-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
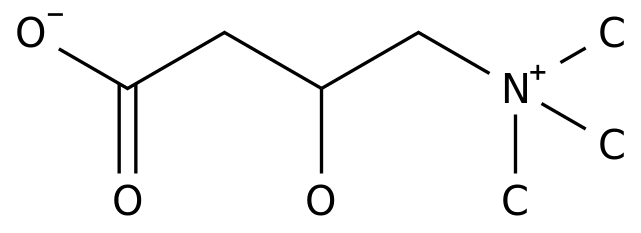
In September 2018, the multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor drug LENVIMA® (lenvatinib mesylate) was approved in China for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma that has not been treated with systemic drugs, breaking my country In ten years, there was only sorafenib as a targeted drug.
Since it was approved for clinical application, the clinical efficacy of lenvatinib mesylate (hereinafter referred to as "lenvatinib") has been widely affirmed.
The higher objective tumor response rate (ORR), longer disease progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) shown by its treatment of Chinese liver cancer patients compared to sorafenib have been verified in subsequent clinical practice .
The combined treatment of lenvatinib and PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors brought an unprecedented 46% ORR (mRECIST standard).
Such a good anti-tumor effect may bring an unprecedented "revolution" to the treatment of advanced liver cancer in my country, change the concept and treatment pattern of liver cancer, and bring dawn to the five-year survival rate of patients with advanced liver cancer in my country.
On March 1 this year, the 2020 new version of the "National Basic Medical Insurance, Work Injury Insurance and Maternity Insurance Drug Catalog" was officially launched nationwide.
The price of lenvatinib is reduced by 80.
7% after being included in the medical insurance, and the single box price is 3,240 yuan; based on the 70% medical insurance reimbursement ratio, the patient pays less than 1,000 yuan per box of the drug; for patients weighing less than 60 kg, the annual payment is 2.
3 About 10,000 yuan, and the annual payment for patients weighing more than 60 kg is 35,000 yuan.
The substantial price reduction of lenvatinib means that more liver cancer patients can be benefited and patients are more likely to complete the course of treatment as prescribed by the doctor.
➤ With the rapid changes in the clinical practice of liver cancer treatment in China, which types of patients benefit the most from the entry of lenvatinib into medical insurance? ➤ How will it promote the clinical practice of systemic therapy combined with local therapy? ➤ What is the role of promoting the optimization of liver cancer treatment plans in different stages? Recently, this platform interviewed Professor Yang Jiamei, Director of the Special Needs Department of Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital.
Professor Yang Jiamei witnessed the beginning of my country's hepatobiliary surgery more than 60 years ago, and personally experienced the development and changes of my country's hepatobiliary surgery, and has rich clinical practice experience in hepatobiliary surgery.
In the face of this "change" brought about by liver cancer system therapy drugs, he also shared his personal views on how to be a hepatobiliary surgeon.
Reporter: Will lenvatinib become a basic drug for the treatment of advanced liver cancer after entering the medical insurance? Professor Yang Jiamei: In the current clinical practice of treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, prevention of recurrence of high-risk patients, and comprehensive treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, lenvatinib is the main targeted therapy drug and a basic drug for the systemic treatment of liver cancer.
At different stages of the development of advanced liver cancer and for patients with different conditions, this type of targeted drugs is gradually taking on the "heavy task" of basic medication.
In particular, lenvatinib has been verified by clinical practice for more than two years, its clinical efficacy is better than sorafenib, very serious side effects are less, and the patient's tolerance is better.
As the availability of medicines is greatly improved after the reimbursement of medical insurance, we will naturally position it as a basic treatment drug for the comprehensive treatment of middle and advanced liver cancer.
Reporter: How to position sorafenib in future clinical practice? Professor Yang Jiamei: Because of the limited anti-tumor efficacy of sorafenib, for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, lenvatinib is generally considered first, especially when the affordability of lenvatinib has been significantly improved.
There is no reason not to prefer lenvatinib.
When patients receiving lenvatinib have disease progression, consider trying sorafenib.
If it does not work, try other second-line therapies, such as regorafenib.
