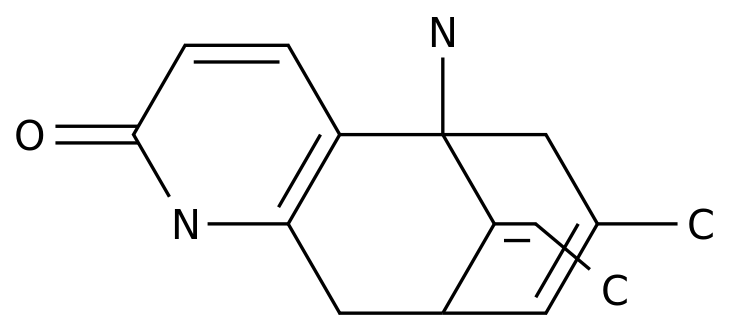
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is a chronic recurrent disorder that has a major impact on public health
Management Immunity
Recently, Translational Psychiatry magazine reported an experimental drug trial that tested the efficacy of ibudilast in improving negative emotions, reducing alcoholism and weakening neural reward signals in AUD individuals
Recently, Translational Psychiatry magazine reported an experimental drug trial that tested the efficacy of ibudilast in improving negative emotions, reducing alcoholism and weakening neural reward signals in AUD individuals
This is an experimental drug trial comparing the efficacy of IUD with placebo in non-treatment-seeking individuals with AUD
Research Process
Research ProcessFifty-two AUD patients who did not seek treatment were randomized to receive IBUD (24 cases) or placebo (28 cases)
The effect of IBUD on the number of days of heavy drinking
The effect of IBUD on the number of days of heavy drinking
Compared with placebo, IBUD reduces the chance of long-term alcohol abuse by 45%.
Effect of Ibudilast on the activation of ventral striatum induced by alcohol
Effect of Ibudilast on the activation of ventral striatum induced by alcoholCompared with placebo, IBUD also attenuated alcohol-induced activation of the ventral striatum (VS) (F(1,44) = 7.
Compared with placebo, IBUD also attenuates alcohol-induced ventral striatum (VS) activation.
The biological behavior mechanism of IBUD , which is to reduce the reward response to alcohol prompts in the brain, thereby reducing the biological behavior mechanism of IBUD , which is to reduce the reward response to alcohol prompts in the brain, thereby reducing heavy drinking
Original source
Grodin, EN, Bujarski, S.
Grodin, EN, Bujarski, S.
, Towns, B.
et al.
Ibudilast, a neuroimmune modulator, reduces heavy drinking and alcohol cue-elicited neural activation: a randomized trial.
Transl Psychiatry 11, 355 (2021).
https:// doi.
org/10.
1038/s41398-021-01478-5 Grodin, EN, Bujarski, S.
, Towns, B.
et al.
Ibudilast, a neuroimmune modulator, reduces heavy drinking and alcohol cue-elicited neural activation: a randomized trial.
Transl Psychiatry 11, 355 (2021).
https://doi.
org/10.
1038/s41398-021-01478-5 et al.
Transl Psychiatry 11,
leave a message here