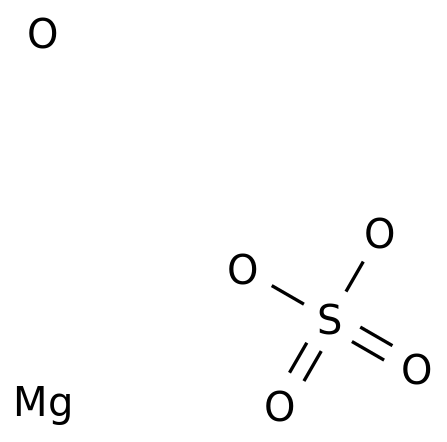
-
Categories
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
-
Food Additives
- Industrial Coatings
- Agrochemicals
- Dyes and Pigments
- Surfactant
- Flavors and Fragrances
- Chemical Reagents
- Catalyst and Auxiliary
- Natural Products
- Inorganic Chemistry
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Biochemical Engineering
- Analytical Chemistry
- Cosmetic Ingredient
-
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Promotion
ECHEMI Mall
Wholesale
Weekly Price
Exhibition
News
-
Trade Service
EditorPancreatic cancer is one of the cancers with the highest mortality rate at present.
It is characterized by rapid progress, early metastasis and difficult diagnosis
.
However, apart from the traditional blood marker CA19-9 and imaging methods, there is no other effective method for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer at this stage
.
Therefore, the development of effective detection methods to achieve early, accurate, and non-invasive detection of pancreatic cancer will improve the diagnostic efficiency of pancreatic cancer and reduce its lethality
.
Metabolomics is another omics method widely used in precision medicine after genomics and proteomics.
The detection of changes in blood metabolites through metabolomics methods is expected to achieve early diagnosis of cancer
.
On December 22, 2021, Professor Yin Yuxin’s team from the Institute of Systems Biomedicine, Peking University School of Basic Medicine published an online paper entitled Metabolic detection and systems analyses of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through machine learning, lipidomics, and multi-omics in Science Advances.
Research thesis, apply machine learning combined with lipidomics and multi-omics technology to comprehensively analyze the metabolic characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (pancreatic cancer), develop a set of artificial intelligence-assisted PDAC serum metabolism detection methods, and display related molecules Mechanism
.
Yin Yuxin's team and collaborators have developed a non-invasive detection method for pancreatic cancer using machine learning-assisted metabolomics
.
Using support vector machine-greedy algorithm and high-resolution mass spectrometry to analyze non-targeted metabolomics data, 17 serum metabolic markers were screened, and a multi-reaction detection mode targeted metabolism detection method based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was established.
Model with artificial intelligence disease classification
.
The method tested a total of more than 1800 samples from 4 cohorts, including 1033 patients with pancreatic cancer at different stages
.
In a large external validation cohort of more than 1000 cases and a prospective clinical cohort containing benign pancreatic lesions, classification detection accuracy of 86.
74% and 85.
00% were achieved respectively, and its detection efficiency was significantly better than CA19-9 and CT examination
.
The study also combined single-cell transcriptome data, tissue proteomics, metabolomics and mass spectrometry imaging and other multi-omics technologies to reveal the mechanism of lipid metabolism changes in pancreatic cancer tissues, opening up the use of machine learning-assisted metabolomics An efficient strategy for early detection of pancreatic cancer
.
In summary, this study established a pancreatic cancer detection and analysis method that combines machine learning and targeted metabolomics
.
It demonstrates the advantages of machine learning-assisted serum metabolomics in detecting pancreatic cancer and its application prospects in cancer diagnosis
.
The clinical application of this method may enable more patients with pancreatic cancer to benefit from early and accurate diagnosis so that they can receive treatment and monitoring in time
.
Postdoctoral Fellow Wang Guangxi, Peking University School of Basic Medicine, Associate Researcher Yao Hantao, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Deputy Chief Physician Gong Yan, General Hospital of the People’s Liberation Army, and Deputy Chief Physician Lu Zipeng, Jiangsu Provincial People’s Hospital are the co-first authors of this paper, and Professor Yin Yuxin, Institute of Systems Biomedicine, Peking University , Associate Professor Guo Limei, Department of Pathology, Department of Pathology, Peking University School of Basic Medicine, Third Hospital of Peking University, Professor Zeng Qiang of the General Hospital of the People's Liberation Army, and Professor Jiang Kuirong, Jiangsu Provincial People's Hospital are the co-corresponding authors
.
