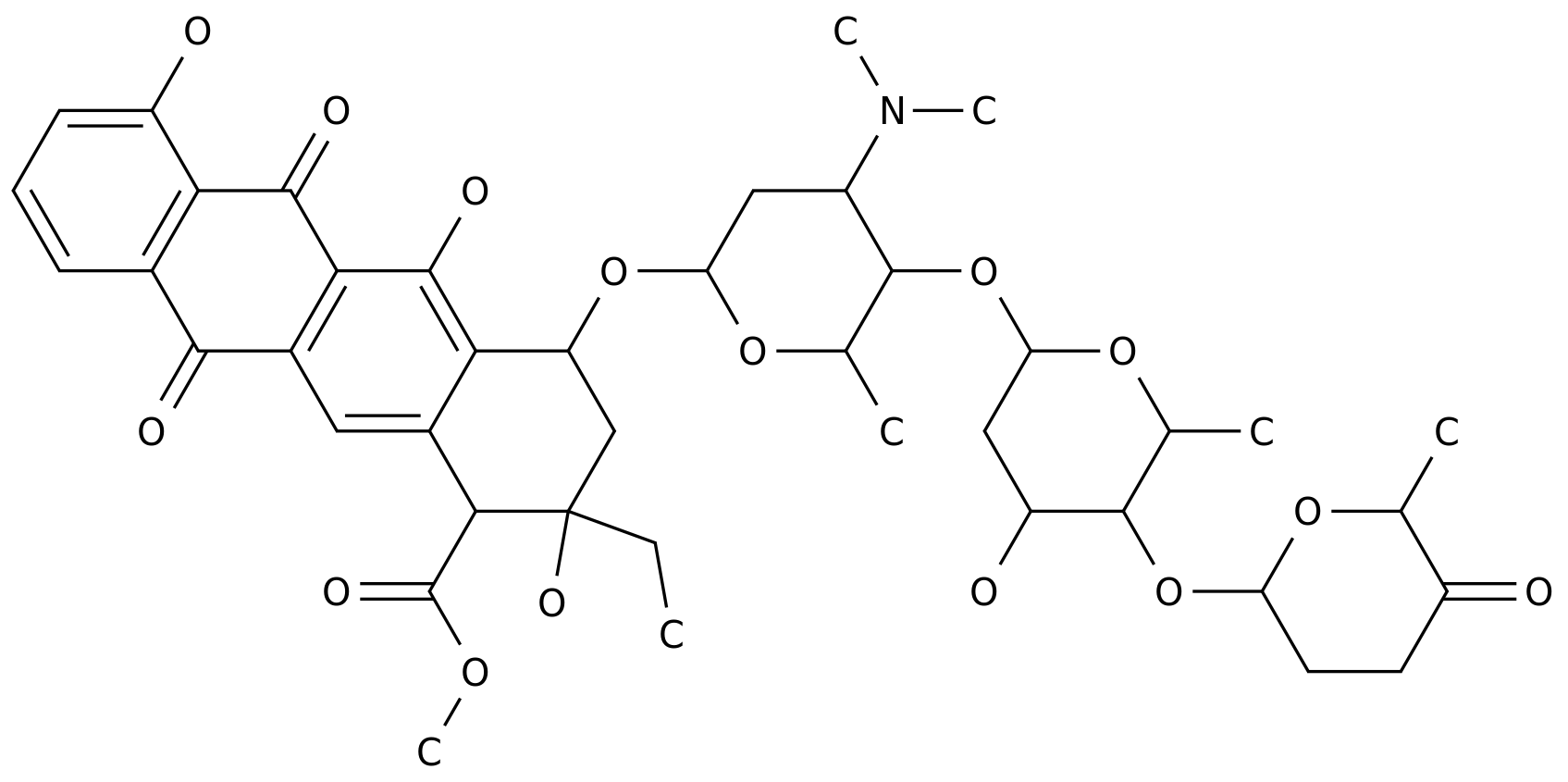
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Innovation: Wu Xiaojian's team from the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and Tan Jing's team from Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center's Center for Cancer Prevention and Treatment have collaborated to reveal the therapeutic potential of PLK1 inhibitors in colorectal cancer, and elucidate the pharmacological mechanism of the combined use of PLK1 inhibitors and oxaliplatin, namely PLK1 inhibitors can inhibit the transcriptional activity of c-MYC on CDC7, leading to down-regulation of CDC7 protein levels, and finally proposed a targeted inhibition of the PLK1-MYC-CDC7 signaling pathway can effectively improve oxaliplatin sensitivity
.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, chemotherapy resistance, PLK1, CDC7 how to overcome chemotherapy resistance has always been a hot and difficult problem in the field of cancer research
.
