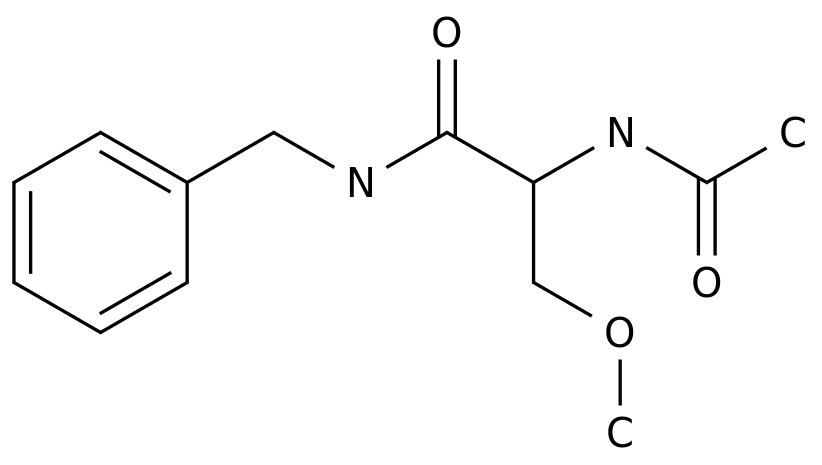
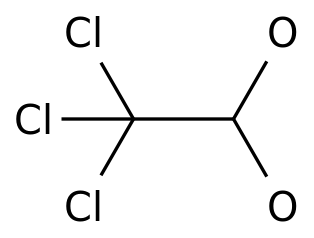
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
All cells in the body rely on the intracellular monitoring system to maintain the homeostasis of their proteome (protease stability).
Neurons are highly sensitive to the attack of protein toxins, so the protein balance in the cell is particularly important for neurons.
As people age, intracellular monitoring functions such as autophagy in neurons gradually decline, and the elimination of harmful proteins in cells decreases, which greatly increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Recently, researchers have discovered that Alzheimer's disease (AD, commonly known as "Alzheimer's disease") is closely related to autophagy in neurons.
Recently, "Cell" magazine published an online research report entitled "Chaperone-mediated autophagy prevents collapse of the neuronal metastable proteome" brought by researchers from the Einstein College of Medicine in the United States, and found that molecular chaperone-mediated autophagy can prevent The breakdown of neuronal metastable proteome.
DOI: 10.
1016/j.
cell.
2021.
03.
048 Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) is a selective degradation pathway of a single protein in the lysosome, which can be mediated by lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2A (L2A) Underlying degradation of lysosome internalization substrate protein.
In this study, the researchers knocked out L2A in the whole body and neurons of the mouse, causing it to block the whole body or neuron-specific CMA, which caused the accumulation of harmful proteins.
The results showed that the loss of neuronal CMA can lead to changes in intracellular proteins, which in turn leads to neuronal dysfunction.
Loss of CMA leads to neuronal dysfunction.
Researchers have found that the transcription of CMA is down-regulated in the brains of AD patients, which may increase the toxic effects of the pathogenic AD protein.As a result, they created CMA deletions in AD model mice and found that CMA deletions and neurodegeneration-related proteins produced a synergistic effect, thereby increasing the susceptibility of neuronal diseases and accelerating the progression of the disease.
CMA inhibition appears in the early stage of AD So, can activating CMA inhibit the occurrence and development of AD? In further experiments, the researchers hypothesized that the CMA activator AR7 can increase the clearance of harmful proteins in neurons after activating CMA, thereby affecting the progression of the disease.
In order to verify this idea, the researchers used a derivative CA77.
1 (CA) to activate CMA in AD model mice, and found that oral CA significantly enhanced the visual memory of mice, while reducing anxiety and depression in mice.
In the occurrence of behavior, these mice performed significantly better in the horizontal grid test.
Histopathological analysis also supports the positive effects of CA on mice.
The observation results show that β-amyloid and related pathological changes in the hippocampus and cortex of mice that are orally administered with CA are significantly reduced, and the microglia on the dorsal side of the hippocampus And the number of astrocytes decreases.
In other words, this drug can activate CMA, reduce neuronal pathological damage, and improve disease symptoms.
CMA activation improves the pathological damage of AD model mice.
In general, this study reveals the role of CMA in maintaining the neuronal proteome in the body under physiological and pathological conditions, and proves the positive effect of CMA activation on AD.
The new drug CA used therein has shown good curative effect in AD model mice and is expected to be used in the treatment of human AD and other neurodegenerative diseases.
At present, researchers have carried out the development of related drugs, and hope that the product can be applied to clinical treatment as soon as possible.
End reference materials: [1]
Neurons are highly sensitive to the attack of protein toxins, so the protein balance in the cell is particularly important for neurons.
As people age, intracellular monitoring functions such as autophagy in neurons gradually decline, and the elimination of harmful proteins in cells decreases, which greatly increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Recently, researchers have discovered that Alzheimer's disease (AD, commonly known as "Alzheimer's disease") is closely related to autophagy in neurons.
Recently, "Cell" magazine published an online research report entitled "Chaperone-mediated autophagy prevents collapse of the neuronal metastable proteome" brought by researchers from the Einstein College of Medicine in the United States, and found that molecular chaperone-mediated autophagy can prevent The breakdown of neuronal metastable proteome.
DOI: 10.
1016/j.
cell.
2021.
03.
048 Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) is a selective degradation pathway of a single protein in the lysosome, which can be mediated by lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2A (L2A) Underlying degradation of lysosome internalization substrate protein.
In this study, the researchers knocked out L2A in the whole body and neurons of the mouse, causing it to block the whole body or neuron-specific CMA, which caused the accumulation of harmful proteins.
The results showed that the loss of neuronal CMA can lead to changes in intracellular proteins, which in turn leads to neuronal dysfunction.
Loss of CMA leads to neuronal dysfunction.
Researchers have found that the transcription of CMA is down-regulated in the brains of AD patients, which may increase the toxic effects of the pathogenic AD protein.As a result, they created CMA deletions in AD model mice and found that CMA deletions and neurodegeneration-related proteins produced a synergistic effect, thereby increasing the susceptibility of neuronal diseases and accelerating the progression of the disease.
CMA inhibition appears in the early stage of AD So, can activating CMA inhibit the occurrence and development of AD? In further experiments, the researchers hypothesized that the CMA activator AR7 can increase the clearance of harmful proteins in neurons after activating CMA, thereby affecting the progression of the disease.
In order to verify this idea, the researchers used a derivative CA77.
1 (CA) to activate CMA in AD model mice, and found that oral CA significantly enhanced the visual memory of mice, while reducing anxiety and depression in mice.
In the occurrence of behavior, these mice performed significantly better in the horizontal grid test.
Histopathological analysis also supports the positive effects of CA on mice.
The observation results show that β-amyloid and related pathological changes in the hippocampus and cortex of mice that are orally administered with CA are significantly reduced, and the microglia on the dorsal side of the hippocampus And the number of astrocytes decreases.
In other words, this drug can activate CMA, reduce neuronal pathological damage, and improve disease symptoms.
CMA activation improves the pathological damage of AD model mice.
In general, this study reveals the role of CMA in maintaining the neuronal proteome in the body under physiological and pathological conditions, and proves the positive effect of CMA activation on AD.
The new drug CA used therein has shown good curative effect in AD model mice and is expected to be used in the treatment of human AD and other neurodegenerative diseases.
At present, researchers have carried out the development of related drugs, and hope that the product can be applied to clinical treatment as soon as possible.
End reference materials: [1]