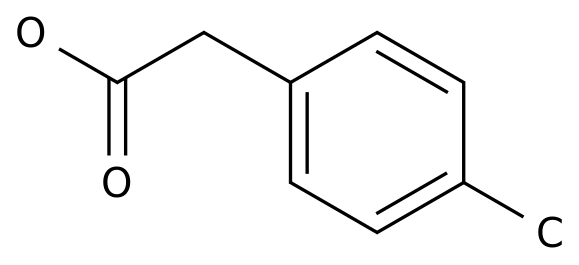
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Cancer has always been a global health problem
Note: The graph on the left shows the estimated number of new cancer cases in 2020
The graph on the right shows the estimated number of cancer deaths in 2020
Data source: GLOBCAN 2020
Graphic source: Global Cancer Observatory
Currently, patients have a variety of treatment options, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy
Targeted therapy: Use is a precision medicine that targets proteins that control the growth, division and spread of cancer cells
Immunotherapy: Harnesses the ability of a patient's own immune system to fight cancer
Table 1: FDA-approved treatments for PD-1 and PD-L1
In addition to this, researchers are currently actively investigating new targets, including T-cell immune receptors (TIGITs) with Ig and EM domains
In January 2021, based on data from the Phase II CITYSCAPE trial, Roche announced that the combination of tiragolumab (an anti-TIGIT antibody) and atezolizumab showed encouraging efficacy and safety in PD-L1-positive metastatic non-small cell lung cancer sex
At present, both small molecule targeted therapy and immunotherapy alone have shown good clinical effects
01 Recombinant drug target protein
01 Recombinant drug target protein
Note: The graph on the left shows the estimated global cancer deaths in 2020
The graph on the right shows the estimated 2020 cancer deaths in women
Data source: GLOBCAN 2020
Graphic source: Global Cancer Observatory
According to statistics, lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in both men and women worldwide, with an estimated 1.
A.
B.
Legend: Products containing the extracellular or intracellular domains of proteins
(A) Binding assay of EGF and EGFR: immobilized human EGF hFc (Cat: 10605-H01H) at a concentration of 2 µg/ml can bind to human EGFR His (Cat: 10001-H08H)
(B) Determination of specific activity of EGFR (AA668-1210)
In addition, in order to protect themselves, tumor cells can also evade detection by the patient's immune system by staying away from immune cells
At present, therapeutic antibodies that block PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1 have been proved to have clinical efficacy by scientific research, and anti-CD47 antibodies can also enhance the phagocytosis of tumor cells by the patient's body by blocking the binding of CD47 to SIRPa role
02 Cytokines
02 CytokinesFunctional analysis of partial antibodies may also require testing on cells, in which case cytokines are often used
Reference source:
Reference source:1.
1.
3.
4.
Lei Zhong et al.
, “Small Molecules in Targeted Cancer Therapy: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives,” SignalTransduction and Targeted Therapy 6, no.
1 (2021): 1–48, https://doi.
org/ 10.
1038/s41392-021-00572-w.
5.
“Herceptin (Trastuzumab) FDA Approval History,” Drugs.
com, accessed January 10, 2022, https:// “Herceptin (Trastuzumab) FDA Approval History,” Drugs.
com, accessed January 10, 2022, https:// 6.
“Iressa (Gefitinib) FDA Approval History - Drugs.
Com,” accessed January 10, 2022, https:// “Iressa (Gefitinib) FDA Approval History - Drugs.
Com,” accessed January 10, 2022, https:// 7.
Raju K.
Vaddepally et al.
, “Review of Indications of FDA-Approved Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors per NCCN Guidelines with the Level of Evidence,” Cancers 12, no.
3 (March 20, 2020), https://doi.
org /10.
3390/cancers12030738.
Raju K.
Vaddepally et al.
, “Review of Indications of FDA-Approved Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors per NCCN Guidelines with the Level of Evidence,” Cancers 12, no.
3 (March 20, 2020), https://doi.
org /10.
