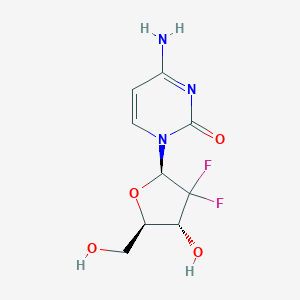
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Editor’s note iNature is China’s largest academic official account.
It is jointly created by the doctoral team of Tsinghua University, Harvard University, Chinese Academy of Sciences and other units.
The iNature Talent Official Account is now launched, focusing on talent recruitment, academic progress, scientific research information, interested parties can Long press or scan the QR code below to follow us
.
Recent studies by iNature have shown that circular RNA (circRNA) plays an important role in the occurrence and development of a variety of cancers including breast cancer (BC)
.
However, the potential functions of most circRNAs and the molecular mechanisms of BC progression are still elusive
.
On June 11, 2021, the Chen Junxia team of Chongqing Medical University published an online study titled "The circACTN4 interacts with FUBP1 to promote tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer by regulating the expression of proto-oncogene MYC" in Molecular Cancer (IF=15.
30) The paper, the study found that CircACTN4 is significantly up-regulated in breast cancer tissues and cells, and its expression is related to the clinical stage and poor prognosis of BC patients
.
The ectopic expression of circACTN4 significantly promoted the growth, invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
.
Knockout of circACTN4 showed the opposite effect
.
CircACTN4 is mainly distributed in the nucleus
.
Further mechanism studies have proved that circACTN4 can competitively bind with FUBP1 and prevent FUBP1 from binding to FIR, thereby activating MYC transcription and promoting tumor progression in breast cancer
.
In addition, the study found that upstream transcription factor 2 (USF2) may promote the biogenesis of circACTN4
.
In summary, the results of this study reveal a key mechanism that USF2-mediated circACTN4 may interact with FUBP1 to promote the occurrence and development of breast cancer by enhancing the expression of MYC
.
CircACTN4 may become a new potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer
.
Breast cancer is the malignant tumor with the highest incidence of women in the world
.
In 2018, approximately 2.
1 million cases of breast cancer were newly diagnosed globally, accounting for approximately 25% of all female malignant tumor cases
.
Although the early detection and effective systemic treatment of breast cancer have improved, it is still the leading cause of cancer deaths in women worldwide
.
Therefore, there is an urgent need to find new therapeutic targets and strategies for breast cancer
.
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a new type of RNA that has been widely discovered in various species through high-throughput sequencing in recent years
.
circRNA is a covalently closed single-stranded transcript, produced by reverse splicing of pre-mRNA, without 5'cap and 3'tail
.
Due to the covalent loop structure, circRNA is resistant to RNA exonuclease and is more stable than linear RNA
.
circRNAs reveal the disease-specific and developmental stage-specific characteristics under different pathological conditions, indicating that circRNAs can be used as new potential biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment
.
Recent studies have shown that circRNAs have important potential roles in regulating gene expression
.
circRNA performs its functions, including as miRNA sponges, RNA binding protein scaffolds, RNA alternative splicing (AS) intermediates, protein translation templates and transcription regulators
.
However, the interaction between circRNAs and proteins has been rarely studied in human cancers
.
More and more evidences show that dysregulated circRNA is involved in the development of various cancers
.
The most commonly reported mechanism of circRNAs can be used as miRNA sponges to reduce the inhibition of miRNA targeted gene expression
.
In breast cancer, circRNAs such as circRNA_0006528, circRAD18, circHMCU and circRNF20 have powerful potential in regulating cell proliferation, migration, metabolism and tumor progression.
Their expression is related to high TNM staging and prognosis
.
Recent studies have reported that circRNAs can interact with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) to perform biological functions
.
For example, the circular RNA CDR1as can directly bind to the p53 DBD domain, thereby disrupting the formation of the p53/MDM2 complex to inhibit glioma formation
.
Circ0005276 binds to FUS to transcriptionally activate XIAP, increasing the proliferation and mobility of prostate cancer cells
.
The RNA binding protein RBM3 regulates the production of circular RNA SCD-circRNA 2 to promote cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma
.
