-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
As we all know, pulmonary sarcoma-like cancer (PSC) is relatively low in non-small cell lung cancer, because of its unique clinical manifestations, in the pathological type of lung cancer can not be ignoredPSC clinical diagnosis is difficult, high degree of malignancy, insensitive to chemotherapy and immunity, the median PFS is only about 1-2 monthsWith the rise of hybrid capture NGS platforms in recent years, the detection of MET exon14 jump mutations has become more commonA study from China found that metexon14 jump mutations had a 31.8 percent rate in pulmonary sarcoma-like cancer (P.ASarcomatoid Carcinoma, PSC), and preclinical studies suggested that such patients could benefit from met-inhibitor targeted treatmentHowever, since only the clinical study of Savolitinib, a Chinese-developed MET inhibitor, has included up to 39% of PSC patients, the efficacy of MET inhibitors on MET exon14 jump mutation PSC is more objective, which brings clinical referenceMET Exon14 jump mutation, activates metkinase pathwayMET gene, full name interstitial epithelial conversion factor, is a high affinity of primary cancer gene receptor tyrosine kinase, whose ligand is hepatocellular growth factor (HGF)Met and HGF can be combined to activate the Ras-MAPK and PI3K-AKt signaling pathways involved in tumor occurrence and metastasis, which is one of the common cancer-causing pathways that can mediate the activation of cancer gene pathways and promote cell proliferation, growth and metastasisC-MET, as we often refer to, is a transmembrane receptor with autonophosphorifying activity produced by met gene codingMET is a gene, and c-MET is a gene-guided proteinMET genes can be activated in many forms, including selective somatic cell mutations, such as Exon14 jump mutations, MET gene amplification, and MET protein overexpressionIn 2014, the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) published 230 comprehensive gene spectroscopy results that could remove lung adenocarcinoma levels of DNA, mRNA, and microRNABy analyzing the results of mRNA and DNA high-throughput sequencing and sequence comparison, it was found that about 4% (10/230) of lung adenocarcinoma caused partial or complete jump loss of MET 14 exons at mRNA levels due to mutations in the 14th exon shear region of met gene DNA levels (splice-sites)The near-membrane domain encoded by MET exon14 is a key negative regulatory area of MET, consisting of a hesythofyton anase (caspase) lysis sequence (ESVD1002) and an E3 ubiquinone-connected enzyme c-Cbl tyrosine binding site (Y1003), which is involved in the incoding and degradation of met proteinsThe absence of the near membrane domain can reduce the met protein ubiquity barrier and the met perforated rate of MET, thus increasing the stability of MET and causing the continuous activation of downstream signals The main causes of met exon14 jumping in the transcription level are point mutations or missing mutations (deletions) in the met exon14 splicing region, and a very small number of Y1003-point mutations The incidence of MET exon14 jump mutation in lung cancer was 3% to 4%, similar to that of ALK rearrangement, and higher in PSC, 8% to 30% In recent years, with the application of hybrid capture NGS platform, met exon14 jump mutation detection has become more popular worse - MET14 exosome son-jumping PSC patients have a higher risk of recurrence
as the detection methods continue to advance, the exploration of PSC molecular characteristics is also deepening The study found that PSC is a kind of NSCLC that drives the higher frequency of gene mutations, and the mutations in EGFR, KRAS, ALK and MET are more common, with the frequency of MET gene mutations being 20% to 31.8%, and data from different studies show similar rates of MET gene mutations in PSC patients in east and west The protein c-MET encoded by the MET gene is a cross-membrane tyrosine kinase receptor, and the MET pathway is involved in regulating cell proliferation, migration and angiogenesis MET gene mutations, including the 14th exon jump reading and gene amplification, can lead to abnormal activation of the MET pathway, which drives the proliferation and migration of cancer cells and promotes tumor development Retrospective studies showed that the incidence of MET14 exosome son-jumping in CHINESE PSC patients was 20.8%-22% 2018, Li et al showed faster progression in late-stage PSC patients with met14 exon-like jump-positive in patients with genetically negative genes During the follow-up period, the median PFS for both groups of patients was: it did not reach vs 3.97 months (p.017) The existence of MET14 exobody jumping makes the treatment situation more difficult for PSC, which is already highly malignant traditional treatment programs have little effect, can new treatments make a breakthrough? Unfortunately, although immunotherapy has made breakthroughs in many areas in recent years, patients with MET14 epithelial son-jumping appear to be ineffective The U.S NCCN GUIDELINES MAKE IT CLEAR THAT LUNG CANCER PATIENTS WITH MET14 EXONS HAVE A LOW RESPONSE TO IMMUNOTHERAPY EVEN WITH HIGH PD-L1 EXPRESSION Met Exon14 jump mutations have a high incidence of re-igniting research interest in pulmonary sarcoma
