Nat Med: Watch out! Heart disease significantly increases mortality in breast cancer patients!
-
Last Update: 2020-07-28
-
Source: Internet
-
Author: User
Search more information of high quality chemicals, good prices and reliable suppliers, visit
www.echemi.com
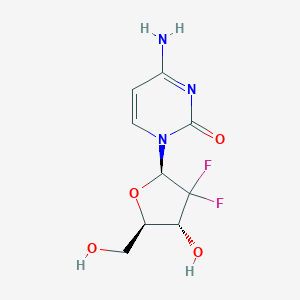
NEW YEAR'S DAY -- Breast cancer patients are more likely to die of cancer after a heart attack, a new study findsThe study, led by researchers at New York University's Grossman School of Medicine, reveals how heart attacks trigger a special, cancer-friendly immune response by blocking blood flow to arteriesThe study authors say the immune system is designed to attack invading bacteria and viral immune systems that also recognize abnormal cancer cells and think they are worth attackingBut it was found that heart attacks and other events of reduced blood flow, such as stroke and heart failure, led to changes in immune cells, which reduced their ability to respond to tumorsFILE PHOTO: A study published online this month found that patients with early-stage breast cancer had a greater risk of recurrence, spread and dying from breast cancer than those who had experienced heart attack, stroke or heart failureThe new study also found that mice with normal blood flow in the coronary arteries tripled the size of tumors in mice with normal blood flow in the coronary arteries to simulate breast cancer within days of a heart attack"Heart attacks by weakening the immune system against cancer cells seem to provide an environment for tumorgrowth," said the newsletter's author, DrDrDrDrDrDrDrShe and Professor of Cardiology At NYU Langone Health Center"While further research is needed, our results support active clinical management of cardiovascular risk factors, not only to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease but also to reduce breast cancer progression." Adding that because every Woman in the United States has breast cancer in their lifetime, there is an urgent need to better understand the interaction between cancer and cardiovascular disease among nearly 10,000 breast cancer survivors in the United StatesPrevious studies have shown that breast cancer increases the risk of heart disease, largely due to wear and tear from chemotherapy and radiotherapyIn the course of searching the literature, the current team was surprised to find that no laboratory examination of whether a heart attack could worsen cancer progression To study the mechanism behind this link, the authors created a model to implant cancer cells in the breast tissue of mice and then surgically shut down ligation on their left coronary artery pre-dealms The human counterpart to this artery is also known as myocardial infarction of the common blood clot that causes a heart attack, or is usually caused by cholesterol deposits or "hardening of the arteries." The team then compared tumor growth in ligation and untied mice with false surgery to explain the changes caused by the surgery itself Although the exact biochemical signals have not yet been determined, studies have found that heart attacks cause system-wide changes in immune cells in the bone marrow, blood and tumors First, the researchers found a "significant increase" in the number of tumor cells in the clumped mice, indicating that they rapidly proliferate cells, a measure of malignant growth Photo Source: Experiments in mice also found an increase in the number of white blood cell mononucleocells that cause heart disease These cells grow and mature in the bone marrow into the blood's activity in abnormal areas such as injuries, infections, and tumors In addition, the authors found that the proportion of immature mononucleocells in tumors after a heart attack increased the programming of these mononucleosis cells so that they no longer attack cancer cells there Other tests have shown that heart attacks alter the activity of genes in mouse immune cells, many of which would have amplified the immune attack Other important driver changes occur not in the genetic code but in the upper structure of the protein that stores the code, which makes it more difficult for the genetic instructions to amplify the immune response to the machines that were supposed to read them Taking into account the evidence of the link between cardiovascular disease and breast cancer, researchers believe it is necessary to further study the effects of measures to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as exercise and treatment of high cholesterol and high blood pressure, in preventing cancer from worsening in patients () References: :
This article is an English version of an article which is originally in the Chinese language on echemi.com and is provided for information purposes only.
This website makes no representation or warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness ownership or reliability of
the article or any translations thereof. If you have any concerns or complaints relating to the article, please send an email, providing a detailed
description of the concern or complaint, to
service@echemi.com. A staff member will contact you within 5 working days. Once verified, infringing content
will be removed immediately.