However, the interaction and relationship between circRNA and protein in breast cancer are still unknown
.
FUBP1 is a multifunctional DNA and RNA binding protein involved in the cellular processes of transcription, translation and RNA splicing
.
It is well known that FUBP1 can bind to the FUSE upstream of the c-MYC promoter, recruit and activate the transcription factor TFIIH, thereby promoting the transcription of the c-myc gene
.
FUBP1 may also bind to FBP Interaction Inhibitor (FIR), form an inhibitory complex with FUSE and TFIIH, and inhibit c-MYC transcription
.
The interaction of FUSE, FUBP1 and FIR in this molecular mechanism can fine-tune c-myc transcription in real time
.
Overexpression of FUBP1 has been found in many cancers, and it leads to dysregulation of targets including MYC oncogenes
.
Studies have shown that the expression of FUBP1 and its target MYC in breast cancer tissues is higher than that in adjacent normal tissues
.
According to reports, lncRNA SNHG1 can directly interact with the central domain of FUBP1 to resist the binding between FIR and FUBP1, thereby regulating the transcription of the oncogene MYC and promoting cancer development
.
So far, the association between circRNA and FUBP1 has not been explored
.
In this study, a circRNA RNA microarray was performed and the expression profile of circRNA in breast cancer tissues was displayed
.
Then focused on the novel circRNA circACTN4 (hsa_circ_0050900) derived from the ACTN4 gene and studied its biological functions and potential molecular mechanisms in the development of breast cancer
.
The results of the study show that circACTN4 is highly expressed in breast cancer tissues and cells, and is positively correlated with advanced tumor staging and poor prognosis
.
In addition, the study proved that USF2 can promote the production of circACTN4
.
Functional studies have shown that circACTN4 can enhance the growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells
.
Further mechanism studies have shown that circACTN4 can competitively bind to FUBP1 and block the binding of FUBP1 to FIR, thereby promoting the transcription of MYC and the development of breast cancer
.
In conclusion, the findings indicate that circACTN4 may become a new therapeutic target and a promising prognostic biomarker for breast cancer
.
Reference message: https://molecular-cancer.
biomedcentral.
com/articles/10.
1186/s12943-021-01383-x
It is jointly created by the doctoral team of Tsinghua University, Harvard University, Chinese Academy of Sciences and other units.
The iNature Talent Official Account is now launched, focusing on talent recruitment, academic progress, scientific research information, interested parties can Long press or scan the QR code below to follow us
.
Recent studies by iNature have shown that circular RNA (circRNA) plays an important role in the occurrence and development of a variety of cancers including breast cancer (BC)
.
However, the potential functions of most circRNAs and the molecular mechanisms of BC progression are still elusive
.
On June 11, 2021, the Chen Junxia team of Chongqing Medical University published an online study titled "The circACTN4 interacts with FUBP1 to promote tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer by regulating the expression of proto-oncogene MYC" in Molecular Cancer (IF=15.
30) The paper, the study found that CircACTN4 is significantly up-regulated in breast cancer tissues and cells, and its expression is related to the clinical stage and poor prognosis of BC patients
.
The ectopic expression of circACTN4 significantly promoted the growth, invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
.
Knockout of circACTN4 showed the opposite effect
.
CircACTN4 is mainly distributed in the nucleus
.
Further mechanism studies have proved that circACTN4 can competitively bind with FUBP1 and prevent FUBP1 from binding to FIR, thereby activating MYC transcription and promoting tumor progression in breast cancer
.
In addition, the study found that upstream transcription factor 2 (USF2) may promote the biogenesis of circACTN4
.
In summary, the results of this study reveal a key mechanism that USF2-mediated circACTN4 may interact with FUBP1 to promote the occurrence and development of breast cancer by enhancing the expression of MYC
.
CircACTN4 may become a new potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer
.
Breast cancer is the malignant tumor with the highest incidence of women in the world
.
In 2018, approximately 2.
1 million cases of breast cancer were newly diagnosed globally, accounting for approximately 25% of all female malignant tumor cases
.
Although the early detection and effective systemic treatment of breast cancer have improved, it is still the leading cause of cancer deaths in women worldwide
.
Therefore, there is an urgent need to find new therapeutic targets and strategies for breast cancer
.
Circular RNA (circRNA) is a new type of RNA that has been widely discovered in various species through high-throughput sequencing in recent years
.
circRNA is a covalently closed single-stranded transcript, produced by reverse splicing of pre-mRNA, without 5'cap and 3'tail
.
Due to the covalent loop structure, circRNA is resistant to RNA exonuclease and is more stable than linear RNA
.
circRNAs reveal the disease-specific and developmental stage-specific characteristics under different pathological conditions, indicating that circRNAs can be used as new potential biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment
.
Recent studies have shown that circRNAs have important potential roles in regulating gene expression
.
circRNA performs its functions, including as miRNA sponges, RNA binding protein scaffolds, RNA alternative splicing (AS) intermediates, protein translation templates and transcription regulators
.
However, the interaction between circRNAs and proteins has been rarely studied in human cancers
.
More and more evidences show that dysregulated circRNA is involved in the development of various cancers
.
The most commonly reported mechanism of circRNAs can be used as miRNA sponges to reduce the inhibition of miRNA targeted gene expression
.
In breast cancer, circRNAs such as circRNA_0006528, circRAD18, circHMCU and circRNF20 have powerful potential in regulating cell proliferation, migration, metabolism and tumor progression.
Their expression is related to high TNM staging and prognosis
.
Recent studies have reported that circRNAs can interact with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) to perform biological functions
.
For example, the circular RNA CDR1as can directly bind to the p53 DBD domain, thereby disrupting the formation of the p53/MDM2 complex to inhibit glioma formation
.
Circ0005276 binds to FUS to transcriptionally activate XIAP, increasing the proliferation and mobility of prostate cancer cells
.
The RNA binding protein RBM3 regulates the production of circular RNA SCD-circRNA 2 to promote cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma
.
However, the interaction and relationship between circRNA and protein in breast cancer are still unknown
.
FUBP1 is a multifunctional DNA and RNA binding protein involved in the cellular processes of transcription, translation and RNA splicing
.
It is well known that FUBP1 can bind to the FUSE upstream of the c-MYC promoter, recruit and activate the transcription factor TFIIH, thereby promoting the transcription of the c-myc gene
.
FUBP1 may also bind to FBP Interaction Inhibitor (FIR), form an inhibitory complex with FUSE and TFIIH, and inhibit c-MYC transcription
.
The interaction of FUSE, FUBP1 and FIR in this molecular mechanism can fine-tune c-myc transcription in real time
.
Overexpression of FUBP1 has been found in many cancers, and it leads to dysregulation of targets including MYC oncogenes
.
Studies have shown that the expression of FUBP1 and its target MYC in breast cancer tissues is higher than that in adjacent normal tissues
.
According to reports, lncRNA SNHG1 can directly interact with the central domain of FUBP1 to resist the binding between FIR and FUBP1, thereby regulating the transcription of the oncogene MYC and promoting cancer development
.
So far, the association between circRNA and FUBP1 has not been explored
.
In this study, a circRNA RNA microarray was performed and the expression profile of circRNA in breast cancer tissues was displayed
.
Then focused on the novel circRNA circACTN4 (hsa_circ_0050900) derived from the ACTN4 gene and studied its biological functions and potential molecular mechanisms in the development of breast cancer
.
The results of the study show that circACTN4 is highly expressed in breast cancer tissues and cells, and is positively correlated with advanced tumor staging and poor prognosis
.
In addition, the study proved that USF2 can promote the production of circACTN4
.
Functional studies have shown that circACTN4 can enhance the growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells
.
Further mechanism studies have shown that circACTN4 can competitively bind to FUBP1 and block the binding of FUBP1 to FIR, thereby promoting the transcription of MYC and the development of breast cancer
.
In conclusion, the findings indicate that circACTN4 may become a new therapeutic target and a promising prognostic biomarker for breast cancer
.
Reference message: https://molecular-cancer.
biomedcentral.
com/articles/10.
1186/s12943-021-01383-x