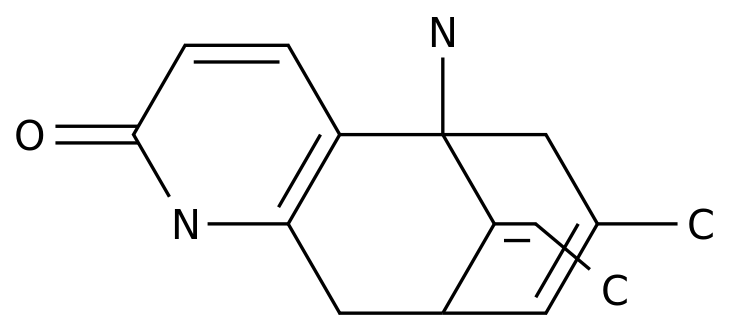
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common degenerative disease of the nervous system.
With age, its prevalence increases year by year.
Although PD is currently more common in the elderly, recent studies have found that the age of onset of some patients is earlier than 50 years, called early-onset Parkinson's disease (EOPD), which accounts for 5% to 10% of PD.
In view of the early age of onset of EOPD, long course of disease, large heterogeneity of clinical manifestations, relatively atypical symptoms, easy to be overlooked and misdiagnosed, domestic experts in the field have formed a consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of early-onset Parkinson's disease for reference .
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common degenerative disease of the nervous system.
With age, its prevalence increases year by year.
Although PD is currently more common in the elderly, recent studies have found that the age of onset of some patients is earlier than 50 years, called early-onset Parkinson's disease (EOPD), which accounts for 5% to 10% of PD.
In view of the early age of onset of EOPD, long course of disease, large heterogeneity of clinical manifestations, relatively atypical symptoms, easy to be overlooked and misdiagnosed, domestic experts in the field have formed a consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of early-onset Parkinson's disease for reference .
The pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of EOPD The pathogenesis of EOPD is not yet fully understood.
It is currently believed that genetic factors and environmental factors play an important role in it.
The clinical manifestations of EOPD include motor symptoms and non-motor symptoms.
Motor symptoms: The first symptom of EOPD is more common with motor retardation, and dystonia can also be the first symptom.
EOPD is mainly manifested by tonic and hypokinetic symptoms.
Static tremor and early balance dysfunction are relatively rare; some patients may be accompanied by dystonia, which is more common in focal dystonia of the feet or lower extremities.Non-motor symptoms: including neuropsychiatric symptoms, sleep disorders, cognitive dysfunction, constipation, etc.
, depression, restless legs syndrome, addictive behaviors are more common, while cognitive dysfunction, neuropsychiatric symptoms, hallucinations, etc.
are relatively rare , The olfactory function is relatively well preserved.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis: Diagnosis of EOPD: According to the age of onset ≤50 years, necessary motor retardation and at least one of resting tremor or myotonia, EOPD is diagnosed according to the "Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson's Disease in China (2016 Edition)".
Differential diagnosis of EOPD: It is necessary to exclude some diseases with a clear cause of secondary Parkinson's syndrome, such as traumatic brain injury, intracranial infection, carbon monoxide poisoning, and the use of antipsychotic drugs.
Anti-PD drug treatment ➤L-dopa preparations: such as dopasserazid, carlevodopa controlled-release tablets, levodopa/carbidopa enteral gel, etc.
Patients with EOPD respond well to levodopa preparations.
Levodopa preparations can significantly improve motor symptoms, but they are relatively prone to motor complications.
For EOPD patients with mental decline, levodopa preparations are generally preferred for treatment; for EOPD patients who strive to significantly improve motor symptoms, levodopa preparations or levodopa preparations combined with catechol-O-methyltransferase are generally selected (COMT) inhibitor for treatment.
For patients under the age of 25, especially adolescents and children, levodopa preparations can affect bone development, so it is not recommended.
➤Non-ergot DR agonists: such as piribedil, pramipexole, ropinirole, rotigotine, etc.
, which can be used as monotherapy drugs for EOPD patients without mental decline.
It is suitable for patients with EOPD in the early stage of the disease, but it is more prone to narcolepsy and impulse control disorders related to non-ergot DR agonists.
It should be used with caution for adolescent patients, and it is not recommended for childhood patients.
➤MAO-B inhibitors: such as selegiline and rasagiline, can also be used as a monotherapy for patients with EOPD without mental decline; and can also be used as a combination of levodopa preparations, especially for symptom fluctuations EOPD patients.
It is not recommended for adolescent patients and childhood patients.
➤COMT inhibitors: such as Entacapone, Entacapone Didopa, etc.
, Entacapone can be used in combination with dopaserizide and other levodopa preparations, which can improve the bioavailability of levodopa and prolong the levodopa The clinical effect of Dopa improves the motor symptoms of patients with EOPD.
It is not recommended for adolescent patients and childhood patients.
➤Anticholinergic drugs: For example, trihexyphenidyl is effective for resting tremor in patients with EOPD.
EOPD patients without resting tremor are not recommended; long-term use can cause cognitive impairment.
It should be used with caution for adolescent and childhood patients.
➤Amantadine: It has a certain effect on slow movement and muscle rigidity, and has a certain help to improve dyskinesia.
