-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
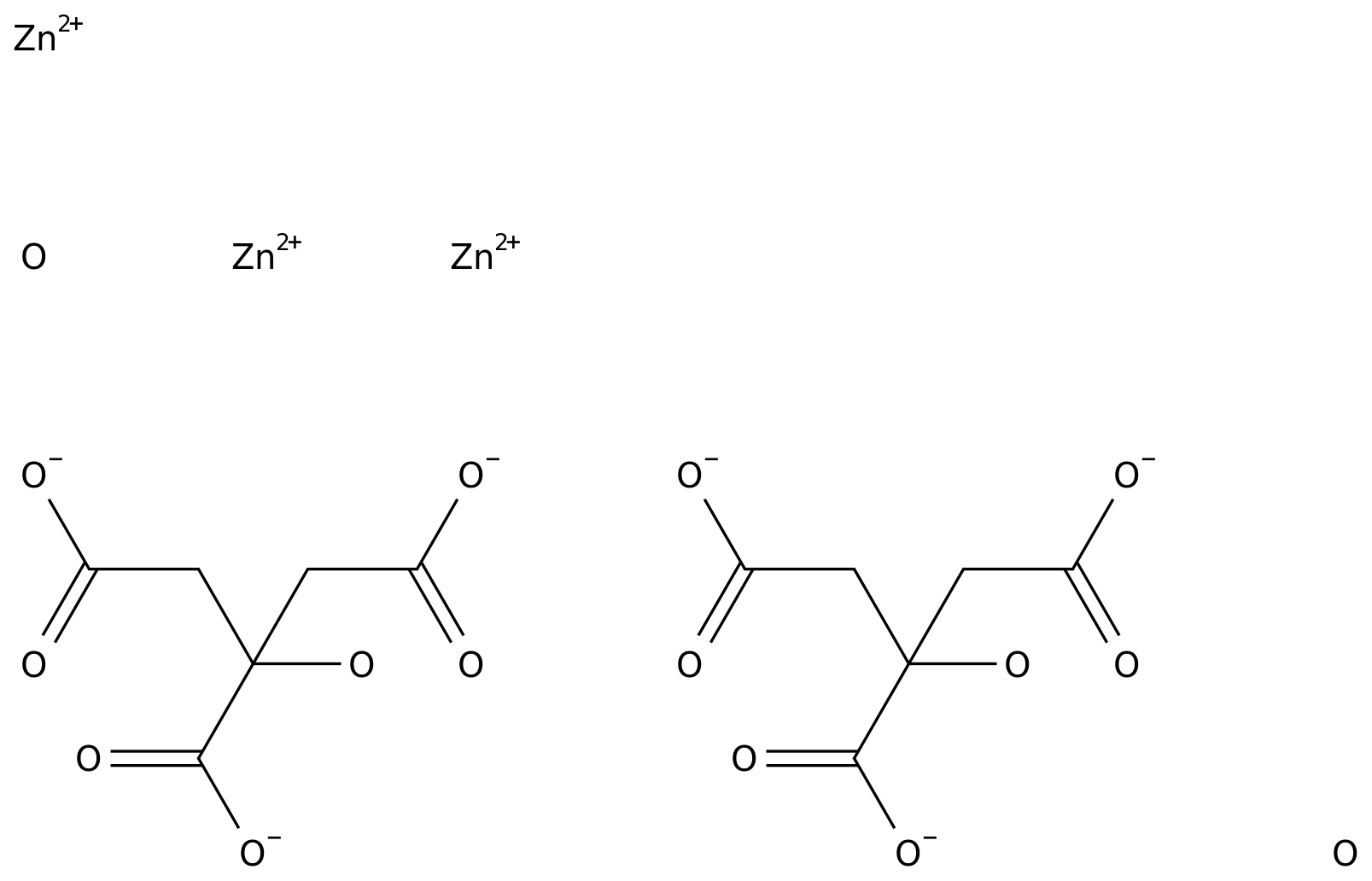
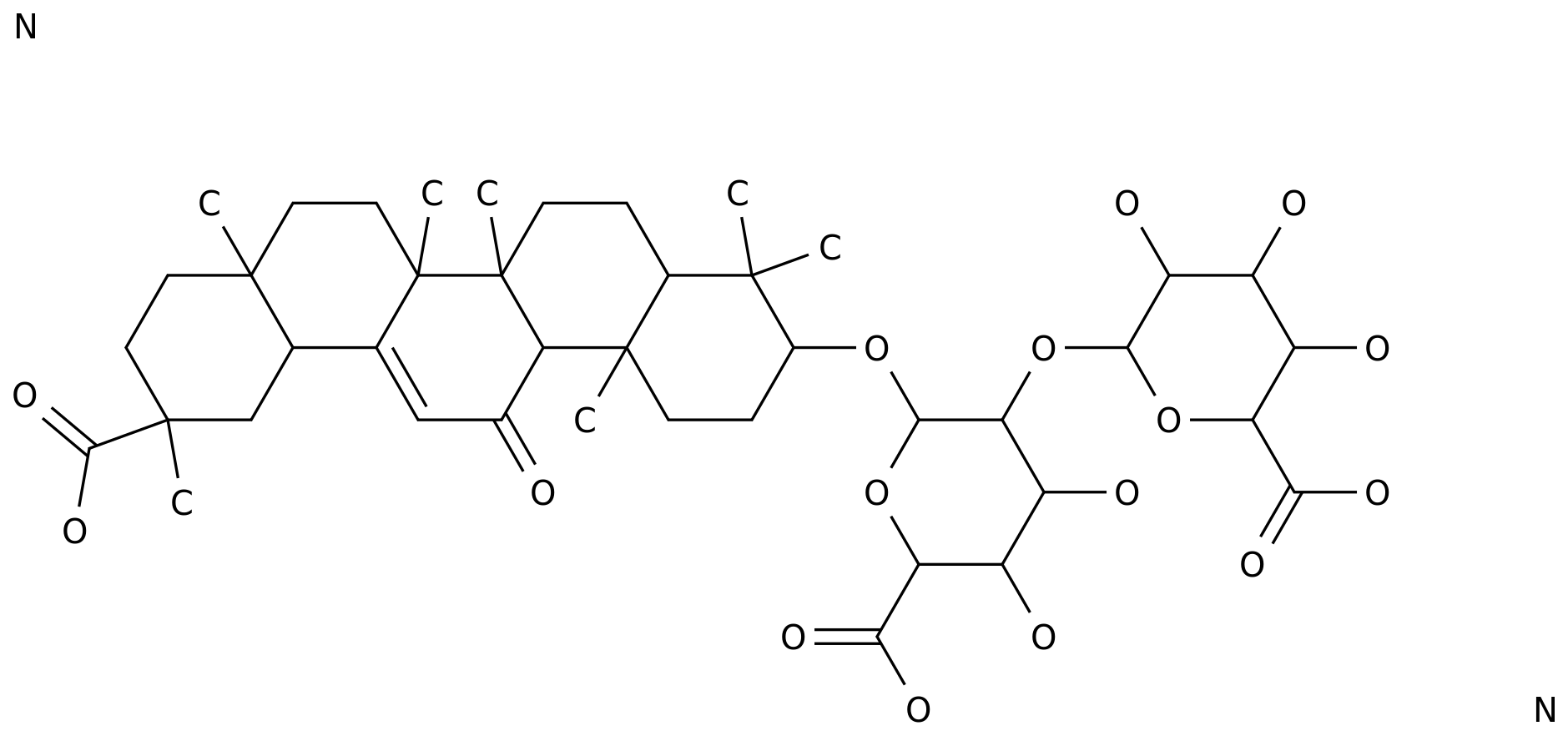
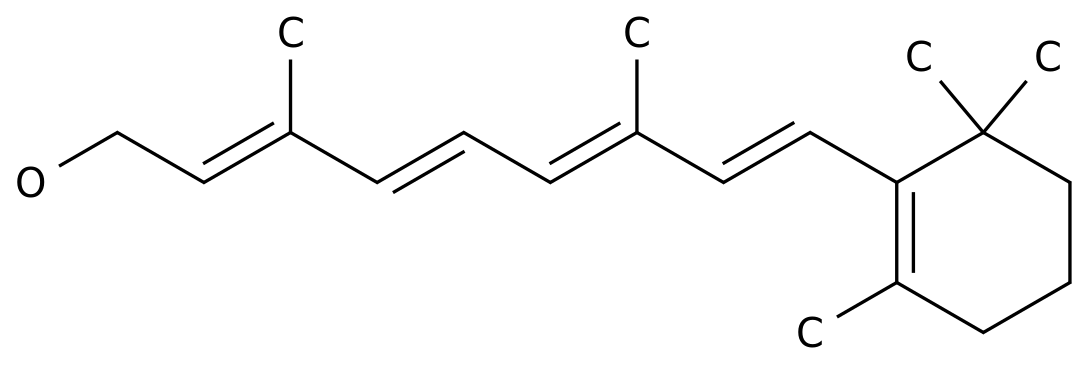
The three components of protein, starch and oil are mixed, and after high moisture extrusion, the protein spherical structure is gradually opened and rearranged, which can form a flat layered fiber structure similar to animal meat, and finally determine the taste
of plant-based meat products.