Reporter: After lenvatinib enters the medical insurance, which patients may benefit the most? Professor Yang Jiamei: For the majority of liver cancer patients in my country, it is good news that lenvatinib has entered the national medical insurance reimbursement list.
70%-80% of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in my country are in the middle or advanced stage when they are first diagnosed.
Some patients have difficulty in undergoing surgical resection because liver cancer has invaded peripheral blood vessels, compressed surrounding organs, or has extrahepatic metastases.
However, the development of systemic drugs represented by lenvatinib and PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the past two years, especially targeted and immunotherapy combined with local treatment methods, such as transhepatic arterial chemoembolization (TACE), or radiotherapy , Can reduce tumor burden, thereby helping to achieve tumor downgrading, so that some patients who were previously unresectable have the opportunity of surgical resection.
At present, surgical resection is still one of the important means to improve the long-term survival of liver cancer patients.
Therefore, the entry of lenvatinib into the medical insurance reimbursement list is a major good news for these patients, because they are now expected to obtain a longer survival period through the downstage and resection of liver cancer.
Reporter: How to formulate the course of systemic treatment for advanced liver cancer? Professor Yang Jiamei: For patients with advanced liver cancer, whether it is lenvatinib or PD-1 monoclonal antibody, or a combination of the two, it needs to be used all the time.
There is no evidence of medication time for reference.
For liver cancer patients who are expected to be resected after downgrading and transformation, we need to conduct regular evaluation through imaging and biochemical examinations.
If the tumor shows shrinkage or partial remission (PR), treatment can be continued until it can be surgically removed.
If a complete remission (CR) of imaging is achieved, my personal opinion is to continue medication and evaluate it after one year of treatment; if it is used for one year, the effect is very good and complete remission (CR) is achieved, then You can consider slowly stopping the drug for observation.
For patients with high-risk recurrence of liver cancer after surgery, lenvatinib is generally considered for a two-year course of treatment; if no signs of tumor recurrence are found after two years of treatment, you can try to stop the drug and observe closely.
If it is to give PD-1 monoclonal antibody treatment to prevent recurrence, my personal opinion is 4-6 courses.
Before lenvatinib and PD-1 monoclonal antibody entered the medical insurance reimbursement list, many such patients were often unable to complete the course of treatment due to economic reasons.
After March 1 this year, this situation should be greatly reduced.
Reporter: Do patients who have obtained CR through lenvatinib and other systemic drugs still need to be surgically removed? Professor Yang Jiamei: There is no definite answer yet, and clinical research is needed.
For example, for patients who have obtained CR but have not undergone surgical resection, we need to follow up for a long time to observe the survival period and compare with the survival period of patients undergoing surgical resection after transformation.
However, the current surgical resection is definitely the safest method, because the CR shown by imaging and biochemical indicators does not represent a complete remission (pCR) of the pathological tissue, and even the pCR does not mean that there is no residue in the tissue or blood.
Tumor cells.
Therefore, surgical resection should be carried out as far as possible, and anti-recurrence treatment should be continued after the operation, unless the patient is unwilling or is not suitable or cannot tolerate the operation for various reasons.
Reporter: In addition to the combination of lenvatinib and PD-1 monoclonal antibody, there are many other targeted and immunotherapeutic combinations to choose from.
How to consider the choice of these programs in the clinic? Professor Yang Jiamei: We need to be based on the efficacy , Side effects, economic affordability and convenience are comprehensively considered.
At present, we cannot judge which combination has better clinical performance, or which type of patient is more suitable.
Generally speaking, oral medication is more convenient, and compliance with intravenous infusion of medication will be better.
In addition, patients with a greater risk of bleeding should be careful when using anti-angiogenic drugs.
It is best to observe the presence of esophageal and gastric varices through gastrointestinal endoscopy.
If it reaches the third degree, it is best not to use anti-angiogenic drugs.
The affordability of drugs is also very important.
When the efficacy and safety are equal, drugs that enter the medical insurance reimbursement list are generally selected.
But for patients with liver cirrhosis with decompensated liver function, we must take special care, because for them, the fatal thing is not the tumor, but the cirrhosis.
