-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
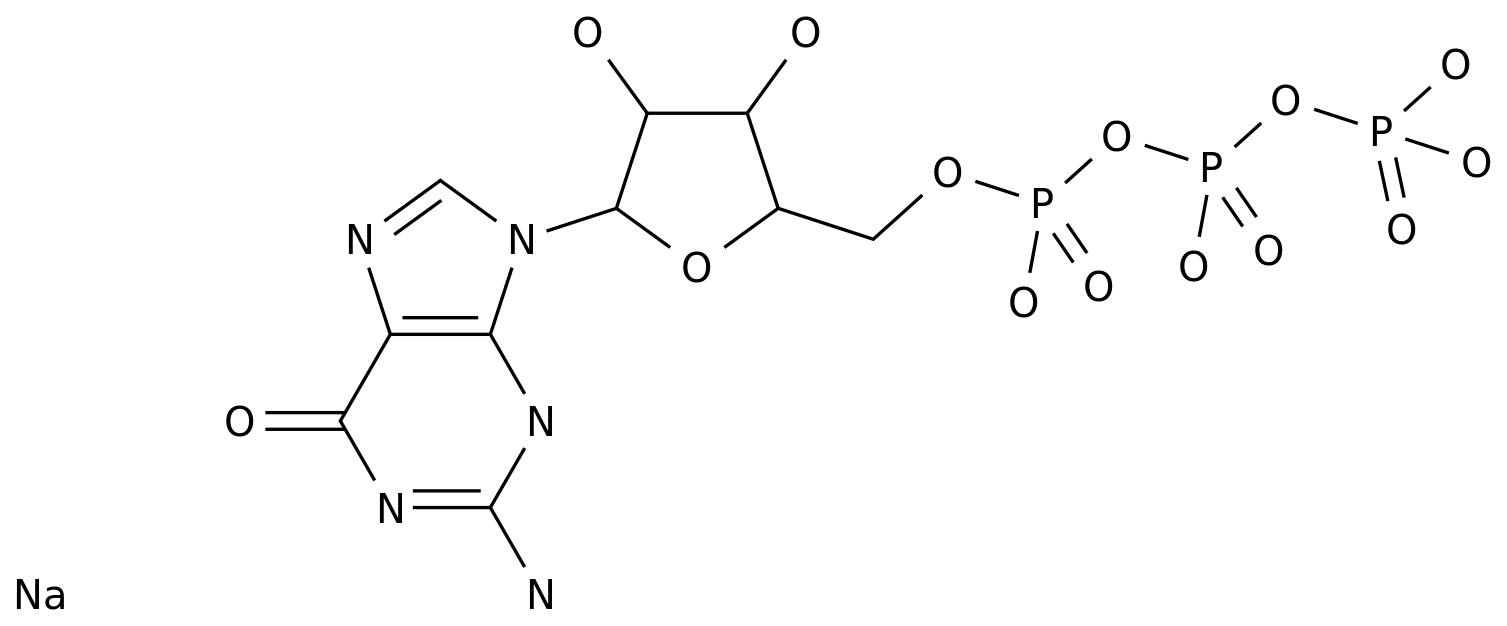
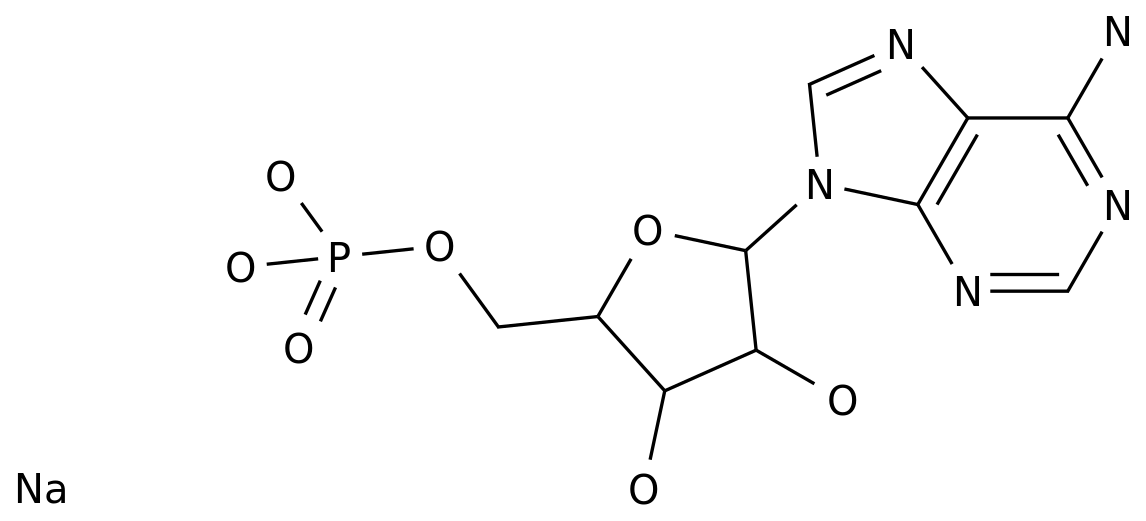
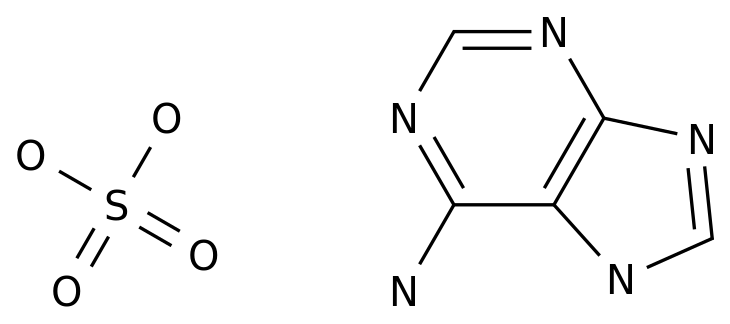
Dideoxyadenosine, also known as ddA, is a synthetic nucleoside analog that has been studied for its potential use as an antiviral drug.
It is a synthetic version of adenosine, a naturally occurring nucleoside that is a component of DNA and RNA.
Dideoxyadenosine has been shown to inhibit the replication of certain viruses, including herpes simplex virus and cytomegalovirus.
There are several synthetic routes that have been developed for the production of dideoxyadenosine.
One common route involves the condensation of erythrose with propionaldehyde in the presence of a base, such as sodium hydroxide.
The resulting intermediate is then converted into dideoxycytidine through a series of chemical reactions, and finally, the dideoxycytidine is converted into dideoxyadenosine through a process known as deprotection.
Another synthetic route involves the use of a process called the "Duke process," which was developed by researchers at Duke University.
This process involves the condensation of N-acetylanthranilic acid with 2-chloro-4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine in the presence of a base, such as sodium hydroxide.
The resulting intermediate is then converted into dideoxyadenosine through a series of chemical reactions.
A third synthetic route involves the use of a process called the "Kim process," which was developed by researchers at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology.
This process involves the condensation of N-phenyl-2-amino-4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine with acetone in the presence of a base, such as sodium hydroxide.
The resulting intermediate is then converted into dideoxyadenosine through a series of chemical reactions.
Overall, the synthetic routes for the production of dideoxyadenosine involve a combination of chemical reactions and modifications to existing compounds.
These routes have been developed in an effort to produce the drug in a cost-effective manner, and the specific route used will depend on a variety of factors, including the availability of raw materials and the desired yield of the final product.