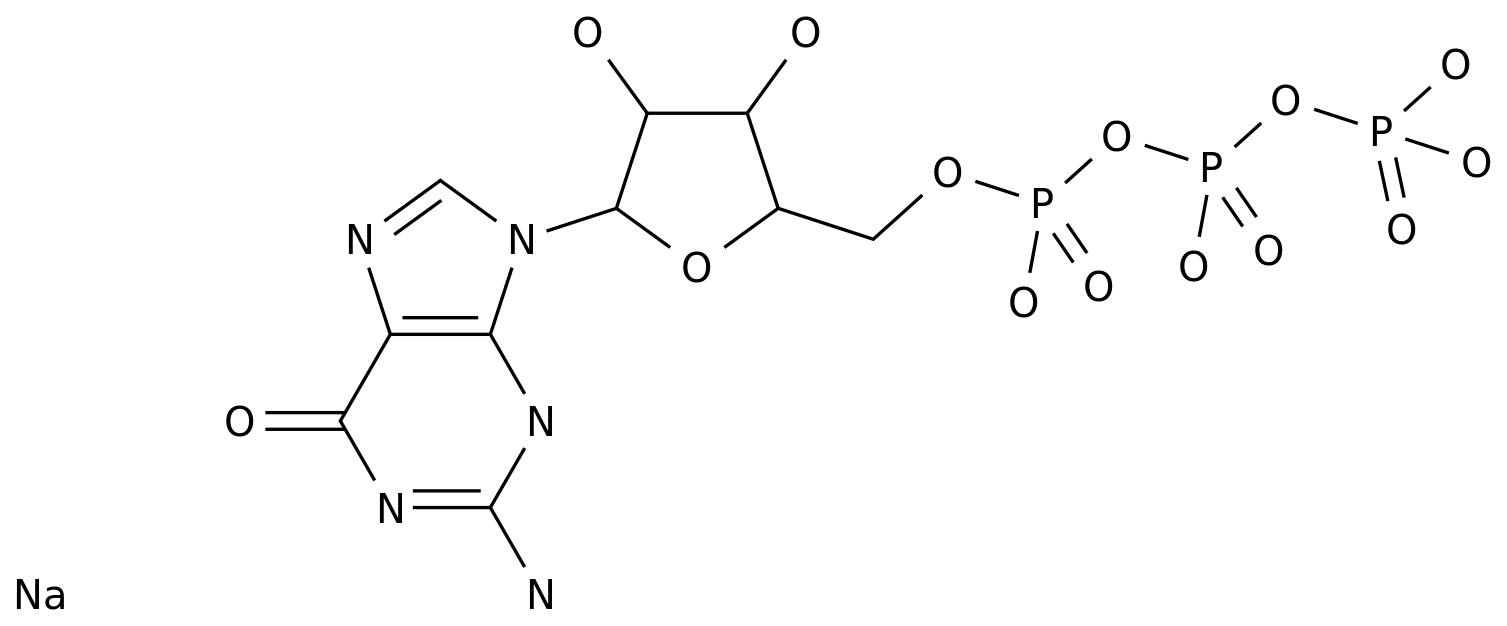
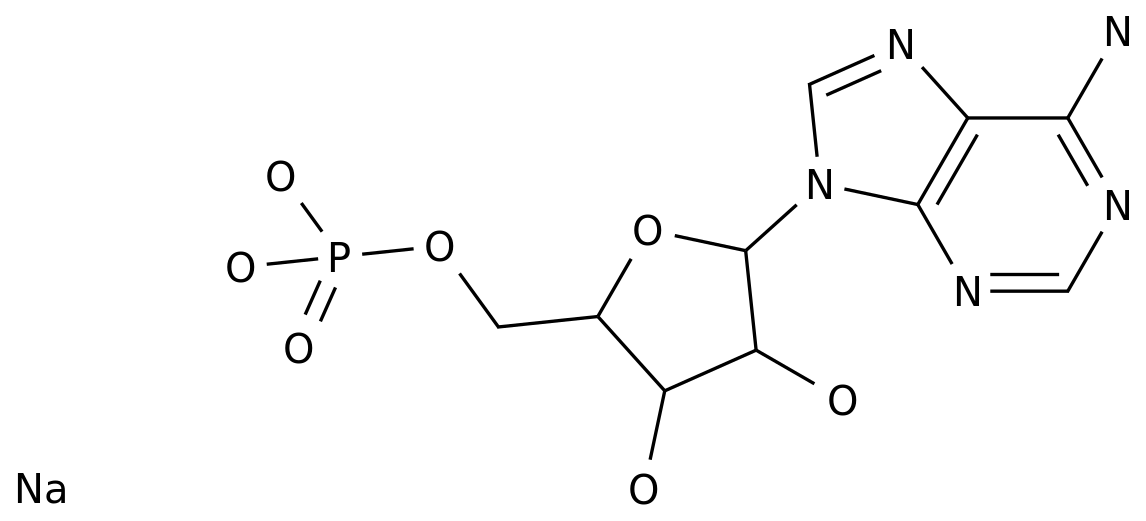
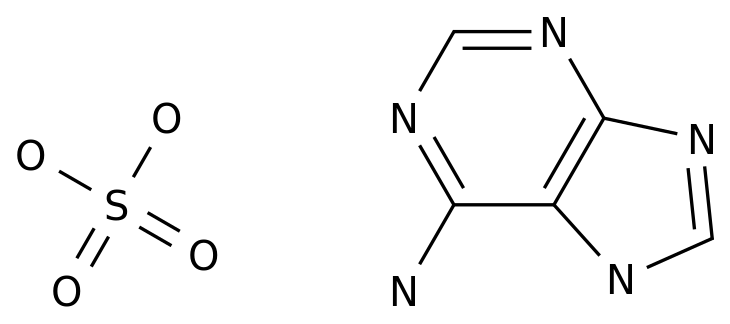
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
1H-1,2,3-Triazole, also known as benzotriazole, is a synthetic compound that is widely used in various industrial applications.
The synthetic routes of 1H-1,2,3-triazole can be broadly classified into three categories: direct synthesis, indirect synthesis, and condensation reaction.
Direct Synthesis:
The direct synthesis of 1H-1,2,3-triazole involves the reaction of aniline with a nitrogen source, such as ammonia or hydrazine.
The reaction typically takes place in the presence of a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide, and is carried out at elevated temperatures.
The reaction produces 1H-1,2,3-triazole as a yellow or greenish-yellow solid.
This method is simple and cost-effective, and is widely used in industrial applications.
Indirect Synthesis:
The indirect synthesis of 1H-1,2,3-triazole involves the synthesis of an intermediate compound, such as melamine or guanamine, which can then be converted into 1H-1,2,3-triazole.
The intermediate compound is typically synthesized by reacting a formaldehyde source, such as paraformaldehyde or methylol compounds, with an amine source, such as ammonia or a primary or secondary amine.
The reaction typically takes place in the presence of an acid catalyst, such as sulfuric acid, and is carried out at elevated temperatures.
The intermediate compound is then hydrolyzed to produce 1H-1,2,3-triazole.
This method is more complex than the direct synthesis method, but it allows for the production of a wider range of products and is more flexible in terms of the starting materials that can be used.