Finding therapeutic targets based on multi-omics sequencing data, and verifying drug trials in the model of patient tumor origin, is one of the effective methods for developing targeted drugs
.
Recently, Wu Xiaojian's research group from the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and Tan Jing's research group from Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center have published the title: Inhibition of the PLK1-coupled cell cycle machinery overcomes resistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal in Advanced Science (IF: 16.
8).
Cancer research paper
.
The study used omics sequencing data to integrate PLK1, a potential related target of colorectal cancer chemotherapy resistance, and validated drug trials on multiple patient tumor-derived models, and systematically explored PLK1 inhibitors in colorectal cancer.
Therapeutic mechanism in
.
The results of this study found that the combined use of PLK1 inhibitors can significantly improve the anti-tumor effect of oxaliplatin, which provides new treatment ideas for patients with colorectal cancer who are resistant to chemotherapy or tumor recurrence
.
Targeted inhibition of the PLK1-MYC-CDC7 signaling pathway can effectively improve oxaliplatin sensitivity.
The research team integrated and analyzed large-scale colorectal cancer patient sample data and found that PLK1 may be a potential drug target for colorectal cancer
.
It was also found that PLK1 was highly expressed in tumor tissues of patients who relapsed after chemotherapy, suggesting that it may be related to chemotherapy resistance (Figure 1)
.
Figure 1 The high expression of PLK1 in tumor tissues of patients who relapsed after chemotherapy.
In order to verify the efficacy of the drug, the research team conducted drug efficacy experiments on colorectal cancer cell lines, patient tumor-derived organoid models and PDX models, confirming that the targeted drug can improve The efficacy of oxaliplatin provides sufficient preclinical research data for clinical translational therapy (Figure 2)
.
Figure 2 Targeted therapy has significant efficacy in organoids and PDX models.
Finally, through the integrated analysis of RNA-seq and ChIP-seq data, it is found that the PLK1-MYC-CDC7 signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating colorectal cancer chemotherapy resistance It provides a clear pharmacological mechanism for the clinical application of PLK1 inhibitors (Figure 3)
.
Figure 3 The pharmacological mechanism of the combined use of PLK1 inhibitors and oxaliplatin.
In summary, the research team explored the therapeutic potential of PLK1 inhibitors in colorectal cancer, and clarified the pharmacological mechanism of the combined use of PLK1 inhibitors and oxaliplatin, namely PLK1 inhibitors can inhibit the transcriptional activity of c-MYC on CDC7, leading to down-regulation of CDC7 protein levels, and finally proposed a targeted inhibition of the PLK1-MYC-CDC7 signaling pathway can effectively improve oxaliplatin sensitivity
.
Chief Physician Wu Xiaojian of the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Researcher Tan Jing of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center and Professor Lan Ping of the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University are the corresponding authors of this paper.
Postdoctoral fellows Yu Liangliang, Dr.
Deng Peng and attending physician Chen Yufeng are the joint firsts of this article.
The author, this research has also received strong support from Professor Yu Qiang from the Singapore Genome Research Institute
.
WILEY paper information: Inhibition of the PLK1-Coupled Cell Cycle Machinery Overcomes Resistance to Oxaliplatin in Colorectal CancerZhaoliang Yu,Peng Deng,Yufeng Chen,Shini Liu,Jinghong Chen,Zihuan Yang,Jianfeng Chen,Xinjuan Fan,Peili Wang,Zerong Cai,Yali Wang,Peishan Hu,Dezheng Lin,Rong Xiao,Yifeng Zou,Yan Huang,Qiang Yu,Ping Lan*,Jing Tan*,Xiaojian Wu*Advanced Science DOI: 10.
1002/advs.
202100759 Click on "Read the original text" in the lower left corner to view the paper Original text
.
Introduction to AdvancedScience Journal "Advanced Science" (Advanced Science) Wiley is a high-quality open source journal founded in 2014.
It publishes innovative achievements and cutting-edge progress in various fields such as materials science, physical chemistry, biomedicine, and engineering
.
The journal is dedicated to disseminating scientific research results to the public to the greatest extent, and all articles are freely available
.
The latest impact factor is 16.
806, and the 2020 SCI journals of the Chinese Academy of Sciences will be divided into the Q1 area of the material science category and the Q1 area of the engineering technology category
.
Press and hold the QR code on the official WeChat platform of AdvancedScienceNewsWiley's scientific research information.
Follow us to share cutting-edge information|Focus on scientific research trends to publish scientific research news or apply for information sharing, please contact: ASNChina@Wiley.
com
.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, chemotherapy resistance, PLK1, CDC7 how to overcome chemotherapy resistance has always been a hot and difficult problem in the field of cancer research
.
