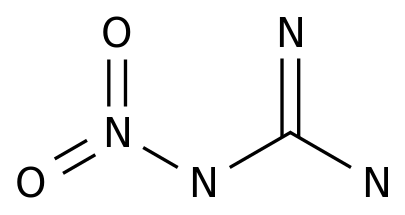
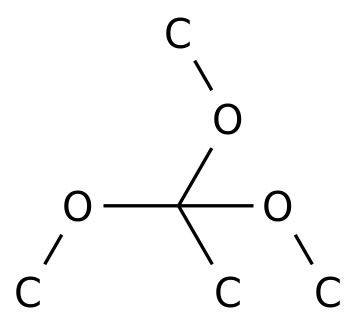
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Pesticides are something that farmers come into contact with in daily life, and they are mainly used to kill insects on crops
.
However, pesticide poisoning is also very common in poisoning and accidental death.
Generally, acute life-related poisoning is the most common, and it is not a small number of people who misuse or commit suicide in clinical practice
.
Pesticide poisoning caused by environmental pollution can also occur in production operations.
It is more common in pesticide factory production and packaging factories.
If farmers spray pesticides in the field or make pesticides and inspect and repair pesticide application tools The probability of pesticide skin infection is very high.
At this time, the pesticide will pass through the skin and respiratory tract, and then enter the human body, resulting in acute poisoning
.
In these processes of contact with pesticides, the amount of pesticides entering the human body exceeds the maximum tolerance of the human body to pesticides, which will affect the normal physiological functions of humans, causing physiological disorders and some pathological changes.
, Are manifestations of poisoning
.
1.
Common sense of first aid care for common pesticide poisoning How should pesticide poisoning be handled? First of all, according to the type of poisoning and the different dosages and ways of pesticides entering the human body, the damage caused to the human body and the impact on the parts of the body are also different
.
Some will only cause partial damage, some will affect the patient's entire body, and severely threaten the patient's life and health
.
Pesticide poisoning is divided into three degrees: mild, moderate, and severe
.
According to the speed, it is divided into acute, subacute and chronic.
The following introduces some common knowledge of emergency care after pesticide poisoning
.
First of all, the first type is organophosphorus pesticides, such as the common dichlorvos, dimethoate, ethion, etc.
are organophosphorus pesticides
.
It is highly fat-soluble and aerosolizes during the spraying process.
It is especially easy to enter the human body through the skin and be inhaled by the respiratory tract, while the absorption of the digestive tract is mostly caused by mistaken ingestion
.
Poisoned people will have slow heart rate, drop in blood pressure, nausea and vomiting
.
In severe cases, it can cause pulmonary edema, brain edema, slurred speech, insomnia, or lethargy
.
After being poisoned, the patient needs to be removed from the scene in time, and the contaminated clothing should be removed in time
.
Patients with oral poisoning need to induce vomiting and gastric lavage in time.
Use clean water or 1:5,000 potassium permanganate solution or 2% sodium bicarbonate solution to lavage the stomach, but for thion and trichlorfon poisoning Disabled
.
You can also use a lot of normal saline, soapy water or clean water to wash the patient's body, pay attention to prohibit the use of trichlorfon poisoning
.
For eye and external auditory canal contamination, you can also use clean water and soapy water for about 10 minutes, and then use 1 to 2 drops of 1% atropine
.
Patients who have difficulty breathing need to be treated with oxygen in a timely manner, and tracheotomy can be performed when necessary
.
Antidote can also be used, and patients with cerebral edema should be treated for dehydration in time
.
The second type is that the most commonly used organochlorine pesticides are hexachlorobenzene and chlorobenzene chloroethane.
The toxicity of the latter is weaker than the former.
It is more common to be inadvertently ingested or poisoned through the respiratory tract, and the patient will become mentally ill.
Lack of vibration, dizziness, convulsions, heart palpitations, epileptic seizures, coma, severe liver damage and even death
.
First aid measures are to leave the scene first, and those who get into the eyes can use 2% sodium bicarbonate solution to rinse
.
Oral patients use 2% sodium bicarbonate solution for gastric lavage, and then use magnesium sulfate for catharsis
.
People with convulsions need to prevent the patient from biting their tongue.
