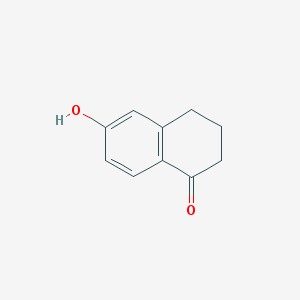
Intestinal infection eventually leads to chronic diseases or is caused by intestinal neurons and macrophages
-
Last Update: 2020-01-14
-
Source: Internet
-
Author: User
Search more information of high quality chemicals, good prices and reliable suppliers, visit
www.echemi.com
In a healthy gut, the immune system resists infection through inflammation, but too much inflammation can cause lasting damage In other words, inflammation tends to do good and bad Some scientists believe that infection may damage the intestinal nervous system, leading to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Researchers at Rockefeller University revealed the cause of gut neuron death and the protective mechanism of the immune system through experiments The research results were published in cell Intestinal associated neurons (eans) are closely related to immune cells, which constantly monitor and regulate intestinal homeostasis In order to understand the effect of infection on the nervous system and analyze the neurons in the gut, the researchers gave the mice Salmonella SPIB, which can cause food poisoning By constructing the intestinal infection model of mice, the long-term gastrointestinal symptoms such as decreased intestinal motility and decreased excited iean were observed It was also found that these cells expressed two genes, nlrp 6 and caspase 11, which promote specific inflammatory response In turn, they can promote programmed cell death When the researchers knocked out these genes in mouse neurons, they found a decrease in the number of neurons Neurons (green) appear near the inflammatory molecule nlrp 6 (pink) along the edge of the small intestine Previous studies in the mucida lab have shown that intestinal macrophages (MMS) express anti-inflammatory genes and work with neurons to move food through the digestive tract This study further revealed that macrophages have some type of receptor molecules, which receive the stress signals released by another group of neurons after infection Once activated, this receptor will induce macrophages to produce polyamine molecules, which will interfere with the cell death process Intestinal bacterial infection model To sum up, this study found that (1) intestinal infection can cause neuron reduction and long-term gastrointestinal symptoms, the former is dependent on the nlrp 6 and caspase 11 genes, (2) MMS can react rapidly to intestinal pathogens, (3) neuron death is limited by mm - β 2-adrenergic-arginase-1-polyamine axis reference material:
This article is an English version of an article which is originally in the Chinese language on echemi.com and is provided for information purposes only.
This website makes no representation or warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness ownership or reliability of
the article or any translations thereof. If you have any concerns or complaints relating to the article, please send an email, providing a detailed
description of the concern or complaint, to
service@echemi.com. A staff member will contact you within 5 working days. Once verified, infringing content
will be removed immediately.