The previous research results of the plant protein structure and function regulation innovation team found that in the process of high-water extrusion, amylopectin is conducive to promoting the "layering" cross-linking of protein molecules, and stearic acid is conducive to promoting covalent bonding of protein molecules and forming fiber structure
.
However, whether amylopectin and stearic acid have a synergistic effect on the formation of protein fiber structure is still unclear, and the mechanism of interaction between protein, starch and oil components to form fiber structure is also unclear, which hinders the effective and precise regulation
of fiber structure of plant-based meat products.
of plant-based meat products.
The previous research results of the plant protein structure and function regulation innovation team found that in the process of high-water extrusion, amylopectin is conducive to promoting the "layering" cross-linking of protein molecules, and stearic acid is conducive to promoting covalent bonding of protein molecules and forming fiber structure
.
However, whether amylopectin and stearic acid have a synergistic effect on the formation of protein fiber structure is still unclear, and the mechanism of interaction between protein, starch and oil components to form fiber structure is also unclear, which hinders the effective and precise regulation
of fiber structure of plant-based meat products.
Therefore, the team took pea protein as the research object to explore the synergistic effect of amylopectin and stearic acid on the formation of pea protein fiber structure extruded by high moisture, and then analyzed the interaction law of protein, amylopectin and stearic acid and their regulatory mechanism
on the fiber structure of plant-based meat products 。 The results show that when protein, amylopectin and stearic acid coexist, amylopectin and stearic acid have a synergistic effect on the protein fiber structure, among which, stearic acid promotes the exposure of protein hydrophobic groups and hinders the rebound and refolding of protein molecular chains, while amylopectin provides a fulcrum to promote the stretching, rearrangement and polymerization of protein molecular chains, thereby promoting the formation
of fiber structure in the mode of "anchor point orientation, flexible crosslinking".
This study revealed the interaction law between the main components in the process of high-moisture extrusion, and laid a theoretical foundation
for the precise regulation of the fiber structure of plant-based meat products.
on the fiber structure of plant-based meat products 。 The results show that when protein, amylopectin and stearic acid coexist, amylopectin and stearic acid have a synergistic effect on the protein fiber structure, among which, stearic acid promotes the exposure of protein hydrophobic groups and hinders the rebound and refolding of protein molecular chains, while amylopectin provides a fulcrum to promote the stretching, rearrangement and polymerization of protein molecular chains, thereby promoting the formation
of fiber structure in the mode of "anchor point orientation, flexible crosslinking".
This study revealed the interaction law between the main components in the process of high-moisture extrusion, and laid a theoretical foundation
for the precise regulation of the fiber structure of plant-based meat products.
Recently, the study was published online in the internationally renowned academic journal Food Hydrocolloids (Region 1 of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, IF=11.
504), with Chen Qiongling, a 2019 doctoral student at the Institute of Agricultural Products Processing of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, as the first author of the paper, and researcher Wang Qiang and associate researcher Zhang Jinchuang as co-corresponding authors
。 The research results were supported
by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFC2101402), the Key Task Youth Innovation Special Project of the Institute of Innovation Engineering, Institute of Agricultural Products Processing, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-Q2022-IFST-05), and the Scientific Research Project of Weifang Institute of Food Science and Processing Technology, Institute of Agricultural Products Processing, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (WFIFST-2022-01).
504), with Chen Qiongling, a 2019 doctoral student at the Institute of Agricultural Products Processing of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, as the first author of the paper, and researcher Wang Qiang and associate researcher Zhang Jinchuang as co-corresponding authors
。 The research results were supported
by the National Key R&D Program of China (2021YFC2101402), the Key Task Youth Innovation Special Project of the Institute of Innovation Engineering, Institute of Agricultural Products Processing, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-Q2022-IFST-05), and the Scientific Research Project of Weifang Institute of Food Science and Processing Technology, Institute of Agricultural Products Processing, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (WFIFST-2022-01).
Original link: https://doi.
org/10.
1016/j.
foodhyd.
2022.
108254
org/10.
1016/j.
foodhyd.
2022.
108254