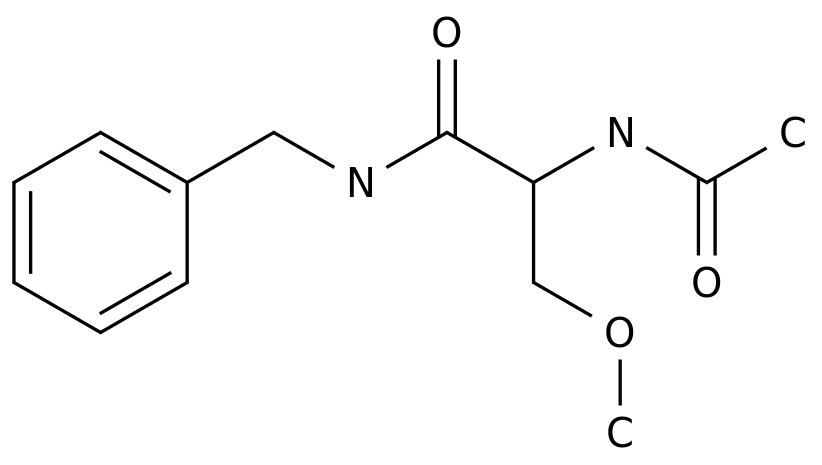
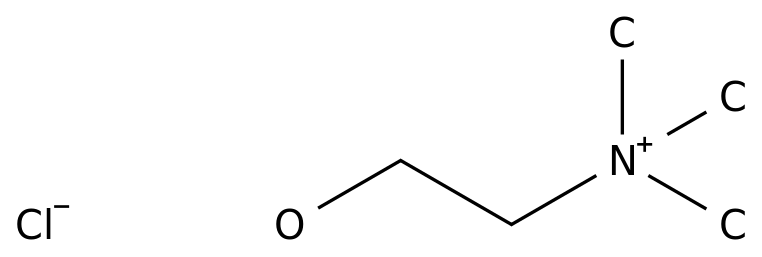
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Aging is accompanied by changes in lung function, which, like other organ systems, gradually decline with age due to factors such as loss of lung elasticity and weakening of respiratory muscles
.
In many studies, poor lung function (PF) is associated with lower quality of life and mortality in older adults
Quality of Life
As a complete assessment of the condition of the entire respiratory system, lung function is usually described using a composite measure including forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and peak expiratory flow (PEF)
.
There is no curative treatment for dementia, but aggressive management of modifiable risk factors can delay the onset of dementia and delay its progression
.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a transitional state between normal cognition and dementia
manage
Some degenerative brain lesions can be assessed by postmortem neuropathology, including Alzheimer's disease (AD) lesions and vascular lesions
.
Brain lesions can provide the pathogenesis associated with various risk factors for dementia
Blood vessel
In this way, Jiao Wang et al.
, from Tianjin Medical University, explored that poor PF is associated with an increased risk of MCI and may accelerate the progression of MCI to dementia, and vascular and neurodegenerative processes may underlie this association
.
To test this hypothesis, they aimed to explore
(1) Association of PF with MCI risk and its progression to dementia,
(2) To explore the association of PF with AD and cerebral vascular lesions using data from a long-term community cohort study, including assessment of brain pathology in participants who died during follow-up
.
They included a total of 1312 dementia-free participants, including the cognitively intact group (n = 985) and the MCI group (n = 327), and followed them for up to 21 years for the development of MCI and dementia
.
PF was assessed with a composite score and tertiled at baseline
They found that compared with the highest PF, the hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals [CIs]) for the lowest PF were 1.
95 (1.
43-2.
66) for MCI in the cognitively intact group and 1.
55 (1.
03-2.
33) for dementia in the MCI group
.
Low PF was further associated with Alzheimer's disease pathology (odds [OR] 1.
32, 95% CI 1.
19-1.
47) and vascular pathology (OR 3.
05, 95% CI 1.
49-6.
25)
.
This study shows that low PF increases the risk of MCI and accelerates the progression of MCI to dementia
.
Both neurodegenerative and vascular mechanisms may underlie the PF-dementia association
Low PF increases MCI risk and accelerates MCI progression to dementia
Original source:
Wang J, Dove A, Song R, et al.
Poor pulmonary function is associated with mild cognitive impairment, its progression to dementia, and brain pathologies: A community‐based cohort study .
Alzheimer's & Dementia.
Poor pulmonary function is associated with mild cognitive impairment, its progression to dementia, and brain pathologies: A community‐based cohort study