with the discovery of MET Exon14 jump mutations, rekindled people's interest in PSC research In 2015, Liu Xuewen of Sun Yat-sen University's Affiliated Oncology Hospital and others found 8 cases (incidence of about 22%) metexon14 deficiency mutations in 36 PSCs through high-throughput sequencing and targeted sequencing of c-MET genes The study also confirmed through cell experiments that MET inhibitors or siRNAs can effectively inhibit the growth and proliferation of downstream signal activation and mutation tumor cells (Hs746T and H596) mediated by c-MET exon14 jump mutation Therefore, met exon14 jump mutation is expected to become a new therapeutic target for PSC MET inhibitors are emerging in met Exon14 jump mutationpulmonary sarcoma
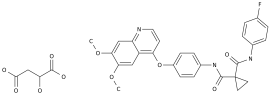
given that met exon14 jump mutations are so high in PSC that they could become potential therapeutic targets for PSC, sparking interest among clinicians Since 2015, there have been persistent reports that PSC with met exon14 jump mutations can benefit from MET inhibitor treatment However, the data reported on cases are not sufficient to change clinical practice, and we look forward to the results of clinical studies Unfortunately, perhaps because the overall prognosis of PSC is too poor, it may affect the efficacy of the entire MET exon14 jump mutation population, which in turn affects the overall test results, not every MET inhibitor study will be included in the psC patients Only the clinical study of The metainhibitor Volitini (NCT02897479), which was independently developed in China, included up to 39% of PSC patients, which reflected the efficacy of MET inhibitors in MET exon14 jump mutation PSC The Wallitinib Phase II registered clinical study, presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO), was originally designed to target only PSC patients with MET exon14 jump mutations, but later expanded to other NSCLC populations with MET exon14 jump mutations As a result, nearly 40% of the patients in the study were PSC patients, more than 90% of all patients in the group were phase IV patients, and more than 1/4 of all patients combined brain metastasis, which should be said to be the highest level of tumor load and malignancy in NSCLC results showed that in patients with MET exon14 jump mutations that failed or were not suitable for chemotherapy, and EGFR/ALK/ROS-1 negative, PSC (n?13) or other NSCLC (n?23) who had not previously been treated with MET inhibitors, had an overall objective remission rate (ORR) of 52.8% and disease control rate (DCR) of 94.4% Whether PSC patients are primary treatment or retreatment, can benefit from the treatment of Volitini, but we also see that the initial treatment of PSC patients ORR only 33.3%, compared with other NSCLC patients relatively lower mitigation rate, indicating that although targeted treatment although there is some efficacy, but PSC patients overall prognosis is relatively poor summary with advances in gene testing techniques, the study found that met exon14 jump mutations have a higher incidence of PSC and are expected to become potential therapeutic targets for these refractory cancers In recent years, there have been persistent reports of clinical cases suggesting that PSC with MET exon14 jump mutations may benefit from MET inhibitor therapy, and the efficacy of MET inhibitors is initially indicated by the Volitinib clinical clinical study data reference 1.Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Comprehensivemolecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma Nature 2014;511:543-50 2.Liu X, Jia Y, Stoopler MB, et al Next-Generation paring of sarcomatoid carcinoma reveals high frequency ofable metgene J Clin Oncol 2015 Jul 27 3.Lee C, Usenko D, Frampton GM, McMahon C, Ali SM, Weiss J MET 14 Deletion in Sarcomatoid Non-Small Cell Care Cancered by Next-Generation And Ageing And Temperature Seda J Thorac Oncol 2015;10: e113-114 4 Volitinib's treatment of MET exon 14 jumping non-small cell lung cancer patients Phase II study: preliminary efficacy and safety results Abstract 5707, 2019 CSCO author: Oncology Information Source: