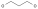-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic cholestatic disorder of unknown etiology characterized by progressive narrowing and destruction of the bile ducts due to diffuse inflammation and fibrosis, eventually leading to cirrhosis and liver failure
.
Although autoimmune responses are thought to play a role in the pathogenesis of PSC, immunosuppressant therapy has failed to show efficacy
.
Therefore, the long-term prognosis for patients with PSC remains unfavorable
.
This condition is characterized by high mortality and liver transplantation (LT) is the only option
for patients with advanced PSC.
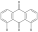
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is currently the most prescribed drug for patients with PSC, with about 45-75% of
patients in the real world.
Based on this, a large, well-characterized retrospective cohort study is needed to determine whether UDCA use is associated with
improved long-term outcomes.
The researchers used retrospective data from the Japanese PSC Registry, which included 435 PSC patients
.
In this study, patients with a complete diagnostic data set were also enrolled, as well as years of diagnosis, treatment regimens, follow-up periods, and outcome data
.
The association between UDCA treatment and all-cause mortality or LT was covariate adjusted using Cox regression and UDCA treatment-weighted inverse probability (IPTW)-adjusted
Cox regression models.
Of the 435 patients with PSC, 110 were excluded due to insufficient or missing data, and the remaining 325 patients (male, 187 (58%); mean age at diagnosis, 45.
8 years) were included in the study
.
The mean follow-up was 5.
1 years, with 57 deaths and 24 LTs
occurring during the observation period.
278 patients (86%) received UDCA
.
The Cox regression model showed that UDCA treatment was associated with improved LT-free survival [adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) 0.
47, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.
28–0.
78, p=0.
003].
In addition, IPTW tuning models showed a significant association between UDCA and LT-free survival (aHR 0.
43, 95% CI 0.
25–0.
75, p=0.
020).
Sensitivity analysis excluding patients treated with benzafibrate showed a similarly significant association
between UDCA treatment and LT-free survival.
This study demonstrated that the use of UDCA is significantly associated with improved LT-free survival in patients with PSC, suggesting that UDCA improves long-term outcomes
in patients with PSC.
Original source:
Toshihiko Arizumi.
et al.
Ursodeoxycholic acid is associated with improved long-term outcome in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Journal of Gastroenterology.
2022.