-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
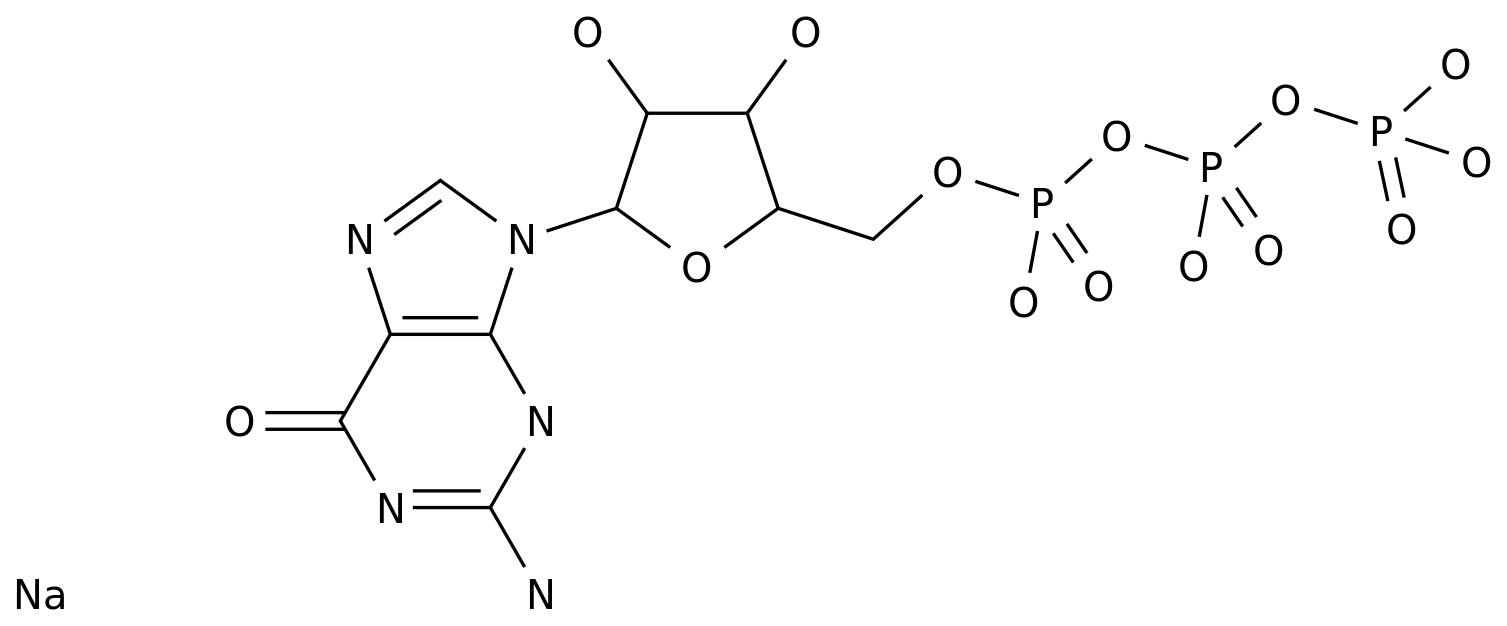
Dideoxyadenosine, also known as didanosine, is a synthetic purine nucleoside analogue that is used as an antiretroviral drug for the treatment of HIV and AIDS.
The production process of didanosine involves several steps, including the synthesis of the starting material, the formation of the nucleoside, and the modification of the nucleoside to create the active metabolite.
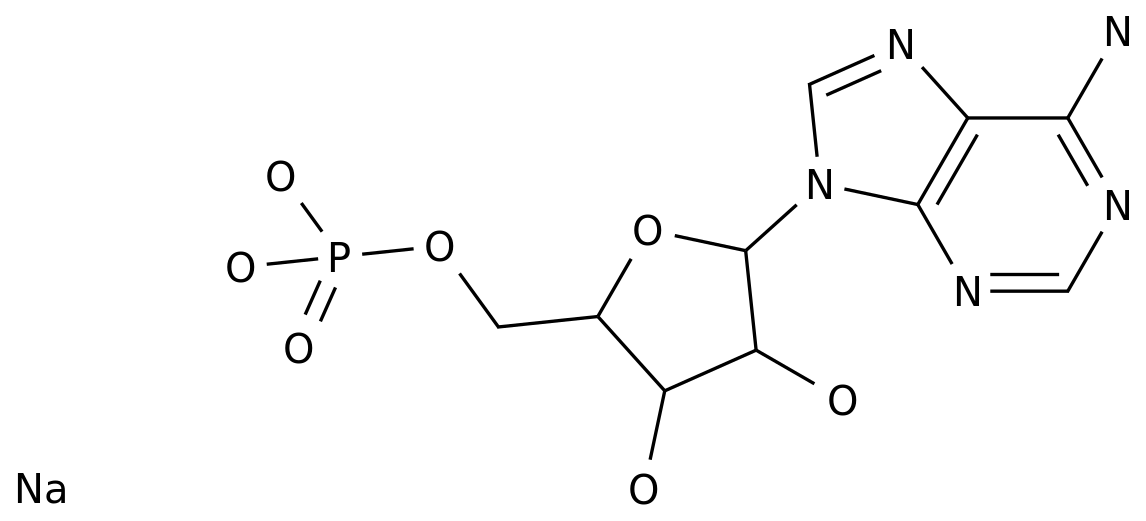
The synthesis of the starting material, 2'-deoxyadenosine, is the first step in the production of didanosine.
This is typically achieved through a multi-step synthesis, starting with the synthesis of 2-chloroadenosine from adenosine.
The 2-chloroadenosine is then converted to 2'-deoxyadenosine through a series of chemical reactions, including hydrolysis, condensation, and reduction.
Once the 2'-deoxyadenosine is synthesized, the next step is to form the nucleoside.
This is achieved through a process called phosphorylation, which involves the addition of a phosphate group to the molecule.
The phosphorylation reaction is typically carried out using a mixture of reagents, including potassium hydroxide, water, and a phosphate donor, such as bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino-hydrochloride (BHA).
After the nucleoside has been formed, the next step is to modify it to create the active metabolite, didanosine.
This modification involves the addition of a methyl group to the molecule, which is achieved through a process called methylation.
The methylation reaction is typically carried out using a methylating agent, such as dimethylformamide (DMF), and a methyl iodide source, such as methyl iodide or phenylsilicic acid (PSA).
The final step in the production of didanosine is the isolation and purification of the final product.
This is typically achieved through a series of chromatographic techniques, such as ion exchange chromatography, hydroxyapatite chromatography, and reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
In conclusion, the production process of didanosine involves several steps, including the synthesis of the starting material, the formation of the nucleoside, and the modification of the nucleoside to create the active metabolite.
The process requires the use of specialized equipment and reagents, and is typically carried out in a controlled environment, such as a laboratory or industrial facility.
The production of didanosine is a complex and multifaceted process, and requires a strong understanding of organic chemistry and pharmaceutical manufacturing.