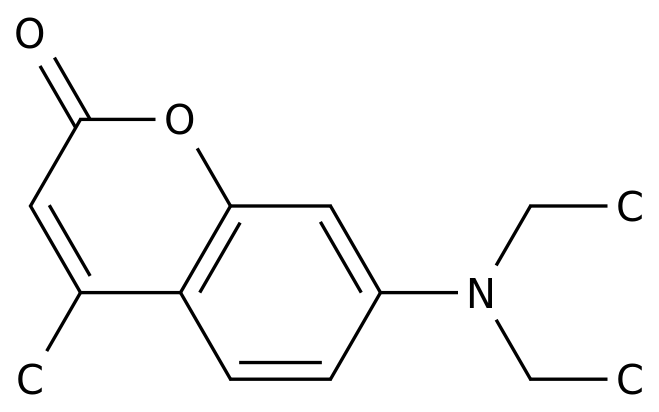
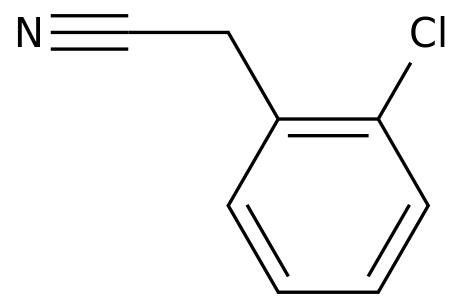
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Achieving high selectivity of methane to methanol under mild conditions Sinochem News.
Recently, researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China designed and constructed a gold single-atom catalyst Au1/BP supported on black phosphorus, which achieved high selectivity of methane under mild conditions Oxidation to methanol.
Oxygen is used as the oxidant to realize the selective oxidation of methane to methanol, which is not only environmentally friendly, but also has atomic economy.
However, the methane molecule has a high degree of tetrahedral symmetry, and its carbon-hydrogen bonds are difficult to activate.
At the same time, the partial oxidation products of methane also have the problem of being easily over-oxidized to carbon dioxide.
Therefore, the activation and directional conversion of methane is hailed as the "Holy Grail" of catalysis and even chemistry.
The study found that under light conditions, with oxygen as the oxidant, the Au1/BP catalyst can catalyze the partial oxidation of methane to methanol in an aqueous solution, and the methanol selectivity is greater than 99%.
Further mechanism studies have shown that the oxygen in methanol generated under light conditions can come from either water or oxygen.
Researchers explored the selectivity of the reaction through theoretical calculations.
It was found that on the surface of the Au1/BP catalyst, the first hydrogenation of methane to form CH3? is very easy, which is an exothermic reaction, while the continued dehydrogenation of CH3? is an endothermic reaction.
Therefore, the Au1/BP catalyst can stabilize CH3? and suppress excessive dehydrogenation.
Moreover, the energy barrier for methanol to be further oxidized is much higher than the apparent activation energy of methane activation and methanol desorption.
The methanol produced by methane oxidation is more likely to desorb from the catalyst surface into the solution instead of being over-oxidized.
The research results revealed the activation mechanism of oxygen and methane during the selective oxidation of methane, and provided a new understanding of the role of water in the reaction process, and provided a new idea for the design of a catalyst for highly selective conversion of methane.
Recently, researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China designed and constructed a gold single-atom catalyst Au1/BP supported on black phosphorus, which achieved high selectivity of methane under mild conditions Oxidation to methanol.
Oxygen is used as the oxidant to realize the selective oxidation of methane to methanol, which is not only environmentally friendly, but also has atomic economy.
However, the methane molecule has a high degree of tetrahedral symmetry, and its carbon-hydrogen bonds are difficult to activate.
At the same time, the partial oxidation products of methane also have the problem of being easily over-oxidized to carbon dioxide.
Therefore, the activation and directional conversion of methane is hailed as the "Holy Grail" of catalysis and even chemistry.
The study found that under light conditions, with oxygen as the oxidant, the Au1/BP catalyst can catalyze the partial oxidation of methane to methanol in an aqueous solution, and the methanol selectivity is greater than 99%.
Further mechanism studies have shown that the oxygen in methanol generated under light conditions can come from either water or oxygen.
Researchers explored the selectivity of the reaction through theoretical calculations.
It was found that on the surface of the Au1/BP catalyst, the first hydrogenation of methane to form CH3? is very easy, which is an exothermic reaction, while the continued dehydrogenation of CH3? is an endothermic reaction.
Therefore, the Au1/BP catalyst can stabilize CH3? and suppress excessive dehydrogenation.
Moreover, the energy barrier for methanol to be further oxidized is much higher than the apparent activation energy of methane activation and methanol desorption.
The methanol produced by methane oxidation is more likely to desorb from the catalyst surface into the solution instead of being over-oxidized.
The research results revealed the activation mechanism of oxygen and methane during the selective oxidation of methane, and provided a new understanding of the role of water in the reaction process, and provided a new idea for the design of a catalyst for highly selective conversion of methane.




![disodium 4,4'-bis[[4-anilino-6-[(2-carbamoylethyl)(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-1,3,5,-triazin-2-yl]amino]stilbene-2,2'-disulphonate CAS NO 27344-06-5](https://file.echemi.com/fileManage/upload/cas/77/e1abc71f-648d-403c-93fe-69b5c9401d56.gif)