-
Categories
-
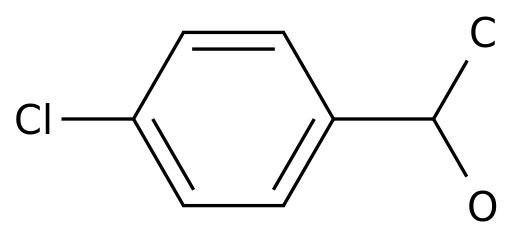
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
The advent of immunotherapy has provided new treatment options for many patients with advanced cancers, and has been shown to shrink tumors and extend survival in many types of cancer.
, however, only 20 to 30 percent of patients currently benefit.
in a small number of patients, immunotherapy can produce serious adverse reactions.
, knowing in advance whether a patient will benefit from immunotherapy will help patients weigh different treatment options.
In a study published recently in Nature's Nature Cancer, scientists customized a individualized test based on a patient's tumor status to assess each patient's response to a particular immunotherapy drug in a simple, fast, and non-invasive way.
team from Canada's Princess Margaret Cancer Centre found that individuals could be predicted to benefit from immunotherapy within six to seven weeks, based on changes in the level of DNA fragments that fall off the tumor into the bloodstream.
, the researchers note that using various scanning methods may take months to detect whether the tumor is shrinking.
using new techniques to detect genomes, the same changes can be detected in dna fragments circulating in the bloodstream, known as circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA).
Professor Scott Bratman, a radiation oncologist and lead author of the paper, said: "The new generation of sequencing techniques allows us to accurately and sensitively detect and measure ctDNA, allowing us to pinpoint whether a cancer is active or not quite quickly.
study, the researchers analyzed changes in ctDNA in 74 patients with different types of advanced cancer who were being treated with the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab.
researchers examined all the genes in the patient's tumor biopsy tissue, paying particular attention to mutations in cancer.
, depending on the type of cancer, the number of cancer mutations in each tissue sample ranged from tens to tens of thousands.
researchers selected 16 gene mutation development and customized individualized testing options for each patient's condition, detecting changes in their ctDNA through simple blood pumping.
. Trevor Pugh, co-author of the study, said, "The novelty is that instead of taking a 'one size fits all' approach, we designed individual blood tests based on each person's list of cancer mutations."
researchers found that in the 6th to 7th weeks after treatment, ctDNA levels in 33 patients decreased from the original baseline level.
these patients have better treatment responses and longer lifetimes.
, 12 patients had ctDNA reduced to undestaed levels during treatment, and they all survived during the 25-month follow-up period.
, the increase in ctDNA levels is mostly associated with rapid disease progression and low survival rates in patients.
Professor Lillian Siu, a senior medical oncologist and co-author of the study, said the study was the first to span multiple tumors and showed that measuring the level of ctDNA could serve as an indicator of whether patients responded well to immunotherapy, "observing ctDNA removal during treatment and its association with long-term survival is novel and exciting, indicating that this biomarker can have a wide range of clinical effects."
" References: Scott Bratman et al., (2020), (2020) Between Theeaned Median tumor DNA analysis as a predictive biomarker in solid tumor patients treated with pembrolizumab. Nature Cancer. DOI: A blood test can predict who benefits from immunotherapy. Retrieved 2020-08-04, from.