-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
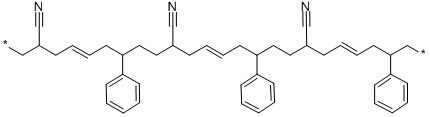
In view of the problem of poor mechanical properties of hydrogel materials, Zhou Feng's research group of Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences recently designed and prepared an ultra-high-strength hydrogel
with a double cross-linking network.
The novel structure of double crosslinking of covalent bonds and coordination bonds greatly improves the mechanical properties
of hydrogels.
The hydrogel exhibits ultra-high tensile strength at break, with fracture stress greater than 6MPa, elongation at break greater than 700%, and excellent
mechanical properties.
Since the coordination bond broken during the tensile process is a reversible non-covalent bond, the coordination bond broken after stretching can be reformed in a short time, so that the hydrogel exhibits excellent fatigue resistance
.
The material is expected to gain important applications
in the fields of joint lubrication materials and artificial blood vessels in the future.
According to reports, hydrogel is a kind of polymer material with three-dimensional network structure containing a large amount of water, which has important application prospects in the fields of joint lubrication, tissue engineering, and drug controlled release carriers, and has attracted widespread attention
.
Hydrogels also have very similar properties to many active tissues of the human body, such as human joint lubricating cartilage, muscle tissue, etc.
, making them the most ideal alternative material for artificial joints and the best substrate material
for the development of muscle-like drives.
However, hydrogels are usually fragile and prone to mechanical rupture after external forces, which greatly limits their application
.
(Lan)