It should be used with caution for adolescent patients, and it is not recommended for childhood patients.
Yimaitong is compiled from: Parkinson's Disease and Dyskinesia Group of Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Parkinson's Disease and Dyskinesia Group of Neurologist Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association.
Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Early-onset Parkinson's Disease ( 2021) [J].
Chinese Journal of Neuromedicine, 2021, 20 (2): 109-116.
With age, its prevalence increases year by year.
Although PD is currently more common in the elderly, recent studies have found that the age of onset of some patients is earlier than 50 years, called early-onset Parkinson's disease (EOPD), which accounts for 5% to 10% of PD.
In view of the early age of onset of EOPD, long course of disease, large heterogeneity of clinical manifestations, relatively atypical symptoms, easy to be overlooked and misdiagnosed, domestic experts in the field have formed a consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of early-onset Parkinson's disease for reference .
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a common degenerative disease of the nervous system.
With age, its prevalence increases year by year.
Although PD is currently more common in the elderly, recent studies have found that the age of onset of some patients is earlier than 50 years, called early-onset Parkinson's disease (EOPD), which accounts for 5% to 10% of PD.
In view of the early age of onset of EOPD, long course of disease, large heterogeneity of clinical manifestations, relatively atypical symptoms, easy to be overlooked and misdiagnosed, domestic experts in the field have formed a consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of early-onset Parkinson's disease for reference .
The pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of EOPD The pathogenesis of EOPD is not yet fully understood.
It is currently believed that genetic factors and environmental factors play an important role in it.
The clinical manifestations of EOPD include motor symptoms and non-motor symptoms.
Motor symptoms: The first symptom of EOPD is more common with motor retardation, and dystonia can also be the first symptom.
EOPD is mainly manifested by tonic and hypokinetic symptoms.
Static tremor and early balance dysfunction are relatively rare; some patients may be accompanied by dystonia, which is more common in focal dystonia of the feet or lower extremities.Non-motor symptoms: including neuropsychiatric symptoms, sleep disorders, cognitive dysfunction, constipation, etc.
, depression, restless legs syndrome, addictive behaviors are more common, while cognitive dysfunction, neuropsychiatric symptoms, hallucinations, etc.
are relatively rare , The olfactory function is relatively well preserved.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis: Diagnosis of EOPD: According to the age of onset ≤50 years, necessary motor retardation and at least one of resting tremor or myotonia, EOPD is diagnosed according to the "Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson's Disease in China (2016 Edition)".
Differential diagnosis of EOPD: It is necessary to exclude some diseases with a clear cause of secondary Parkinson's syndrome, such as traumatic brain injury, intracranial infection, carbon monoxide poisoning, and the use of antipsychotic drugs.
Anti-PD drug treatment ➤L-dopa preparations: such as dopasserazid, carlevodopa controlled-release tablets, levodopa/carbidopa enteral gel, etc.
Patients with EOPD respond well to levodopa preparations.
Levodopa preparations can significantly improve motor symptoms, but they are relatively prone to motor complications.
For EOPD patients with mental decline, levodopa preparations are generally preferred for treatment; for EOPD patients who strive to significantly improve motor symptoms, levodopa preparations or levodopa preparations combined with catechol-O-methyltransferase are generally selected (COMT) inhibitor for treatment.
For patients under the age of 25, especially adolescents and children, levodopa preparations can affect bone development, so it is not recommended.
➤Non-ergot DR agonists: such as piribedil, pramipexole, ropinirole, rotigotine, etc.
, which can be used as monotherapy drugs for EOPD patients without mental decline.
It is suitable for patients with EOPD in the early stage of the disease, but it is more prone to narcolepsy and impulse control disorders related to non-ergot DR agonists.
It should be used with caution for adolescent patients, and it is not recommended for childhood patients.
➤MAO-B inhibitors: such as selegiline and rasagiline, can also be used as a monotherapy for patients with EOPD without mental decline; and can also be used as a combination of levodopa preparations, especially for symptom fluctuations EOPD patients.
It is not recommended for adolescent patients and childhood patients.
➤COMT inhibitors: such as Entacapone, Entacapone Didopa, etc.
, Entacapone can be used in combination with dopaserizide and other levodopa preparations, which can improve the bioavailability of levodopa and prolong the levodopa The clinical effect of Dopa improves the motor symptoms of patients with EOPD.
It is not recommended for adolescent patients and childhood patients.
➤Anticholinergic drugs: For example, trihexyphenidyl is effective for resting tremor in patients with EOPD.
EOPD patients without resting tremor are not recommended; long-term use can cause cognitive impairment.
It should be used with caution for adolescent and childhood patients.
➤Amantadine: It has a certain effect on slow movement and muscle rigidity, and has a certain help to improve dyskinesia.
It should be used with caution for adolescent patients, and it is not recommended for childhood patients.
Yimaitong is compiled from: Parkinson's Disease and Dyskinesia Group of Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Parkinson's Disease and Dyskinesia Group of Neurologist Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association.
Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Early-onset Parkinson's Disease ( 2021) [J].
Chinese Journal of Neuromedicine, 2021, 20 (2): 109-116.