastinotomy for exploration of mediastinal lymph nodes
.
Expanded mediastinoscopes are not easy to maneuver and are therefore less routinely used
.
EUS-FNA: Esophageal endoscopic ultrasonographic fine-needle aspiration can be used for the evaluation of all mediastinal lymph nodes
.
In addition to evaluating the left adrenal gland and left hepatic lobe, EUS can also evaluate the inferior mediastinal lymph nodes (7, 8, 9)
.
.
In addition to evaluating the left adrenal gland and left hepatic lobe, EUS can also evaluate the inferior mediastinal lymph nodes (7, 8, 9)
.
leave a message here