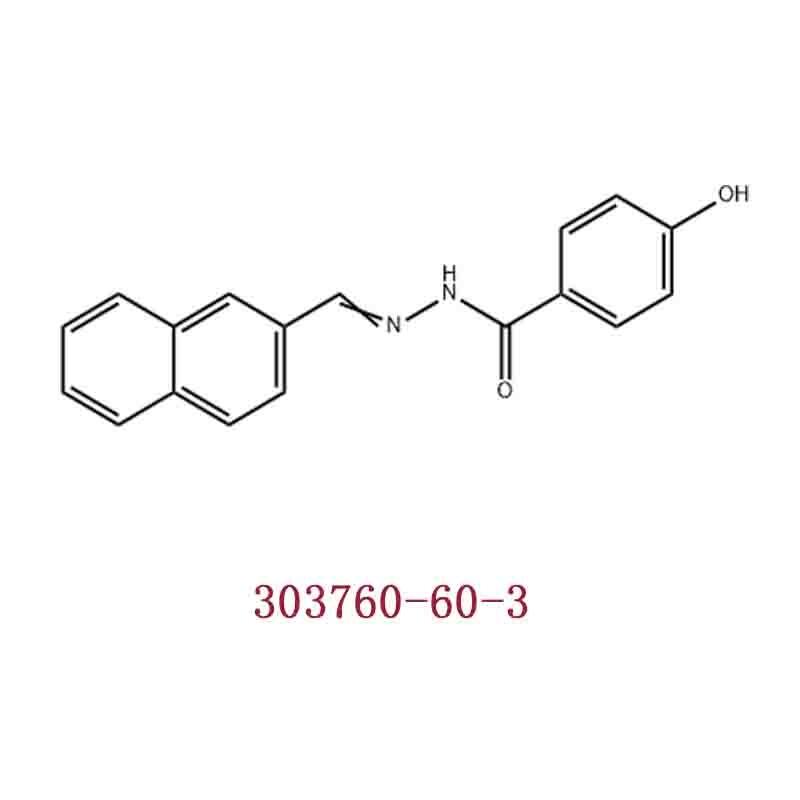
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
The utilization of 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) as a important monomer in the production of engineering plastics has been the subject of much research and development in the chemical industry.
This compound, also known as polyamide-12, is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic that is widely used in applications such as automotive, electrical, and mechanical components.
One of the main advantages of using 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) as a monomer is its excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance.
It has a high melting point and a broad melting range, making it suitable for use in high-temperature applications.
Additionally, it is highly resistant to most organic solvents, acids, and bases, making it ideal for use in environments where it may come into contact with aggressive chemicals.
The high strength and stiffness of 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) make it an ideal material for use in the production of mechanical components such as gears, bearings, and shafts.
It has a high load-carrying capacity and excellent resistance to wear and tear, making it ideal for use in demanding applications.
Another advantage of 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) is its excellent dimensional stability.
It has a low co-efficient of thermal expansion, making it less likely to warp or distort under temperature changes.
This makes it an ideal material for use in the production of components that require consistent and precise dimensions.
In the production of engineering plastics, 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) is often used in combination with other monomers to create a polymer with specific properties.
For example, the addition of a small amount of maleic anhydride to 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) can create a copolymer with improved thermal stability and processing properties.
In the production of engineering plastics, the use of 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) as a monomer is an excellent solution for a wide range of applications.
Its excellent thermal stability, chemical resistance, strength, and stiffness make it an ideal material for the production of mechanical components, while its dimensional stability and processability make it an excellent choice for the production of precise and consistent components.
As the demand for high-performance engineering plastics continues to grow, the use of 1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine, 6-(2,5-dichlorophenyl)-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) is likely to become increasingly popular in the chemical industry.