-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
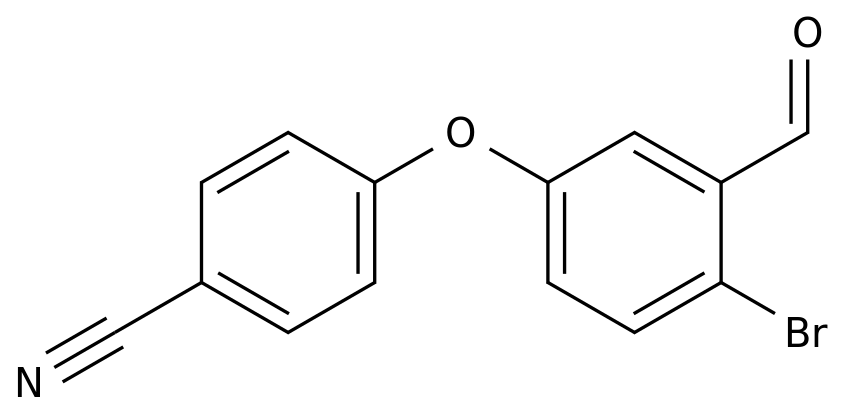
2-Bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde is an organic compound that is commonly used as an intermediate in the production of various chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and dyes.
The synthesis of 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde can be achieved through several different methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The following are some of the synthetic routes that are commonly used in the chemical industry to produce 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
- Nitrating-Hydrolysis Method
The nitrating-hydrolysis method is one of the most commonly used synthetic routes for 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
This method involves the nitration of o-phenylendiamine with nitric acid under ice-cold conditions, followed by hydrolysis of the resulting nitro compound with sodium hydroxide.
The resulting product is then recrystallized to obtain pure 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde. - Halogenation-Hydrolysis Method
Another commonly used method for synthesizing 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde is the halogenation-hydrolysis method.
In this method, o-phenylendiamine is treated with chlorine or bromine in the presence of a solvent such as carbon tetrachloride or carbon disulfide.
The resulting halogenated compound is then hydrolyzed with sodium hydroxide to produce 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde. - Reduction of Benzaldehyde
2-Bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde can also be synthesized by reducing benzaldehyde with sodium borohydride in the presence of a solvent such as ethanol.
The resulting product is then treated with nitric acid to remove any remaining borohydride groups. - Reduction of Nitrobenzene
Another method for synthesizing 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde involves the reduction of nitrobenzene with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst such as palladium on barium sulfate.
The resulting product is then treated with sodium hydroxide to produce 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Routes
Each of the above synthetic routes for 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The nitrating-hydrolysis method is relatively simple and inexpensive, but it requires the use of hazardous reagents such as nitric acid and sodium hydroxide.
The halogenation-hydrolysis method is more efficient and selective than the nitrating-hydrolysis method, but it requires the use of toxic reagents such as carbon tetrachloride and carbon disulfide.
The reduction of benzaldehyde and nitrobenzene, on the other hand, are relatively mild and safe, but they require specialized equipment and catalysts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several synthetic routes for 2-bromo-5-hydroxybenzaldehyde that are commonly used in the chemical industry.
The choice of route depends on factors such as the availability and cost of reagents, the desired yield and purity of the product, and the safety and environmental considerations of the process.
It is important to carefully evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each route before making a decision on which to use.