3390/cancers12030738.
8.
P.
Zatloukalová et al.
, “[The Role of PD-1/PD-L1 Signaling Pathway in Antitumor Immune Response],” Klinicka Onkologie: CasopisCeske a Slovenske Onkologicke Spolecnosti 29 Suppl 4, no.
Suppl 4 (Fall 2016) : 72–77.
P.
Zatloukalová et al.
, “[The Role of PD-1/PD-L1 Signaling Pathway in Antitumor Immune Response],” Klinicka Onkologie: CasopisCeske a Slovenske Onkologicke Spolecnosti 29 Suppl 4, no.
Suppl 4 (Fall 2016) : 72–77.
9.
Hyun Tae Lee et al.
, “Molecular Mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade via Anti-PD-L1 Antibodies Atezolizumab and Durvalumab,” Scientific Reports 7 (July 17, 2017), https://doi.
org /10.
1038/s41598-017-06002-8.
Hyun Tae Lee et al.
, “Molecular Mechanism of PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade via Anti-PD-L1 Antibodies Atezolizumab and Durvalumab,” Scientific Reports 7 (July 17, 2017), https://doi.
org /10.
1038/s41598-017-06002-8.
10.
Hyun Tae Lee, Sang Hyung Lee, and Yong-Seok Heo, “Molecular Interactions of Antibody Drugs Targeting PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 in Immuno-Oncology,” Molecules 24, no.
6 (March 26, 2019), https://doi.
org/10.
3390/molecules24061190.
Hyun Tae Lee, Sang Hyung Lee, and Yong-Seok Heo, “Molecular Interactions of Antibody Drugs Targeting PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 in Immuno-Oncology,” Molecules 24, no.
6 (March 26, 2019), https://doi.
org/10.
3390/molecules24061190.
11.
Francesco Passiglia et al.
, “
Francesco Passiglia et al.
, “
Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors Combinations in Metastatic NSCLC: New Options on the Horizon?
Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors Combinations in Metastatic NSCLC: New Options on the Horizon? ,” ImmunoTargets and Therapy 10 (February 5, 2021): 9–26, https://doi.
org/10.
2147/ITT.
S253581.
org/10.
2147/ITT.
S253581.
12.
“Genentech's Novel Anti-TIGIT Tiragolumab Granted FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation in Combination With Tecentriq for PD-L1-High Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer,” January 5, 2021, https:// /20210104005887/en/Genentech%E2%80%99s-Novel-Anti-TIGIT-Tiragolumab-GrantedFDA-Breakthrough-Therapy-Designation-in-Combination-With-Tecentriq-for-PD-L1-High-Non-Small-Cell -Lung-Cancer
“Genentech's Novel Anti-TIGIT Tiragolumab Granted FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation in Combination With Tecentriq for PD-L1-High Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer,” January 5, 2021, https:// /20210104005887/en/Genentech%E2%80%99s-Novel-Anti-TIGIT-Tiragolumab-GrantedFDA-Breakthrough-Therapy-Designation-in-Combination-With-Tecentriq-for-PD-L1-High-Non-Small-Cell -Lung-Cancer
13.
Johann S.
Bergholz et al.
, “Integrating Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy in Cancer Treatment: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications,” Clinical Cancer Research 26, no.
21 (November 1, 2020): 5557–66, https:// doi.
org/10.
1158/1078-0432.
CCR-19-2300.
Johann S.
Bergholz et al.
, “Integrating Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy in Cancer Treatment: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications,” Clinical Cancer Research 26, no.
21 (November 1, 2020): 5557–66, https:// doi.
org/10.
1158/1078-0432.
CCR-19-2300.
14.
Deric L.
Wheeler, Emily F.
Dunn, and Paul M.
Harari, “Understanding Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors—Impact on Future Treatment
Deric L.
Wheeler, Emily F.
Dunn, and Paul M.
Harari, “Understanding Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors—Impact on Future Treatment
Strategies,” Nature Reviews.
