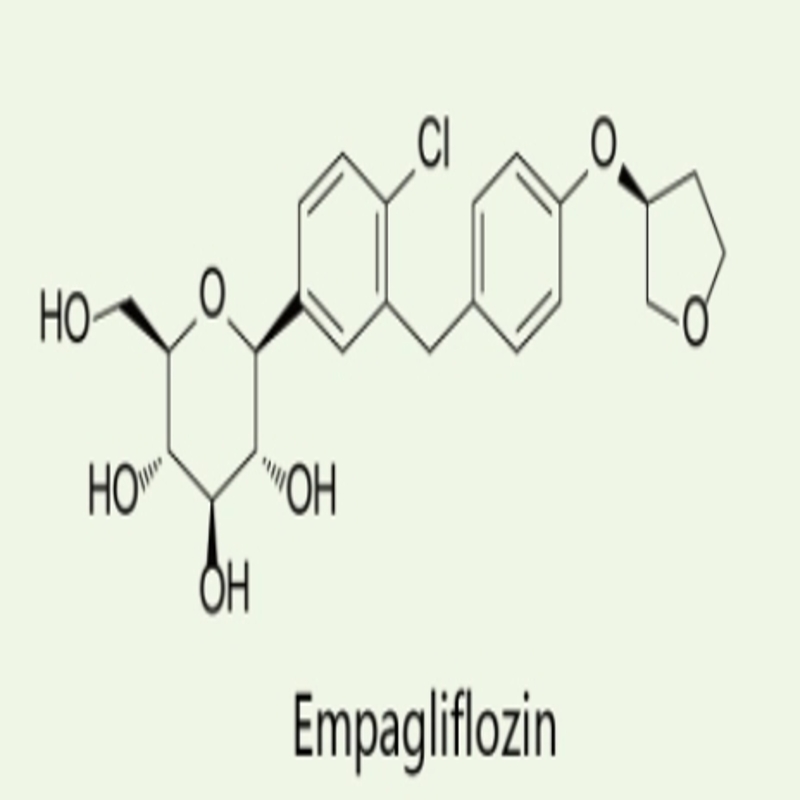
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Background: Dyslipidemia is very common in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM)
.
Many studies have attempted to unravel the causal relationship between dyslipidemia and susceptibility to T2 DM
Background: Dyslipidemia is very common in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2 DM)
Methods: Using univariate and multivariate two-sample MR, we utilized data from the African Partnership for Chronic Disease Research (APCDR) (N=13,612, 36.
Results: In African ancestry, elevated LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol levels were associated with an increased risk of T2 DM (odds ratio (OR) per standard deviation increase in LDL cholesterol [95% confidence interval, P value]] =1.
Figure 1.
Forest plot showing odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals between lipid traits and genetically predicted risk of T2 DM using different magnetic resonance methods
.
Forest plot showing odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals between lipid traits and genetically predicted risk of T2 DM using different magnetic resonance methods
.
Figure 2.
Forest plot showing odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals for univariate and multivariate MR versus T2 DM
.
Forest plot showing odds ratios and their 95% confidence intervals for univariate and multivariate MR versus T2 DM
.
CONCLUSIONS: Consistent with the MR findings in Europeans, HDL-C protects against T2 DM susceptibility, and inhibition of HMGCR increases T2 DM susceptibility in individuals of African ancestry
.
However, LDL-C may increase T2 DM susceptibility in individuals of African ancestry compared with individuals of European ancestry
CONCLUSIONS: Consistent with the MR findings in Europeans, HDL-C protects against T2 DM susceptibility, and inhibition of HMGCR increases T2 DM susceptibility in individuals of African ancestry
Original source: Soremekun O, Karhunen V, He Y, et al.
Lipid traits and type 2 diabetes risk in African ancestry individuals: A Mendelian Randomization study.
EBioMedicine 2022 Mar 21;78 Leave a comment here