Original link: https:// Platemaker: Notes for reprinting on the 11th [Non-original article] The copyright of this article belongs to the author of the article.
Personal forwarding and sharing are welcome.
Reprinting without permission is prohibited.
The author has all legal rights, and offenders must be investigated
.
It is characterized by rapid progress, early metastasis and difficult diagnosis
.
However, apart from the traditional blood marker CA19-9 and imaging methods, there is no other effective method for the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer at this stage
.
Therefore, the development of effective detection methods to achieve early, accurate, and non-invasive detection of pancreatic cancer will improve the diagnostic efficiency of pancreatic cancer and reduce its lethality
.
Metabolomics is another omics method widely used in precision medicine after genomics and proteomics.
The detection of changes in blood metabolites through metabolomics methods is expected to achieve early diagnosis of cancer
.
On December 22, 2021, Professor Yin Yuxin’s team from the Institute of Systems Biomedicine, Peking University School of Basic Medicine published an online paper entitled Metabolic detection and systems analyses of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through machine learning, lipidomics, and multi-omics in Science Advances.
Research thesis, apply machine learning combined with lipidomics and multi-omics technology to comprehensively analyze the metabolic characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (pancreatic cancer), develop a set of artificial intelligence-assisted PDAC serum metabolism detection methods, and display related molecules Mechanism
.
Yin Yuxin's team and collaborators have developed a non-invasive detection method for pancreatic cancer using machine learning-assisted metabolomics
.
Using support vector machine-greedy algorithm and high-resolution mass spectrometry to analyze non-targeted metabolomics data, 17 serum metabolic markers were screened, and a multi-reaction detection mode targeted metabolism detection method based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was established.
Model with artificial intelligence disease classification
.
The method tested a total of more than 1800 samples from 4 cohorts, including 1033 patients with pancreatic cancer at different stages
.
In a large external validation cohort of more than 1000 cases and a prospective clinical cohort containing benign pancreatic lesions, classification detection accuracy of 86.
74% and 85.
00% were achieved respectively, and its detection efficiency was significantly better than CA19-9 and CT examination
.
The study also combined single-cell transcriptome data, tissue proteomics, metabolomics and mass spectrometry imaging and other multi-omics technologies to reveal the mechanism of lipid metabolism changes in pancreatic cancer tissues, opening up the use of machine learning-assisted metabolomics An efficient strategy for early detection of pancreatic cancer
.
In summary, this study established a pancreatic cancer detection and analysis method that combines machine learning and targeted metabolomics
.
It demonstrates the advantages of machine learning-assisted serum metabolomics in detecting pancreatic cancer and its application prospects in cancer diagnosis
.
The clinical application of this method may enable more patients with pancreatic cancer to benefit from early and accurate diagnosis so that they can receive treatment and monitoring in time
.
Postdoctoral Fellow Wang Guangxi, Peking University School of Basic Medicine, Associate Researcher Yao Hantao, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Deputy Chief Physician Gong Yan, General Hospital of the People’s Liberation Army, and Deputy Chief Physician Lu Zipeng, Jiangsu Provincial People’s Hospital are the co-first authors of this paper, and Professor Yin Yuxin, Institute of Systems Biomedicine, Peking University , Associate Professor Guo Limei, Department of Pathology, Department of Pathology, Peking University School of Basic Medicine, Third Hospital of Peking University, Professor Zeng Qiang of the General Hospital of the People's Liberation Army, and Professor Jiang Kuirong, Jiangsu Provincial People's Hospital are the co-corresponding authors
.
Original link: https:// Platemaker: Notes for reprinting on the 11th [Non-original article] The copyright of this article belongs to the author of the article.
Personal forwarding and sharing are welcome.
Reprinting without permission is prohibited.
The author has all legal rights, and offenders must be investigated
.