Clinical Oncology 7, no.
9 (September 2010): 493–507, https://doi.
org/10.
1038/nrclinonc.
2010.
97.
Clinical Oncology 7, no.
9 (September 2010): 493–507, https://doi.
org/10.
1038/nrclinonc.
2010.
97.
15.
Remah Ali and Michael K.
Wendt, “The Paradoxical Functions of EGFR during Breast Cancer Progression,” Signal Transduction
Remah Ali and Michael K.
Wendt, “The Paradoxical Functions of EGFR during Breast Cancer Progression,” Signal Transduction
and Targeted Therapy 2, no.
1 (2017): 1–7, https://doi.
org/10.
1038/sigtrans.
2016.
42.
1 (2017): 1–7, https://doi.
org/10.
1038/sigtrans.
2016.
42.
16.
“Contribution of EGFR and ErbB-3 Heterodimerization to the EGFR Mutation-Induced Gefitinib- and Erlotinib-Resistance in
“Contribution of EGFR and ErbB-3 Heterodimerization to the EGFR Mutation-Induced Gefitinib- and Erlotinib-Resistance in
Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Treatments,” PLOS ONE 10, no.
5 (May 20, 2015): e0128360,
5 (May 20, 2015): e0128360,
https://doi.
org/10.
1371/journal.
pone.
0128360.
org/10.
1371/journal.
pone.
0128360.
17.
H.
Harjunpää and C.
Guillerey, “TIGIT as an Emerging Immune Checkpoint,” Clinical & Experimental Immunology 200, no.
2
H.
Harjunpää and C.
Guillerey, “TIGIT as an Emerging Immune Checkpoint,” Clinical & Experimental Immunology 200, no.
2
(2020): 108–19, https://doi.
org/10.
1111/cei.
13407.
org/10.
1111/cei.
13407.
18.
Wenting Zhang et al.
, “Advances in Anti-Tumor Treatments Targeting the CD47/SIRPα Axis,” Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020),
Wenting Zhang et al.
, “Advances in Anti-Tumor Treatments Targeting the CD47/SIRPα Axis,” Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020),
https://doi.
org/10.
3389/fimmu.
2020.
00018.
org/10.
3389/fimmu.
2020.
00018.
19.
Zatloukalová et al.
, “[The Role of PD-1/PD-L1 Signaling Pathway in Antitumor Immune Response].
”
Zatloukalová et al.
, “[The Role of PD-1/PD-L1 Signaling Pathway in Antitumor Immune Response].
”
20.
Theresa L.
Whiteside and Ronald B.
Heberman, “Antitumor Effector Cells in Humans,” Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine.
6th Edition,
Theresa L.
Whiteside and Ronald B.
Heberman, “Antitumor Effector Cells in Humans,” Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine.
6th Edition,
2003, https:// https:// 21.
“TIGIT - an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics,” accessed March 29, 2021,
“TIGIT - an Overview | ScienceDirect Topics,” accessed March 29, 2021,
https:// 22.
Fanqiao Meng et al.
, “Overexpression of TIGIT in NK and T Cells Contributes to Tumor Immune Escape in Myelodysplastic
Fanqiao Meng et al.
, “Overexpression of TIGIT in NK and T Cells Contributes to Tumor Immune Escape in Myelodysplastic
Syndromes,” Frontiers in Oncology 10 (2020), https://doi.
org/10.
3389/fonc.
2020.
01595.
org/10.
3389/fonc.
2020.
01595.
23.
Xiaowan Yin et al.
, “Expression of the Inhibitory Receptor TIGIT Is Up-Regulated Specifically on NK Cells With CD226 Activating
Xiaowan Yin et al.
, “Expression of the Inhibitory Receptor TIGIT Is Up-Regulated Specifically on NK Cells With CD226 Activating
Receptor From HIV-Infected Individuals,” Frontiers in Immunology 9 (2018), https://doi.
org/10.
3389/fimmu.
2018.
02341
org/10.
3389/fimmu.
2018.
02341