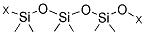-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
*Only for medical professionals to read the reference theory must be combined with reality, as well as the doctor-patient relationship! In the impression of many people, according to the experience of many doctors, patients with liver injury should not use quinolone antibiotics such as levofloxacin and moxifloxacin.
However, consulting the literature and the instructions, these views have no basis! At least, quinolone antibiotics can be used for mild to moderate liver damage, and there is no need to reduce the dose! why? 1 Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs The "Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs (2014 Edition)" even directly wrote: patients with impaired liver function, quinolone antibiotics such as levofloxacin, do not need to be reduced
.
Figure 1 "Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs (2015 Edition)" is the same point of view! Figure 2 feels very exaggerated.
There is no need to reduce the dose.
It is safer than many cephalosporin antibiotics! Although we have promulgated many guidelines, expert consensus, and various guiding principles, it may not be useful when litigating a lawsuit! So, let's take a look at the manual again! 2 Instructions 1.
Moxifloxacin injection imported from Moxifloxacin, the instructions read: Patients with liver function Child-Pugh Class A and B, do not need to adjust the dose! The instructions in Figure 3 escort you.
Patients with liver injury (Child-Pugh grade A, B) can use moxifloxacin
.
So, what about C-level? Not recommended! What should I do when I need it? Can only figure it out! Figure 42.
Levofloxacin The instruction manual for levofloxacin reads: In the clouds, erratic, and seemingly understandable, it can only be understood without words! I try my best to spread it! First of all, the instructions gave us a small look, suggesting that we can use levofloxacin for liver damage! Because levofloxacin is mainly excreted from the urinary system as a prototype
.
Figure 5 Since it is mainly excreted from the urinary system as a prototype, there is generally no hepatotoxicity in theory! However, the instructions continue to imply that we: levofloxacin can be used for liver damage
.
Figure 6 Change another manual! Figure 7 In addition, in large-scale studies, levofloxacin is generally safe, and the possibility of severe liver damage is extremely small! Figure 83 What to do in reality? Drugs that are mainly excreted by the kidneys do not necessarily have nephrotoxicity! For example, normal saline, I think most of it must be excreted through the kidneys.
Do you think normal saline is highly nephrotoxic? Theory must be combined with reality and the doctor-patient relationship! "Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs (2015 Edition)", although it was promulgated by the General Office of the National Health and Family Planning Commission, it may not beat the instructions in reality! Therefore, quinolones should be used with caution in severe liver damage! On the earth where we live, no medicine is without side effects! All antibiotics may have liver and kidney toxicity, but some drugs are less toxic or have a smaller chance of occurrence
.
For example: Zhang Fei, liver function is normal, lung infection, anti-infective treatment with levofloxacin, transaminase continues to rise a few days later, no other cause can be found, then it is still necessary to consider liver damage caused by drugs! Never because the “Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs” promulgated by the state said that liver injury does not need to be reduced, and it may be safer to replace antibiotics
.
There is no need to reduce the amount of liver damage, which does not mean that the medicine has no hepatotoxicity! Because of individual differences, levofloxacin is not hepatotoxic to most people, but in rare cases, it may cause liver failure in some patients
.
At the end of the article
However, consulting the literature and the instructions, these views have no basis! At least, quinolone antibiotics can be used for mild to moderate liver damage, and there is no need to reduce the dose! why? 1 Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs The "Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs (2014 Edition)" even directly wrote: patients with impaired liver function, quinolone antibiotics such as levofloxacin, do not need to be reduced
.
Figure 1 "Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs (2015 Edition)" is the same point of view! Figure 2 feels very exaggerated.
There is no need to reduce the dose.
It is safer than many cephalosporin antibiotics! Although we have promulgated many guidelines, expert consensus, and various guiding principles, it may not be useful when litigating a lawsuit! So, let's take a look at the manual again! 2 Instructions 1.
Moxifloxacin injection imported from Moxifloxacin, the instructions read: Patients with liver function Child-Pugh Class A and B, do not need to adjust the dose! The instructions in Figure 3 escort you.
Patients with liver injury (Child-Pugh grade A, B) can use moxifloxacin
.
So, what about C-level? Not recommended! What should I do when I need it? Can only figure it out! Figure 42.
Levofloxacin The instruction manual for levofloxacin reads: In the clouds, erratic, and seemingly understandable, it can only be understood without words! I try my best to spread it! First of all, the instructions gave us a small look, suggesting that we can use levofloxacin for liver damage! Because levofloxacin is mainly excreted from the urinary system as a prototype
.
Figure 5 Since it is mainly excreted from the urinary system as a prototype, there is generally no hepatotoxicity in theory! However, the instructions continue to imply that we: levofloxacin can be used for liver damage
.
Figure 6 Change another manual! Figure 7 In addition, in large-scale studies, levofloxacin is generally safe, and the possibility of severe liver damage is extremely small! Figure 83 What to do in reality? Drugs that are mainly excreted by the kidneys do not necessarily have nephrotoxicity! For example, normal saline, I think most of it must be excreted through the kidneys.
Do you think normal saline is highly nephrotoxic? Theory must be combined with reality and the doctor-patient relationship! "Guiding Principles for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs (2015 Edition)", although it was promulgated by the General Office of the National Health and Family Planning Commission, it may not beat the instructions in reality! Therefore, quinolones should be used with caution in severe liver damage! On the earth where we live, no medicine is without side effects! All antibiotics may have liver and kidney toxicity, but some drugs are less toxic or have a smaller chance of occurrence
.
For example: Zhang Fei, liver function is normal, lung infection, anti-infective treatment with levofloxacin, transaminase continues to rise a few days later, no other cause can be found, then it is still necessary to consider liver damage caused by drugs! Never because the “Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Drugs” promulgated by the state said that liver injury does not need to be reduced, and it may be safer to replace antibiotics
.
There is no need to reduce the amount of liver damage, which does not mean that the medicine has no hepatotoxicity! Because of individual differences, levofloxacin is not hepatotoxic to most people, but in rare cases, it may cause liver failure in some patients
.
At the end of the article