Patients with respiratory failure should be mechanically ventilated when necessary, and adrenaline should not be used
.
Organonitrogen pesticide poisoning, patients will have headaches, fatigue, frequent urination, urgency and other symptoms.
First aid measures are the same as above.
Adrenal cortex hormones and hemostatic drugs can be given to patients with hematuria.
Potassium supplements should be given to patients with hypokalemia.
According to the patient's performance Perform oxygen inhalation, fluid replacement and other treatments
.
The remaining organosulfur pesticide poisoning and fluoroacetamide poisoning are the same as the above-mentioned pesticide poisoning treatment process
.
That is to say, in the common pesticide poisoning, the first thing is to leave the scene, choose the correct treatment method and prescribe the right medicine according to the way of poisoning, and timely treatment is the key. .
2.
Pesticide poisoning nursing tips 1.
Routine nursing measures (1) Closely observe the changes in the condition of pesticide poisoning patients, and apply ECG monitoring equipment to them so that medical staff can control the changes in their vital signs in real time, and prepare various rescue drugs and Related equipment
.
(2) Record the patient's daily intake in detail.
Because pesticide poisoning patients are in frequent vomiting, sweating, gastric lavage and other links, the body will lose a lot of water, which makes the patient very prone to dehydration, body water and electrolyte disorders, etc.
, and it is necessary to treat the patient Rehydration support measures should be taken in time, but the rehydration speed should not be too fast to avoid complications of pulmonary edema
.
(3) Diet care.
Patients who are usually poisoned by pesticides need to undergo gastric lavage, vomiting and other treatments.
Patients need to fast for 1 to 2 days so that doctors can perform gastric lavage and thoroughly remove pesticide residues in the stomach
.
Therefore, when the patient resumes his diet, he needs to gradually transition from a liquid diet to a semi-liquid diet, and then switch to a soft food, so that the patient can eat normally
.
2.
Special nursing care of comatose patients: some patients with deep pesticide poisoning will have symptoms such as coma, lethargy, and irritability.
Special personnel are required to look after and observe the patient's breathing, consciousness, pulse, muscle tremor, and oral and nasal secretion.
In order to ensure that the patient’s respiratory tract is always in a smooth state
.
For patients who need to stay in bed for a long time to recover, it is necessary to actively prevent the occurrence of pressure ulcers, turn them over and pat their backs regularly, so as to improve the quality of life of patients; Care of patients with fever: When patients with pesticide poisoning have fever symptoms, they need to take the patient's body temperature Real-time monitoring is carried out to facilitate the timely treatment of patients with high fever, reduce the occurrence of complications, and ensure the patient's physical health; patients need to be treated with catheterization care after hospitalization, and the indwelling catheter is convenient for medical staff to observe the amount of urine in the patient.
Color and nature to avoid urinary tract infections
.
3.
In the psychological care part, patients who are poisoned by pesticides due to their own factors usually do not cooperate with the doctor's various treatment measures
.
Family members need to be patiently persuaded to help patients get rid of negative emotions, establish confidence in disease recovery and a positive attitude, which will help patients recover quickly
.
3.
Tips for preventing pesticide poisoning.
Pesticides can help farmers and planters kill pests and increase crop yields
.
However, improper use by some planters can cause pesticide poisoning
.
Therefore, in order to effectively prevent pesticide poisoning, growers need to pay attention to the following points in their daily work: Weakness, older age, pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and minors cannot undertake the work of pesticide management and use; pesticide needs Put it in a special locked place, and have a special person responsible for pesticide storage, and formulate a strict pesticide use, storage and purchase system to fundamentally reduce the probability of pesticide poisoning; the configuration of pesticides needs to be handled by a special person to operate it Personnel need to be equipped with relevant protective tools and stay away from daily life and water sources to avoid being absorbed by others or polluting water sources during the pesticide preparation process; when agricultural planters use pesticides, they need to strictly follow the operating specifications and wash themselves after work.
Protection operations, so as not to bring pesticide pollution back to the living area and affect the quality of daily life of the staff
.
Pesticide poisoning generally develops fiercely and progresses rapidly, and most of the pesticides are compound preparations with strong toxicity, which also brings a lot of trouble to the rescue work
.