Both large molecule and small molecule drugs will increase the burden on the liver, and these patients cannot withstand any blow to liver function, so the treatment of such patients is still very tricky.
Reporter: TACE is a common method for the treatment of advanced liver cancer.
In clinical practice, how can it be used in combination with system therapy? Professor Yang Jiamei: TACE still occupies a very important position in the comprehensive treatment of liver cancer.
For example, for some liver cancer patients who we think the operation is very difficult, or the operation risk is high, as long as the liver function is good, we will choose TACE treatment as the first choice.
The combination of TACE therapy and targeting and PD-1 monoclonal antibody can produce a synergistic effect, play an effect of 1+1 greater than 2, and significantly improve the survival benefit of patients.
If lenvatinib is used after TACE, or combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibody treatment at the same time, before starting treatment, I will definitely add platinum-based chemotherapy drugs or combined radiotherapy to release more exposed tumor antigens, thereby improving immunity The efficacy of treatment.
This kind of chemotherapy induction or radiotherapy induction is through continuous learning, thinking and summarizing.
Reporter: Can a hepatobiliary surgeon walk the rivers and lakes with only a knife? Professor Yang Jiamei: A surgeon cannot be a "swordsman", but a "surgeon".
It’s certainly not a good surgeon who can
go all over the world with a single knife.
A surgeon must have a comprehensive grasp of all aspects of knowledge, especially the perioperative management of surgery, including the entire management of the patient.
Only with multidisciplinary knowledge can he Improve the efficacy of surgery; otherwise, if only surgery is performed, and the understanding of medical treatment and perioperative treatment is insufficient, the efficacy of surgery will certainly not be very high; the most rigid indicators for evaluating the efficacy of surgery are the long-term survival rate and quality of life after surgery.
.
so, if a surgeon for perioperative knowledge is very poor, I think is definitely not a good surgeon.
by a knife travels certainly not a foreign scientist.
reporters: to become a qualified hepatobiliary surgeon What's the key? Professor Yang Jiamei: If you want to be an excellent surgeon, you must always remember to learn, that is, live and learn.
Medical knowledge is updated very quickly, basically one in five years.
Fan. If you can't keep up with the rhythm, you will be questioned if you use the knowledge ten years ago to talk about it.
Therefore, we must continue to learn, accept new ideas and concepts, develop new technologies, apply new research results, and integrate into the development trend of world medicine in order to become a qualified hepatobiliary surgeon in the new era.
Since it was approved for clinical application, the clinical efficacy of lenvatinib mesylate (hereinafter referred to as "lenvatinib") has been widely affirmed.
The higher objective tumor response rate (ORR), longer disease progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) shown by its treatment of Chinese liver cancer patients compared to sorafenib have been verified in subsequent clinical practice .
The combined treatment of lenvatinib and PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors brought an unprecedented 46% ORR (mRECIST standard).
Such a good anti-tumor effect may bring an unprecedented "revolution" to the treatment of advanced liver cancer in my country, change the concept and treatment pattern of liver cancer, and bring dawn to the five-year survival rate of patients with advanced liver cancer in my country.
On March 1 this year, the 2020 new version of the "National Basic Medical Insurance, Work Injury Insurance and Maternity Insurance Drug Catalog" was officially launched nationwide.
The price of lenvatinib is reduced by 80.
7% after being included in the medical insurance, and the single box price is 3,240 yuan; based on the 70% medical insurance reimbursement ratio, the patient pays less than 1,000 yuan per box of the drug; for patients weighing less than 60 kg, the annual payment is 2.
3 About 10,000 yuan, and the annual payment for patients weighing more than 60 kg is 35,000 yuan.
The substantial price reduction of lenvatinib means that more liver cancer patients can be benefited and patients are more likely to complete the course of treatment as prescribed by the doctor.
➤ With the rapid changes in the clinical practice of liver cancer treatment in China, which types of patients benefit the most from the entry of lenvatinib into medical insurance? ➤ How will it promote the clinical practice of systemic therapy combined with local therapy? ➤ What is the role of promoting the optimization of liver cancer treatment plans in different stages? Recently, this platform interviewed Professor Yang Jiamei, Director of the Special Needs Department of Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital.