Finding therapeutic targets based on multi-omics sequencing data, and verifying drug trials in the model of patient tumor origin, is one of the effective methods for developing targeted drugs
.
Recently, Wu Xiaojian's research group from the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University and Tan Jing's research group from Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center have published the title: Inhibition of the PLK1-coupled cell cycle machinery overcomes resistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal in Advanced Science (IF: 16.
8).
Cancer research paper
.
The study used omics sequencing data to integrate PLK1, a potential related target of colorectal cancer chemotherapy resistance, and validated drug trials on multiple patient tumor-derived models, and systematically explored PLK1 inhibitors in colorectal cancer.
Therapeutic mechanism in
.
The results of this study found that the combined use of PLK1 inhibitors can significantly improve the anti-tumor effect of oxaliplatin, which provides new treatment ideas for patients with colorectal cancer who are resistant to chemotherapy or tumor recurrence
.
Targeted inhibition of the PLK1-MYC-CDC7 signaling pathway can effectively improve oxaliplatin sensitivity.
The research team integrated and analyzed large-scale colorectal cancer patient sample data and found that PLK1 may be a potential drug target for colorectal cancer
.
It was also found that PLK1 was highly expressed in tumor tissues of patients who relapsed after chemotherapy, suggesting that it may be related to chemotherapy resistance (Figure 1)
.
Figure 1 The high expression of PLK1 in tumor tissues of patients who relapsed after chemotherapy.
In order to verify the efficacy of the drug, the research team conducted drug efficacy experiments on colorectal cancer cell lines, patient tumor-derived organoid models and PDX models, confirming that the targeted drug can improve The efficacy of oxaliplatin provides sufficient preclinical research data for clinical translational therapy (Figure 2)
.
Figure 2 Targeted therapy has significant efficacy in organoids and PDX models.
Finally, through the integrated analysis of RNA-seq and ChIP-seq data, it is found that the PLK1-MYC-CDC7 signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating colorectal cancer chemotherapy resistance It provides a clear pharmacological mechanism for the clinical application of PLK1 inhibitors (Figure 3)
.
Figure 3 The pharmacological mechanism of the combined use of PLK1 inhibitors and oxaliplatin.
In summary, the research team explored the therapeutic potential of PLK1 inhibitors in colorectal cancer, and clarified the pharmacological mechanism of the combined use of PLK1 inhibitors and oxaliplatin, namely PLK1 inhibitors can inhibit the transcriptional activity of c-MYC on CDC7, leading to down-regulation of CDC7 protein levels, and finally proposed a targeted inhibition of the PLK1-MYC-CDC7 signaling pathway can effectively improve oxaliplatin sensitivity
.
Chief Physician Wu Xiaojian of the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Researcher Tan Jing of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center and Professor Lan Ping of the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University are the corresponding authors of this paper.
Postdoctoral fellows Yu Liangliang, Dr.
Deng Peng and attending physician Chen Yufeng are the joint firsts of this article.
The author, this research has also received strong support from Professor Yu Qiang from the Singapore Genome Research Institute
.
WILEY paper information: Inhibition of the PLK1-Coupled Cell Cycle Machinery Overcomes Resistance to Oxaliplatin in Colorectal CancerZhaoliang Yu,Peng Deng,Yufeng Chen,Shini Liu,Jinghong Chen,Zihuan Yang,Jianfeng Chen,Xinjuan Fan,Peili Wang,Zerong Cai,Yali Wang,Peishan Hu,Dezheng Lin,Rong Xiao,Yifeng Zou,Yan Huang,Qiang Yu,Ping Lan*,Jing Tan*,Xiaojian Wu*Advanced Science DOI: 10.
1002/advs.
202100759 Click on "Read the original text" in the lower left corner to view the paper Original text
.
Introduction to AdvancedScience Journal "Advanced Science" (Advanced Science) Wiley is a high-quality open source journal founded in 2014.
It publishes innovative achievements and cutting-edge progress in various fields such as materials science, physical chemistry, biomedicine, and engineering
.
The journal is dedicated to disseminating scientific research results to the public to the greatest extent, and all articles are freely available
.
The latest impact factor is 16.
806, and the 2020 SCI journals of the Chinese Academy of Sciences will be divided into the Q1 area of the material science category and the Q1 area of the engineering technology category
.
Press and hold the QR code on the official WeChat platform of AdvancedScienceNewsWiley's scientific research information.
Follow us to share cutting-edge information|Focus on scientific research trends to publish scientific research news or apply for information sharing, please contact: ASNChina@Wiley.
com