After the occurrence of pesticide poisoning, some first aid measures can effectively increase the success rate of rescue of patients with pesticide poisoning, and to a certain extent save the lives of patients
.
It also reminds farmers to take protective measures when spraying crops with pesticides to reduce contact with pesticides, and place pesticides such dangerous goods safely to prevent accidental ingestion
.
It is also beneficial to master pesticide first aid knowledge in daily life
.
.
However, pesticide poisoning is also very common in poisoning and accidental death.
Generally, acute life-related poisoning is the most common, and it is not a small number of people who misuse or commit suicide in clinical practice
.
Pesticide poisoning caused by environmental pollution can also occur in production operations.
It is more common in pesticide factory production and packaging factories.
If farmers spray pesticides in the field or make pesticides and inspect and repair pesticide application tools The probability of pesticide skin infection is very high.
At this time, the pesticide will pass through the skin and respiratory tract, and then enter the human body, resulting in acute poisoning
.
In these processes of contact with pesticides, the amount of pesticides entering the human body exceeds the maximum tolerance of the human body to pesticides, which will affect the normal physiological functions of humans, causing physiological disorders and some pathological changes.
, Are manifestations of poisoning
.
1.
Common sense of first aid care for common pesticide poisoning How should pesticide poisoning be handled? First of all, according to the type of poisoning and the different dosages and ways of pesticides entering the human body, the damage caused to the human body and the impact on the parts of the body are also different
.
Some will only cause partial damage, some will affect the patient's entire body, and severely threaten the patient's life and health
.
Pesticide poisoning is divided into three degrees: mild, moderate, and severe
.
According to the speed, it is divided into acute, subacute and chronic.
The following introduces some common knowledge of emergency care after pesticide poisoning
.
First of all, the first type is organophosphorus pesticides, such as the common dichlorvos, dimethoate, ethion, etc.
are organophosphorus pesticides
.
It is highly fat-soluble and aerosolizes during the spraying process.
It is especially easy to enter the human body through the skin and be inhaled by the respiratory tract, while the absorption of the digestive tract is mostly caused by mistaken ingestion
.
Poisoned people will have slow heart rate, drop in blood pressure, nausea and vomiting
.
In severe cases, it can cause pulmonary edema, brain edema, slurred speech, insomnia, or lethargy
.
After being poisoned, the patient needs to be removed from the scene in time, and the contaminated clothing should be removed in time
.
Patients with oral poisoning need to induce vomiting and gastric lavage in time.
Use clean water or 1:5,000 potassium permanganate solution or 2% sodium bicarbonate solution to lavage the stomach, but for thion and trichlorfon poisoning Disabled
.
You can also use a lot of normal saline, soapy water or clean water to wash the patient's body, pay attention to prohibit the use of trichlorfon poisoning
.
For eye and external auditory canal contamination, you can also use clean water and soapy water for about 10 minutes, and then use 1 to 2 drops of 1% atropine
.
Patients who have difficulty breathing need to be treated with oxygen in a timely manner, and tracheotomy can be performed when necessary
.
Antidote can also be used, and patients with cerebral edema should be treated for dehydration in time
.
The second type is that the most commonly used organochlorine pesticides are hexachlorobenzene and chlorobenzene chloroethane.
The toxicity of the latter is weaker than the former.
It is more common to be inadvertently ingested or poisoned through the respiratory tract, and the patient will become mentally ill.
Lack of vibration, dizziness, convulsions, heart palpitations, epileptic seizures, coma, severe liver damage and even death
.
First aid measures are to leave the scene first, and those who get into the eyes can use 2% sodium bicarbonate solution to rinse
.
Oral patients use 2% sodium bicarbonate solution for gastric lavage, and then use magnesium sulfate for catharsis
.
People with convulsions need to prevent the patient from biting their tongue.
Patients with respiratory failure should be mechanically ventilated when necessary, and adrenaline should not be used
.
Organonitrogen pesticide poisoning, patients will have headaches, fatigue, frequent urination, urgency and other symptoms.
First aid measures are the same as above.
Adrenal cortex hormones and hemostatic drugs can be given to patients with hematuria.
Potassium supplements should be given to patients with hypokalemia.
According to the patient's performance Perform oxygen inhalation, fluid replacement and other treatments
.