Professor Yang Jiamei witnessed the beginning of my country's hepatobiliary surgery more than 60 years ago, and personally experienced the development and changes of my country's hepatobiliary surgery, and has rich clinical practice experience in hepatobiliary surgery.
In the face of this "change" brought about by liver cancer system therapy drugs, he also shared his personal views on how to be a hepatobiliary surgeon.
Reporter: Will lenvatinib become a basic drug for the treatment of advanced liver cancer after entering the medical insurance? Professor Yang Jiamei: In the current clinical practice of treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, prevention of recurrence of high-risk patients, and comprehensive treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, lenvatinib is the main targeted therapy drug and a basic drug for the systemic treatment of liver cancer.
At different stages of the development of advanced liver cancer and for patients with different conditions, this type of targeted drugs is gradually taking on the "heavy task" of basic medication.
In particular, lenvatinib has been verified by clinical practice for more than two years, its clinical efficacy is better than sorafenib, very serious side effects are less, and the patient's tolerance is better.
As the availability of medicines is greatly improved after the reimbursement of medical insurance, we will naturally position it as a basic treatment drug for the comprehensive treatment of middle and advanced liver cancer.
Reporter: How to position sorafenib in future clinical practice? Professor Yang Jiamei: Because of the limited anti-tumor efficacy of sorafenib, for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma, lenvatinib is generally considered first, especially when the affordability of lenvatinib has been significantly improved.
There is no reason not to prefer lenvatinib.
When patients receiving lenvatinib have disease progression, consider trying sorafenib.
If it does not work, try other second-line therapies, such as regorafenib.
Reporter: After lenvatinib enters the medical insurance, which patients may benefit the most? Professor Yang Jiamei: For the majority of liver cancer patients in my country, it is good news that lenvatinib has entered the national medical insurance reimbursement list.
70%-80% of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in my country are in the middle or advanced stage when they are first diagnosed.
Some patients have difficulty in undergoing surgical resection because liver cancer has invaded peripheral blood vessels, compressed surrounding organs, or has extrahepatic metastases.
However, the development of systemic drugs represented by lenvatinib and PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in the past two years, especially targeted and immunotherapy combined with local treatment methods, such as transhepatic arterial chemoembolization (TACE), or radiotherapy , Can reduce tumor burden, thereby helping to achieve tumor downgrading, so that some patients who were previously unresectable have the opportunity of surgical resection.
At present, surgical resection is still one of the important means to improve the long-term survival of liver cancer patients.
Therefore, the entry of lenvatinib into the medical insurance reimbursement list is a major good news for these patients, because they are now expected to obtain a longer survival period through the downstage and resection of liver cancer.
Reporter: How to formulate the course of systemic treatment for advanced liver cancer? Professor Yang Jiamei: For patients with advanced liver cancer, whether it is lenvatinib or PD-1 monoclonal antibody, or a combination of the two, it needs to be used all the time.
There is no evidence of medication time for reference.
For liver cancer patients who are expected to be resected after downgrading and transformation, we need to conduct regular evaluation through imaging and biochemical examinations.
If the tumor shows shrinkage or partial remission (PR), treatment can be continued until it can be surgically removed.
If a complete remission (CR) of imaging is achieved, my personal opinion is to continue medication and evaluate it after one year of treatment; if it is used for one year, the effect is very good and complete remission (CR) is achieved, then You can consider slowly stopping the drug for observation.
For patients with high-risk recurrence of liver cancer after surgery, lenvatinib is generally considered for a two-year course of treatment; if no signs of tumor recurrence are found after two years of treatment, you can try to stop the drug and observe closely.
If it is to give PD-1 monoclonal antibody treatment to prevent recurrence, my personal opinion is 4-6 courses.
Before lenvatinib and PD-1 monoclonal antibody entered the medical insurance reimbursement list, many such patients were often unable to complete the course of treatment due to economic reasons.
After March 1 this year, this situation should be greatly reduced.
Reporter: Do patients who have obtained CR through lenvatinib and other systemic drugs still need to be surgically removed? Professor Yang Jiamei: There is no definite answer yet, and clinical research is needed.
