-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
-
Cosmetic Ingredient
- Water Treatment Chemical
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
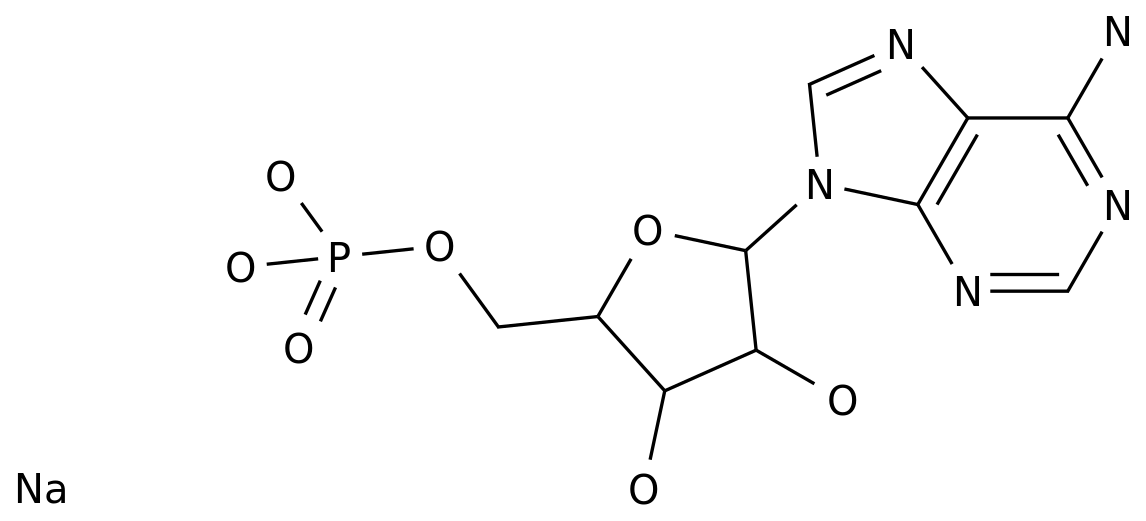
Dideoxyadenosine, also known as didox, is a synthetic nucleoside that is used in the chemical industry for a variety of applications.
Upstream and downstream products refer to the various compounds and materials that are produced as a result of the production and use of didox.
Upstream products are the raw materials and intermediates that are used to produce didox.
These products include the starting materials, such as adenosine and 2,2-dioxyadenosine, as well as the various reagents and chemicals used in the production process.
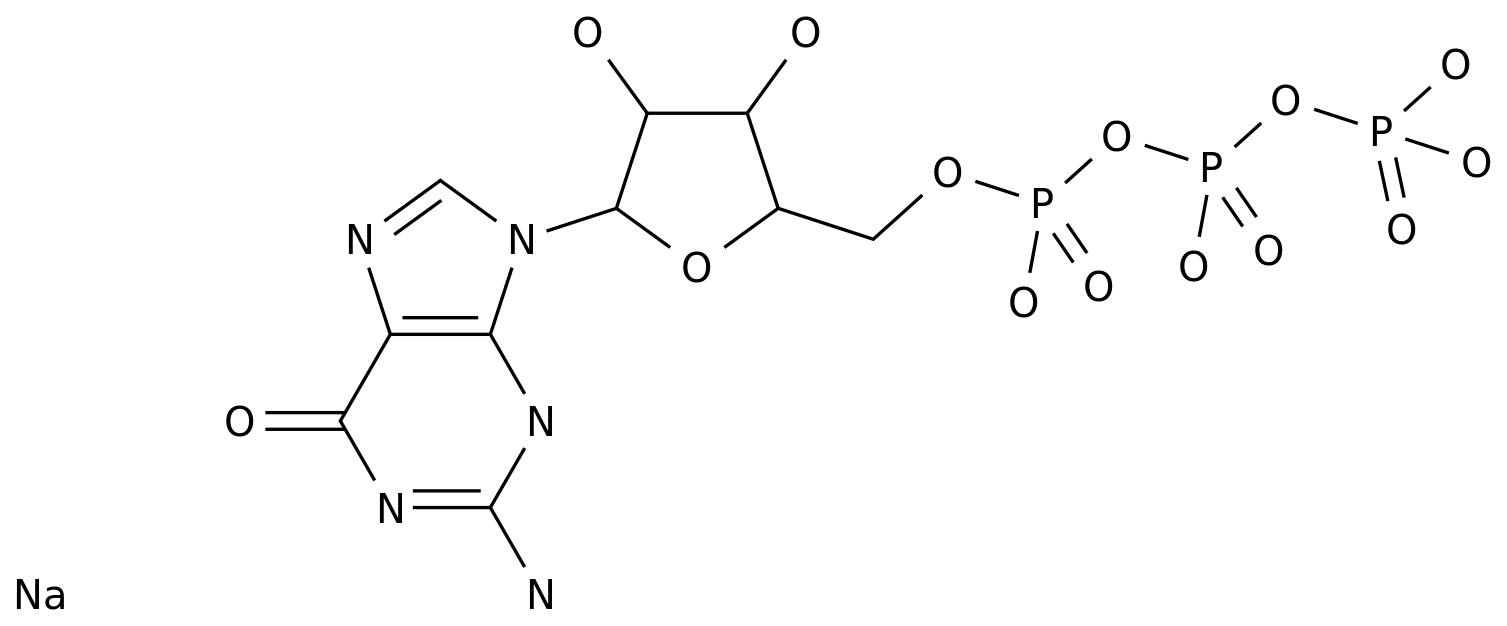
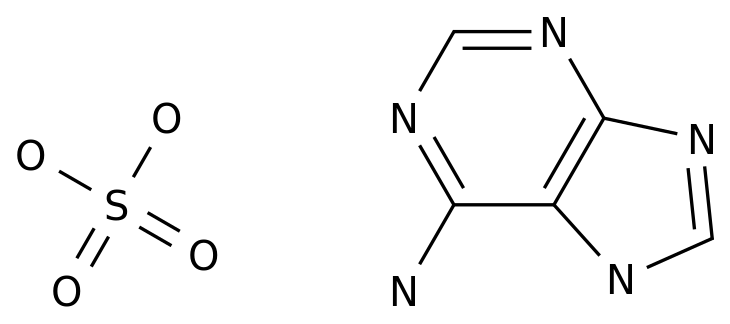
The upstream products for didox production include precursors such as 2,2-dioxypurine riboside and 2,2-dioxypurine.
These compounds are then transformed through a series of chemical reactions to produce didox.
Downstream products, on the other hand, are the final products that are produced using didox.
These products are often used in a variety of applications, such as in the production of antiviral drugs, nucleoside analogs, and other pharmaceuticals.
Some examples of downstream products include AZT, 3TC, and ddI, which are all antiviral drugs that are used to treat HIV and AIDS.
In addition to its use in the production of antiviral drugs, didox is also used in the production of other pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
For example, it can be used as a building block for the synthesis of other nucleoside analogs, which are used in a variety of applications, including the production of anticancer drugs and other pharmaceuticals.
Didox can also be used as a chemical intermediate in the production of other chemicals, such as dyes, fragrances, and other specialty chemicals.
The production of didox involves a series of chemical reactions, including hydrolysis, halogenation, and condensation reactions.
The process typically involves the use of various chemical reagents and solvents, as well as specialized equipment such as reactors and distillation columns.
The production process for didox is typically carried out in a controlled environment, such as a laboratory or industrial facility, and is typically conducted by trained chemists or chemical engineers.
In summary, didox is a synthetic nucleoside that is used in the chemical industry for a variety of applications.
Upstream products for didox production include precursors such as 2,2-dioxypurine riboside and 2,2-dioxypurine, while downstream products include antiviral drugs such as AZT, 3TC, and ddI, as well as other pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
The production process for didox involves a series of chemical reactions, including hydrolysis, halogenation, and condensation reactions, and is typically carried out in a controlled environment by trained chemists or chemical engineers.