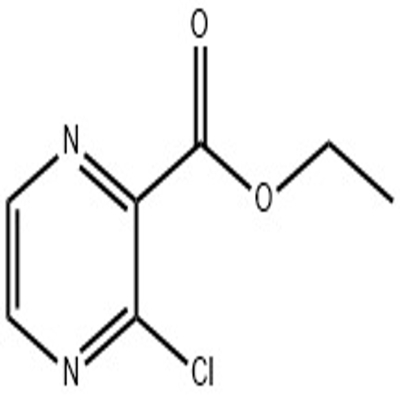
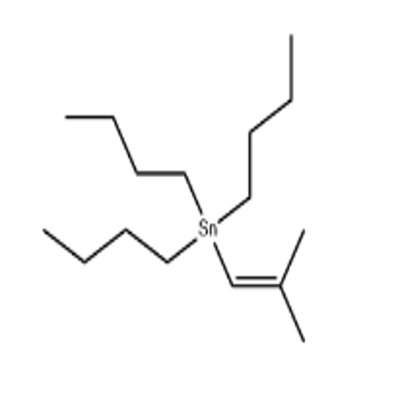
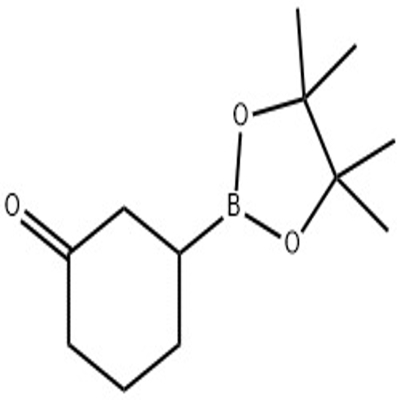
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Traditionally, diabetes has been divided into two types as a disease that affects more than 100 million Americans.
, Victoria Salem, a clinical scientist at Imperial College London who was not involved in the study, told the BBC that clinicians are aware that type 1 and type 2 diabetes are "not a very accurate classification" of the disease.
To determine a more granular classification, researchers from the Diabetes Center at Lund University in Sweden and the Finnish Institute of Molecular Medicine previously analyzed the medical records and blood of 14,775 patients and studied various diabetes-related indicators, such as long-term blood sugar control, insulin resistance and glycation of hemoglobin, and the genetic association of the disease.
their study revealed five groups of diabetics with different genetic characteristics, complications and disease progression rates.
Class 1 (cluster 1) is often similar to typical type 1 diabetes: when young, other healthy individuals have autoimmune diseases that prevent them from producing insulin, these diseases begin to occur;
Patients in category 2 also had the highest risk of retinal lesions; patients in category 3 (cluster 3) had severe insulin resistance, a higher risk of developing diabetic kidney disease than those in category 4 (cluster 4) and category 5 (cluster 5), patients in category 4 (cluster 4) had mild obesity-related diabetes; and patients in category 5 (cluster 5) included those with mild age-related diabetes.
between tissues is a fundamental feature of metabolic regulation, and the liver is at the heart of this process.
liver factor (hepatokine) is a protein secreted by the liver that regulates body metabolism.
in a new study, researchers from research institutions such as the University of Melbourne, Monash University, the University of Adelaide and Flinders University in Australia identified spark-related modular calcium binding protein 1 (sparc-related calcium-binding protein 1, SMOC1) as a glucose-reactive liver factor and glucose steady-state regulator protein.
study was recently published in the journal Science Translational Medicine under the title "SMOC1 is a glucose-responsive hepatokine and therapeutic target for glycemic control".
injection of SMOC1 in the acute abdominal cavity improved blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity in mice, but their insulin secretion did not change.
SMOC1 inhibits camp (3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate) - cAMP dependent protein kinase (PKA) - cAMP reaction element binding protein (CREB) signal transducement, resulting in a decrease in glycogloglogen expression, inhibit the liver glucose output, thereby playing its beneficial role in reducing sugar.
Excessive expression of SMOC1 in the liver or weekly abdominal injection of stable SMOC1-FC fusion protein in the liver for four weeks induced a lasting improvement in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in db/db mice, with no adverse effects on fatness, liver tissue pathology, or inflammation.
, circulating SMOC1 is associated with insulin sensitivity in the liver and body, while in obese, insulin-resistant humans, its levels decrease.
findings together identified SMOC1 as a potential drug target for managing blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes.
: Magdalene K. Montgomery et al. SMOC1 is a glucose-responsive hepatokine and therapeutic target for glycemic control. Science Translational Medicine, 2020, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aaz8048. This article is sourced from Bio Valley, for more information please download Bio Valley APP (