Condensation Reaction:
The condensation reaction of 1H-1,2,3-triazole involves the reaction of two molecules of aniline with a diazonium salt.
The reaction typically takes place in the presence of a solvent, such as methanol or ethanol, and is carried out at room temperature.
The reaction produces 1H-1,2,3-triazole as a yellow or greenish-yellow solid.
This method is more complex than the direct synthesis method, but it allows for the production of a wider range of products and is more flexible in terms of the starting materials that can be used.
In industrial applications, 1H-1,2,3-triazole is widely used as an intermediate compound in the production of dyes, pigments, and pharmaceuticals.
It is also used as a catalyst in the production of polyurethanes and in the polymerization of epoxy resins.
Additionally, it is used as an antioxidant in gasoline and as a corrosion inhibitor in cooling systems.
In conclusion, the synthetic routes of 1H-1,2,3-triazole are varied and can be tailored to suit the specific needs of industrial applications.
The direct synthesis method is simple and cost-effective, while the indirect synthesis method allows for the production of a wider range of products and is more flexible in terms of the starting materials that can be used.
The condensation reaction method is more complex, but it allows for the production of a wider range of products and is more flexible in terms of the starting materials that can be used.
Overall, 1H-1,2,3-triazole is a versatile synthetic compound with a wide range of industrial applications.