For example, for patients who have obtained CR but have not undergone surgical resection, we need to follow up for a long time to observe the survival period and compare with the survival period of patients undergoing surgical resection after transformation.
However, the current surgical resection is definitely the safest method, because the CR shown by imaging and biochemical indicators does not represent a complete remission (pCR) of the pathological tissue, and even the pCR does not mean that there is no residue in the tissue or blood.
Tumor cells.
Therefore, surgical resection should be carried out as far as possible, and anti-recurrence treatment should be continued after the operation, unless the patient is unwilling or is not suitable or cannot tolerate the operation for various reasons.
Reporter: In addition to the combination of lenvatinib and PD-1 monoclonal antibody, there are many other targeted and immunotherapeutic combinations to choose from.
How to consider the choice of these programs in the clinic? Professor Yang Jiamei: We need to be based on the efficacy , Side effects, economic affordability and convenience are comprehensively considered.
At present, we cannot judge which combination has better clinical performance, or which type of patient is more suitable.
Generally speaking, oral medication is more convenient, and compliance with intravenous infusion of medication will be better.
In addition, patients with a greater risk of bleeding should be careful when using anti-angiogenic drugs.
It is best to observe the presence of esophageal and gastric varices through gastrointestinal endoscopy.
If it reaches the third degree, it is best not to use anti-angiogenic drugs.
The affordability of drugs is also very important.
When the efficacy and safety are equal, drugs that enter the medical insurance reimbursement list are generally selected.
But for patients with liver cirrhosis with decompensated liver function, we must take special care, because for them, the fatal thing is not the tumor, but the cirrhosis.
Both large molecule and small molecule drugs will increase the burden on the liver, and these patients cannot withstand any blow to liver function, so the treatment of such patients is still very tricky.
Reporter: TACE is a common method for the treatment of advanced liver cancer.
In clinical practice, how can it be used in combination with system therapy? Professor Yang Jiamei: TACE still occupies a very important position in the comprehensive treatment of liver cancer.
For example, for some liver cancer patients who we think the operation is very difficult, or the operation risk is high, as long as the liver function is good, we will choose TACE treatment as the first choice.
The combination of TACE therapy and targeting and PD-1 monoclonal antibody can produce a synergistic effect, play an effect of 1+1 greater than 2, and significantly improve the survival benefit of patients.
If lenvatinib is used after TACE, or combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibody treatment at the same time, before starting treatment, I will definitely add platinum-based chemotherapy drugs or combined radiotherapy to release more exposed tumor antigens, thereby improving immunity The efficacy of treatment.
This kind of chemotherapy induction or radiotherapy induction is through continuous learning, thinking and summarizing.
Reporter: Can a hepatobiliary surgeon walk the rivers and lakes with only a knife? Professor Yang Jiamei: A surgeon cannot be a "swordsman", but a "surgeon".
It’s certainly not a good surgeon who can
go all over the world with a single knife.
A surgeon must have a comprehensive grasp of all aspects of knowledge, especially the perioperative management of surgery, including the entire management of the patient.
Only with multidisciplinary knowledge can he Improve the efficacy of surgery; otherwise, if only surgery is performed, and the understanding of medical treatment and perioperative treatment is insufficient, the efficacy of surgery will certainly not be very high; the most rigid indicators for evaluating the efficacy of surgery are the long-term survival rate and quality of life after surgery.
.
so, if a surgeon for perioperative knowledge is very poor, I think is definitely not a good surgeon.
by a knife travels certainly not a foreign scientist.
reporters: to become a qualified hepatobiliary surgeon What's the key? Professor Yang Jiamei: If you want to be an excellent surgeon, you must always remember to learn, that is, live and learn.
Medical knowledge is updated very quickly, basically one in five years.
Fan. If you can't keep up with the rhythm, you will be questioned if you use the knowledge ten years ago to talk about it.
Therefore, we must continue to learn, accept new ideas and concepts, develop new technologies, apply new research results, and integrate into the development trend of world medicine in order to become a qualified hepatobiliary surgeon in the new era.