The remaining organosulfur pesticide poisoning and fluoroacetamide poisoning are the same as the above-mentioned pesticide poisoning treatment process
.
That is to say, in the common pesticide poisoning, the first thing is to leave the scene, choose the correct treatment method and prescribe the right medicine according to the way of poisoning, and timely treatment is the key. .
2.
Pesticide poisoning nursing tips 1.
Routine nursing measures (1) Closely observe the changes in the condition of pesticide poisoning patients, and apply ECG monitoring equipment to them so that medical staff can control the changes in their vital signs in real time, and prepare various rescue drugs and Related equipment
.
(2) Record the patient's daily intake in detail.
Because pesticide poisoning patients are in frequent vomiting, sweating, gastric lavage and other links, the body will lose a lot of water, which makes the patient very prone to dehydration, body water and electrolyte disorders, etc.
, and it is necessary to treat the patient Rehydration support measures should be taken in time, but the rehydration speed should not be too fast to avoid complications of pulmonary edema
.
(3) Diet care.
Patients who are usually poisoned by pesticides need to undergo gastric lavage, vomiting and other treatments.
Patients need to fast for 1 to 2 days so that doctors can perform gastric lavage and thoroughly remove pesticide residues in the stomach
.
Therefore, when the patient resumes his diet, he needs to gradually transition from a liquid diet to a semi-liquid diet, and then switch to a soft food, so that the patient can eat normally
.
2.
Special nursing care of comatose patients: some patients with deep pesticide poisoning will have symptoms such as coma, lethargy, and irritability.
Special personnel are required to look after and observe the patient's breathing, consciousness, pulse, muscle tremor, and oral and nasal secretion.
In order to ensure that the patient’s respiratory tract is always in a smooth state
.
For patients who need to stay in bed for a long time to recover, it is necessary to actively prevent the occurrence of pressure ulcers, turn them over and pat their backs regularly, so as to improve the quality of life of patients; Care of patients with fever: When patients with pesticide poisoning have fever symptoms, they need to take the patient's body temperature Real-time monitoring is carried out to facilitate the timely treatment of patients with high fever, reduce the occurrence of complications, and ensure the patient's physical health; patients need to be treated with catheterization care after hospitalization, and the indwelling catheter is convenient for medical staff to observe the amount of urine in the patient.
Color and nature to avoid urinary tract infections
.
3.
In the psychological care part, patients who are poisoned by pesticides due to their own factors usually do not cooperate with the doctor's various treatment measures
.
Family members need to be patiently persuaded to help patients get rid of negative emotions, establish confidence in disease recovery and a positive attitude, which will help patients recover quickly
.
3.
Tips for preventing pesticide poisoning.
Pesticides can help farmers and planters kill pests and increase crop yields
.
However, improper use by some planters can cause pesticide poisoning
.
Therefore, in order to effectively prevent pesticide poisoning, growers need to pay attention to the following points in their daily work: Weakness, older age, pregnant women, breastfeeding women, and minors cannot undertake the work of pesticide management and use; pesticide needs Put it in a special locked place, and have a special person responsible for pesticide storage, and formulate a strict pesticide use, storage and purchase system to fundamentally reduce the probability of pesticide poisoning; the configuration of pesticides needs to be handled by a special person to operate it Personnel need to be equipped with relevant protective tools and stay away from daily life and water sources to avoid being absorbed by others or polluting water sources during the pesticide preparation process; when agricultural planters use pesticides, they need to strictly follow the operating specifications and wash themselves after work.
Protection operations, so as not to bring pesticide pollution back to the living area and affect the quality of daily life of the staff
.
Pesticide poisoning generally develops fiercely and progresses rapidly, and most of the pesticides are compound preparations with strong toxicity, which also brings a lot of trouble to the rescue work
.
After the occurrence of pesticide poisoning, some first aid measures can effectively increase the success rate of rescue of patients with pesticide poisoning, and to a certain extent save the lives of patients
.
It also reminds farmers to take protective measures when spraying crops with pesticides to reduce contact with pesticides, and place pesticides such dangerous goods safely to prevent accidental ingestion
.
It is also beneficial to master pesticide first aid knowledge in daily life
.